* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download anatomical terms of the body
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
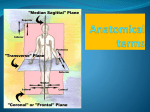
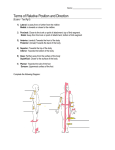
Anatomical Planes of the Body Plane Description Frontal plane A frontal plane divides the body into an anterior position and a posterior portion. Midsagittal plane A midsagittal plane is a vertical plane that divides the body lengthwise into two identical right and left sections. It runs exactly down the middle of the body. Sagittal plane A sagittal plane can run vertically down through the body at any point, not necessarily dividing it into identical right and left sections. The right and left sections are called longitudinal sections. Transverse plane A transverse plane divides the body horizontally into superior (top) and inferior (bottom) portions. These portions do not have to be equal and create cross sections. Positional Terms Name Description Anatomical position Standing straight, looking forward, arms at side, palms facing forward, thumbs to the outside Midline An imaginary plumb line dropped from the middle of the head, to the ground, in the anatomical position Supine Lying on the back with face up Prone Lying on the stomach with face down Anterior or Ventral Front or toward the front of the body Posterior or Dorsal Back or toward the back of the body Cephalic Pertaining to the head, near or toward the head Caudal Nearer or toward the lower part of the body Superior Above or higher than another part Inferior Below or lower than another part Medial or central In the middle or closer to the midline of the body Lateral or peripheral On the side or farther away from the midline of the body Proximal Nearer to the point of attachment (if a muscle) or the trunk of the body Distal Farther from the point of attachment or the trunk of the body Superficial Nearer to the surface of the body Deep Farther from the surface of the body Note: Except for the first two, I�ve grouped these terms in pairs of antonyms to help you remember them more easily. Regions of the Head and Neck Region Location Buccal Cheek Cervical The neck region Cephalic Head Cranial Skull Frontal Forehead Nasal Nose Occipital Back of head Opthalmic Eye Oral Mouth Orbital Bony eye sockets Regions of the Thorax (upper trunk) Region Location Axillary Armpit Costal Ribs Deltoid Curve of the shoulder formed by the large deltoid muscle Mammary Breast Pectoral Anterior chest Scapular Scapula or shoulder blade area Thoracic Chest Vertebral Backbone Regions of the Abdomen Region Location Abdomen/Celiac Trunk region inferior to the ribs Gluteal Buttocks Groin/Inguinal Area where the thigh meets the body trunk Lumbar Lower back, between the ribs and the hips Pelvic Lowest part of abdominal area Perineal Area between anus and external genitalia Pubic Genital region Sacral End of vertebral column Umbilical Pertaining to the naval (belly button) Regions of the Upper and Lower Extremities Region Location Antecubital The anterior surface of the elbow Brachial Upper arm—between the shoulder and elbow Carpal Wrist Cubital Elbow Digital Fingers or toes Femoral Thigh Forearm Lower arm-between the elbow and the wrist Lower leg Between the knee and ankle Palmar Palm Pedal Foot Popliteal Posterior knee region Sural Posterior calf area—between the knee and ankle Terminology of Movement Movement Description Flexion Bending a joint to bring bones closer together, decreasing angle of the joint. Ex. Bending the elbow, bending the knee. Extension Straightening a joint from a flexed position, increasing the distance between bones. Ex: Straightening the elbow, straightening the knee. Abduction Moving a limb, wrist, or finger away from the midline of the body or midline of the hand. Ex: Sideward movement of the upper arm away from the trunk, as in the first half of a jumping jack movement; spreading the fingers apart. Adduction The return movement from abduction; moving closer towards the midline of the body or hand. Ex.: Bringing the arms back down to the side. Internal rotation Moving a bone around a longitudinal axis so that the anterior surface of the limb turns towards the midline. Ex. Arms at side, palms forward, rotating inward at the shoulder. External rotation Opposite movement of internal rotation. Ex. Arms at side, palms facing backwards, rotating outward at the shoulder. Pronation Rotation of the forearm so that the palm of the hand faces backwards. Supination Rotation of the forearm so that the palm of the hand is turned to face forward. Inversion Turning the foot inward so that the sole is closer to the midline of the body. Eversion Turning the foot outward so that the sole is farther away from the midline of the body. Dorsiflexion A movement of the ankle which brings the toes and foot closer to the anterior surface of the lower leg. Plantarflexion A movement of the ankle which points the toes and foot away from the anterior surface of the lower leg. Protraction Protraction A forward movement of the shoulder blade (scapula) or lower jaw. Retraction A backward movement (pinching together) of the shoulder blades or backward movement of the lower jaw. Elevation Moving the shoulders upward (shrugging). Depression Pressing the shoulders downward. Circumduction A circular movement that combines flexion, abduction, extension, adduction, and rotation. Ex. Moving the arms at the shoulder joint in large circles.