* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Body Organizations
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
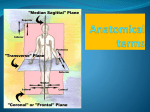
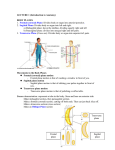
Body Organizations Flashcards 1. What are the two main regions of the body? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 3. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) a) Head b) Neck c) Trunk (has 3 parts) 3. What are the three parts of the Trunk (Axial Region)? What organs does each part contain? 1) Thorax (chest area). Above diaphragm. Contains heart and lungs. 2) Abdomen (not called the stomach!). Contains the digestive organs 3) Pelvis (covered by the G-String) Contains urinary and reproductive organs 4. What makes up the Upper Limbs of the Appendicular Region? 5. What is the term for the thumb? 6. What is the term for the arm? 7. What is the term for the area where blood is drawn? In what body region is it found? 8. What makes up the Lower Limbs of the Appendicular Region? 9. What is the term for the big toe? 10. What is the term for the area behind the knee? 11. What bone contains the area behind the knee? Appendicular Region - limbs a) Upper Limbs 1) Axilla (armpit) 2) Arm (shoulder to elbow) 3) Forearm (elbow to wrist). Don’t confuse with arm! 4) Wrist 5) Hand: 4 fingers with 3 phalanges each; thumb with 2 phalanges Pollex Brachium Antecubital fossa; it is in the brachium Lower Limbs 1) Thigh (hip to knee). Don’t confuse with leg! 2) Leg (knee to ankle) 3) Ankle 4) Foot: 5 digits; big toe is the hallux Hallux Popliteal fossa The back of the femur Body Organizations Flashcards 12. What describes ANATOMICAL POSITION? ANATOMICAL POSITION: The person is standing up straight The palms face anteriorly The knees, elbow, and neck are straight (not bent) The toes point anteriorly, but the fingers point inferiorly 13. If a person starts in anatomical position and then pronates their hands 90 degrees, which way do the palms face? 14. If a person starts in anatomical position and then pronates their hands 180 degrees, which way do the palms face? They face each other 15. What is Superior? Superior: towards the top of the head “The head is superior to the abdomen” 16. What is Inferior? Inferior: towards the bottom of the feet Posteriorly “The pelvis is inferior to the neck” 17. What is Anterior? Anterior (ventral): towards the front of the body “The breastbone is anterior to the spine” “The nose is anterior to the eyes.” 18. What is Posterior? Posterior (dorsal): towards the back of the body “The spine is posterior to the heart.” 19. What is Medial? Medial (not middle!): towards the midline. “The heart is medial to the lungs.” 20. What is Lateral? Lateral: towards the sides, away from the midline of the body. “The Lungs are lateral to the heart.” “The arms are lateral to the chest” 21. What is Proximal? Proximal: Close to the point of origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk (in most cases, closer to the heart). “The elbow is proximal to the wrist.” Don’t confuse with superior Body Organizations Flashcards 22. What is Distal? Distal: away from the point of origin (in most cases, away from the heart). “The fingers are distal to the wrist.” “The knee is distal to the thigh” NOTE: Do not get inferior mixed up with distal. Inferior means towards the feet, and distal means farther from the heart. 23. What is Superficial? Superficial (external): Toward or at the body surface “The skin is superficial to the muscles.” 24. What is Deep? Deep (internal): Away from the body surface; more internal. Do NOT use the term “interior”. “Bones are deep to the muscles.” “The lungs are deep to the skin” 25. What is Intermediate? Intermediate: Between a more medial and a more lateral structure “The collarbone is intermediate between the breastbone and shoulder” 26. What is the Frontal (coronal) Plane? Frontal (coronal) Plane: Divides body or organ into anterior/posterior. 27. What is the Sagittal Plane? Sagittal Plane: Divides body or organ into left and right. a) Midsagittal (median) plane: down the midline, dividing EQUALLY right and left. b) Parasagittal plane: divides into UNEQUAL right and left parts. 28. What is the Transverse Plane? Transverse Plane (Cross sec): Divides body or organ into superior/inferior parts 29. What are the 3 Body Cavities? Body Cavities 1. Thoracic cavity (contains lungs and heart) 2. Abdominal cavity (contains digestive organs) Body Organizations Flashcards 3. Pelvic cavity (contains reproductive organs) 30. What separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities? The thoracic and abdominal cavities are separated by the diaphragm. 31. What are the 2 Body Membranes and the space that separates them? Body Membranes 1. Parietal serosa (lines the body wall) 2. Visceral serosa (lines the organ such as heart or lungs) 3. Serous cavity (space between the parietal and visceral serosa; contains fluid) 32. What is Flexion/Extension? Flexion (reduces angle of joint) Extension (increases angle of the joint; returns part to anatomical position). Hyperextension goes even farther than anatomical position. 33. What are Abduction/ Adduction/ Rotation/ Circumduction? Abduction (takes body part away from midline in the frontal plane) Adduction (returns body part to midline in the frontal plane) Rotation (to pivot on the axis of a bone, such as shaking head “no”) Circumduction: (Using the body part to draw a circle in the air) 34. What is internal and external rotation? Internal rotation: to move a limb towards the midline of the body in the transverse plane External rotation: to move a limb away from the midline of the body in the transverse plane 35. What is Inversion/Eversion? Inversion (turns foot toward midline in the frontal plane) Eversion (turns foot away from midline in the frontal plane) Body Organizations Flashcards 36. What is Dorsiflexion/Plantarflexion? 37. What is Protraction/Retraction? Dorsiflexion: flexion of the ankle joint; to raise toes up in the air (sagittal plane) Plantarflexion: extension of the ankle joint; to point the toes downward (sagittal plane) Protraction: sticks body part out anteriorly (jutting out the jaw) Retraction: opposite movement to protraction (pulls body part posteriorly, such as the scapula) 38. What is Elevation/Depression? Elevation: lifting a body part superiorly (raising shoulders upward) Depression: moving the elevated part inferiorly (pulls body part inferiorly) 39. What is Opposition? Opposition (brings thumb to touch tips of fingers) 40. What is Pronation and Supination? Pronation: In the ankle, pronation is turning the sole of foot away from midline; tri-plane movement of eversion, abduction, and plantarflexion. In the wrists, pronation is turning the palms from anterior to posterior. Supination: In the ankle, supination is turning the sole of the foot toward midline; tri-plane movement of inversion, adduction, and dorsiflexion. In the wrists, supination is turning the palms from posterior to anterior. 41. What is prone, and how does it differ from pronation? Prone: a POSITION, not a movement; body is lying face down. Pronation is a movement. 42. What is supine, and how does it differ from supination? Supine: a POSITION, not a movement; body is lying on the back. Supination is a movement. 43. What is the difference between Adduction/Abduction and Flexion/Extension at the shoulders and hips? Adduction/Abduction: moving your arms/thighs away from the body laterally, in the frontal plane. Flexion/Extension: moving your arms/thighs away from the body in front of you, in the sagittal plane.