Fitness Notes
... Midline: the median line of the body; lines up with the nose, naval, pubic synthesis and heels ...
... Midline: the median line of the body; lines up with the nose, naval, pubic synthesis and heels ...
BIOII Level 1 Name__________________________ Anatomical
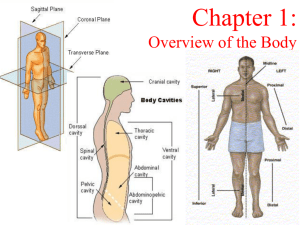
... Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more Objectives 1. Describe the anatomical position verbally or by demonstrating it 2. Demonstrate ability to use anatomical terms describing body landmarks, directions, planes, and surfaces. 3. Name the body cavities, and indicate importan ...
... Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more Objectives 1. Describe the anatomical position verbally or by demonstrating it 2. Demonstrate ability to use anatomical terms describing body landmarks, directions, planes, and surfaces. 3. Name the body cavities, and indicate importan ...
Directional Terms and Body Planes
... with regards to anatomical position … even if the body in question is in a different position. Example: The head is superior (above) to the feet, whether you are standing up, laying down, or doing a handstand. ...
... with regards to anatomical position … even if the body in question is in a different position. Example: The head is superior (above) to the feet, whether you are standing up, laying down, or doing a handstand. ...
Body Organization: regions, sections, planes, and cavities
... with regards to anatomical position … even if the body in question is in a different position. Example: The head is superior (above) to the feet, whether you are standing up, laying down, or doing a handstand. ...
... with regards to anatomical position … even if the body in question is in a different position. Example: The head is superior (above) to the feet, whether you are standing up, laying down, or doing a handstand. ...
Clues
... 21. An abdominal region that is located on the stomach. 23. The part of the serous membrane that is in contact with the organ. 25. The ___ portion of the body consists of the head, neck and trunk. 26. To lie or be placed with the anterior surface facing down. 27. Meaning behind the peritoneum. 28. A ...
... 21. An abdominal region that is located on the stomach. 23. The part of the serous membrane that is in contact with the organ. 25. The ___ portion of the body consists of the head, neck and trunk. 26. To lie or be placed with the anterior surface facing down. 27. Meaning behind the peritoneum. 28. A ...
Kingdom Animalia
... 2. Eumetazoa - animals with well defined tissue layers B. The Radiata-Bilateria Split The eumetazoa are divided into 2 major branches depending on the type of body symmetry (=body plan or organization) that evolved. 1. Some organisms exhibit radial symmetry, and are called the Radiata 2. Other eumet ...
... 2. Eumetazoa - animals with well defined tissue layers B. The Radiata-Bilateria Split The eumetazoa are divided into 2 major branches depending on the type of body symmetry (=body plan or organization) that evolved. 1. Some organisms exhibit radial symmetry, and are called the Radiata 2. Other eumet ...
Vertebrate Zoology BIOL 322/Architectural Patterns Ch 9 final
... epithelium = a sheet of cells that covers an external or internal surface on many surfaces, epithelial cells are often modified into glands classified on the basis of cell form and number of cell layers e.g., columnar epithelium (looks like a column) (lining crop of bird) cuboidal epitheli ...
... epithelium = a sheet of cells that covers an external or internal surface on many surfaces, epithelial cells are often modified into glands classified on the basis of cell form and number of cell layers e.g., columnar epithelium (looks like a column) (lining crop of bird) cuboidal epitheli ...
One of the branches of physiology is cytology, which is the study of P
... Anatomy and Physiology Introduction and Anatomical Terms Review Completion: add the word or words that correctly complete each of the following statements. ...
... Anatomy and Physiology Introduction and Anatomical Terms Review Completion: add the word or words that correctly complete each of the following statements. ...
anatomical terms 1
... ANTERIOR – the front of the body or body part • ANTERIOR--means toward the front of the body. One can move a body part anteriorly by moving it towards the front of the body. A body part can have an anterior aspect, that being that component closest to the front of the body. From the word "ante" whi ...
... ANTERIOR – the front of the body or body part • ANTERIOR--means toward the front of the body. One can move a body part anteriorly by moving it towards the front of the body. A body part can have an anterior aspect, that being that component closest to the front of the body. From the word "ante" whi ...
Ch28
... Class Trematoda - The trematodes are all parasitic flukes, and as adults they are almost all found as internal parasites of vertebrates. Examples: Clonorchis, Schistosoma Class Cestoda - The cestodes, or tapeworms, usually have long flat bodies made up of many reproductive units (proglottids) and ha ...
... Class Trematoda - The trematodes are all parasitic flukes, and as adults they are almost all found as internal parasites of vertebrates. Examples: Clonorchis, Schistosoma Class Cestoda - The cestodes, or tapeworms, usually have long flat bodies made up of many reproductive units (proglottids) and ha ...
Ch. 27 Invertebrates
... ~ small, , unsegmented worms ~ some are parasitic ~ slender, elongated body ~ simplest org. with a body cavity : pseudocoelomates = false coelom or body cavity ~ have bodies shaped like pencils sharpened at both ...
... ~ small, , unsegmented worms ~ some are parasitic ~ slender, elongated body ~ simplest org. with a body cavity : pseudocoelomates = false coelom or body cavity ~ have bodies shaped like pencils sharpened at both ...
anatomical terminology, directional terms, planes, sections, and
... D. Tranverse/Cross/Horizontal plane- divides the body into superior and inferior portions ...
... D. Tranverse/Cross/Horizontal plane- divides the body into superior and inferior portions ...
Lecture Outline
... pair of pedipalps to manipulate the food (or transfer sperm!). 4. Unique respiratory organs called book lungs reside in an invagination of the abdominal wall; they greatly increase the surface area available for gas exchange. ...
... pair of pedipalps to manipulate the food (or transfer sperm!). 4. Unique respiratory organs called book lungs reside in an invagination of the abdominal wall; they greatly increase the surface area available for gas exchange. ...
Anatomy of the Heart Definitions
... The inferior vena cava is one of the two main veins bringing de-oxygenated blood from the body to the heart. Veins from the legs and lower torso feed into the inferior vena cava, which empties into the right atrium of the heart. Aorta The aorta is the largest single blood vessel in the body. It is a ...
... The inferior vena cava is one of the two main veins bringing de-oxygenated blood from the body to the heart. Veins from the legs and lower torso feed into the inferior vena cava, which empties into the right atrium of the heart. Aorta The aorta is the largest single blood vessel in the body. It is a ...
Body System Show 4
... – My Body for Kids: Heart/Circulatory System – Yucky Body Facts – Interactive Body Review Games ...
... – My Body for Kids: Heart/Circulatory System – Yucky Body Facts – Interactive Body Review Games ...
Body System Checklist
... The goal of your powerpoint is to provide enough information so your students understand the anatomy (structure) and physiology (function) of the your system. If you are not sure if you are covering everything that is needed or if it is not making sense, please speak with the teacher. Your powerpoin ...
... The goal of your powerpoint is to provide enough information so your students understand the anatomy (structure) and physiology (function) of the your system. If you are not sure if you are covering everything that is needed or if it is not making sense, please speak with the teacher. Your powerpoin ...
Chapter 29: Introduction to Invertebrates
... Parasitic flatworms are flukes (trematodes) and tapeworms (cestodes) Well-developed nerves and gastrovascular cavity are unnecessary ...
... Parasitic flatworms are flukes (trematodes) and tapeworms (cestodes) Well-developed nerves and gastrovascular cavity are unnecessary ...
Body Directions And Systems
... The liver belongs to the _______________ system. The spleen belongs to the ______________ system. In terms of nearness to the surface, the liver is ____________ to the skin. In terms of closeness to the trunk, the elbow is ______________ to the fingers. If you were to sit on a horse’s back you would ...
... The liver belongs to the _______________ system. The spleen belongs to the ______________ system. In terms of nearness to the surface, the liver is ____________ to the skin. In terms of closeness to the trunk, the elbow is ______________ to the fingers. If you were to sit on a horse’s back you would ...
Introduction To Animal Evolution
... • a.nonesponges • b._____-has a top and bottom only • c. ______ has ventral, dorsal, anterior, posterior, and right and left. ...
... • a.nonesponges • b._____-has a top and bottom only • c. ______ has ventral, dorsal, anterior, posterior, and right and left. ...
Directional planes - River Dell Regional School District
... What region did the knife enter? How do you know? ...
... What region did the knife enter? How do you know? ...
Autopsy

An autopsy—also known as a post-mortem examination, necropsy, autopsia cadaverum, or obduction—is a highly specialized surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse to determine the cause and manner of death and to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present. It is usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathologist.The word “autopsy” means to study and directly observe the body (Adkins and Barnes, 317). This includes an external examination of the deceased and the removal and dissection of the brain, kidneys, lungs and heart. When a coroner receives a body, he or she must first review the circumstances of the death and all evidence, then decide what type of autopsy should be performed if any. If an autopsy is recommended, the coroner can choose between an external autopsy (the deceased is examined, fingerprinted, and photographed but not opened; blood and fluid samples are taken), an external and partial internal autopsy (the deceased is opened but only affected organs are removed and examined), or a full external and internal autopsy.Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. For example, a forensic autopsy is carried out when the cause of death may be a criminal matter, while a clinical or academic autopsy is performed to find the medical cause of death and is used in cases of unknown or uncertain death, or for research purposes. Autopsies can be further classified into cases where external examination suffices, and those where the body is dissected and internal examination is conducted. Permission from next of kin may be required for internal autopsy in some cases. Once an internal autopsy is complete the body is reconstituted by sewing it back together.