Motor system - Brain Facts
... example, make them unable to open a door or to handle previously familiar tools. Such persons also have difficulties with proper orientation of the hand with relation to an object, and they easily miss an object even though they see it clearly. This kind of symptom is called apraxia. Recent studies, ...
... example, make them unable to open a door or to handle previously familiar tools. Such persons also have difficulties with proper orientation of the hand with relation to an object, and they easily miss an object even though they see it clearly. This kind of symptom is called apraxia. Recent studies, ...
Reflex Arc - wwhsanatomy
... control activities of the muscular system VISERAL REFLEXES or autonomic involuntary reflexes- control the actions of smooth and cardiac muscles and glands ...
... control activities of the muscular system VISERAL REFLEXES or autonomic involuntary reflexes- control the actions of smooth and cardiac muscles and glands ...
8: Control of Movement Biological Bases of Behavior
... Vestibulospinal tract: control of posture u Tectospinal tract: coordinate eye and head/trunk movements u Reticulospinal tract: walking, sneezing, muscle tone u Ventral corticospinal tract: muscles of upper leg/trunk u ...
... Vestibulospinal tract: control of posture u Tectospinal tract: coordinate eye and head/trunk movements u Reticulospinal tract: walking, sneezing, muscle tone u Ventral corticospinal tract: muscles of upper leg/trunk u ...
Control of Movement
... Motor cortex is somatotopically organized (motor homunculus) Motor cortex receives input from Premotor cortex Supplemental motor area Frontal association cortex Primary somatosensory cortex ...
... Motor cortex is somatotopically organized (motor homunculus) Motor cortex receives input from Premotor cortex Supplemental motor area Frontal association cortex Primary somatosensory cortex ...
Central Control of Motor Function
... Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum The basal ganglia and cerebellum are large collections of nuclei that modify movement on a minute-to-minute basis. The motor cortex sends information to both, and both structures send information back via the thalamus. Output of the cerebellum is excitatory and inhibi ...
... Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum The basal ganglia and cerebellum are large collections of nuclei that modify movement on a minute-to-minute basis. The motor cortex sends information to both, and both structures send information back via the thalamus. Output of the cerebellum is excitatory and inhibi ...
Reflexes
... The segmental level is the lowest level of motor hierarchy It consists of segmental circuits of the spinal cord Its circuits control locomotion and specific, oft-repeated motor activity These circuits are called central pattern ...
... The segmental level is the lowest level of motor hierarchy It consists of segmental circuits of the spinal cord Its circuits control locomotion and specific, oft-repeated motor activity These circuits are called central pattern ...
Population vectors and motor cortex: neural coding or
... © 2000 Nature America Inc. • http://neurosci.nature.com ...
... © 2000 Nature America Inc. • http://neurosci.nature.com ...
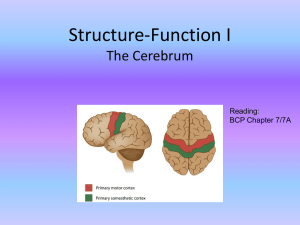
Structure-Function I
... major bundles include: Association • short (arcuate) fibers: primary somatosensory with primary motor • long (fasciculus) fibers: connect Wernicke’s and Broca’s areas Commissural • corpus callosum • anterior Projection • corona radiata • internal capsule sensory input from thalamus motor output ...
... major bundles include: Association • short (arcuate) fibers: primary somatosensory with primary motor • long (fasciculus) fibers: connect Wernicke’s and Broca’s areas Commissural • corpus callosum • anterior Projection • corona radiata • internal capsule sensory input from thalamus motor output ...
Motor System I: The Pyramidal Tract
... Contraction of specific muscles always related to site of stimulation on area 4. From this, the concept of a “motor homunculus” has emerged. Stimulation of area 4 causes flick-like flexions or extensions involving few muscles. Stimulation of area 6 or other areas may result in patterned movements in ...
... Contraction of specific muscles always related to site of stimulation on area 4. From this, the concept of a “motor homunculus” has emerged. Stimulation of area 4 causes flick-like flexions or extensions involving few muscles. Stimulation of area 6 or other areas may result in patterned movements in ...
THE BASAL GANGLIA - Selam Higher Clinic
... Brief coordinated sterotyped movements and vocalizations Most are suppressed for short period ...
... Brief coordinated sterotyped movements and vocalizations Most are suppressed for short period ...
Chapter 15
... – colliculi receive visual (superior) and auditory (inferior) sensations – axons of upper motor neurons in colliculi descend in tectospinal tracts – these axons cross to opposite side, before descending to synapse on lower motor neurons in brain stem or spinal cord ...
... – colliculi receive visual (superior) and auditory (inferior) sensations – axons of upper motor neurons in colliculi descend in tectospinal tracts – these axons cross to opposite side, before descending to synapse on lower motor neurons in brain stem or spinal cord ...
Brain Regions Involved in USCBP Reaching Models
... objective of the coordination. As an example, we can weigh more on faster movement, or on the accurate movement, or accurate grasping. So based on the different objective, we may have variability in coordination. However, this coordination is not free from the actuators. First, if there is a signal ...
... objective of the coordination. As an example, we can weigh more on faster movement, or on the accurate movement, or accurate grasping. So based on the different objective, we may have variability in coordination. However, this coordination is not free from the actuators. First, if there is a signal ...
Lecture 11
... 3. ventral (anterior,motor) root a. motor nerve AXONS only i. skeletal motor neurons (ant. horn) ii. smooth/cardiac/gland neurons (lat. horn) B. The Simple Reflex Arc 1. A special type of conduction pathway 2. Receptor - responds to internal/external stimulus 3. Sensory Neuron - passes impulse to CN ...
... 3. ventral (anterior,motor) root a. motor nerve AXONS only i. skeletal motor neurons (ant. horn) ii. smooth/cardiac/gland neurons (lat. horn) B. The Simple Reflex Arc 1. A special type of conduction pathway 2. Receptor - responds to internal/external stimulus 3. Sensory Neuron - passes impulse to CN ...
MOTOR SYSTEM – Muscle, LMC, Spinal cord mechanisms of control
... called central pattern generator (CPG); CPGs are in the spinal cord and brainstem for respiration, chewing, swallowing, and locomotion - once a CPG is activated it can product the complex muscle instruction by its own subroutine; does not need descending cortical input or sensory feedback - A CPG re ...
... called central pattern generator (CPG); CPGs are in the spinal cord and brainstem for respiration, chewing, swallowing, and locomotion - once a CPG is activated it can product the complex muscle instruction by its own subroutine; does not need descending cortical input or sensory feedback - A CPG re ...
control of movement by the CNS - motor neurons found in anterior
... related to ‘working memory’.. premotor neurons often inactive during actual movement active during prep: selecting appropriate cortical and postural synergies - motor field one corticospinal axon synapses with a set of motor nuclei (>1 spinal segment) set of muscles influenced constitutes the motor ...
... related to ‘working memory’.. premotor neurons often inactive during actual movement active during prep: selecting appropriate cortical and postural synergies - motor field one corticospinal axon synapses with a set of motor nuclei (>1 spinal segment) set of muscles influenced constitutes the motor ...
Structure of the Nervous System Functional Classes of Neurons
... the muscles of the neck. Each trunk then splits in two, to form six divisions. These six divisions will regroup to become the three cords. The cords are named by their position with respect to the axillary artery. These cords branch the branch to travel to specific muscles. Each branch is a n ...
... the muscles of the neck. Each trunk then splits in two, to form six divisions. These six divisions will regroup to become the three cords. The cords are named by their position with respect to the axillary artery. These cords branch the branch to travel to specific muscles. Each branch is a n ...
File
... areas, as well as input from the limbic system. Most of the output goes to the primary motor cortex. Do not exert direct control over lower motor neurons. Provide the patterned background movements needed for conscious motor activities by adjusting the motor commands issued in other nuclei. ...
... areas, as well as input from the limbic system. Most of the output goes to the primary motor cortex. Do not exert direct control over lower motor neurons. Provide the patterned background movements needed for conscious motor activities by adjusting the motor commands issued in other nuclei. ...
Nervous System: Reflexes and Peripheral Nervous System
... automatic responses to specific stimuli ...
... automatic responses to specific stimuli ...
L4- Student Copy Motor Tracts
... are sent through pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts to terminate on motor neurons in the spinal cord and brain stem . The activity of the lower motor neuron (LMN, spinal or cranial) is influenced by (1) Upper Motor Neurons (UMNs ) coming from supraspinal centers via ) via descending motor tracts ...
... are sent through pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts to terminate on motor neurons in the spinal cord and brain stem . The activity of the lower motor neuron (LMN, spinal or cranial) is influenced by (1) Upper Motor Neurons (UMNs ) coming from supraspinal centers via ) via descending motor tracts ...
Post-Polio Motor Neurons and Units: What We Know
... The project, headed by David B. Gray, PhD, in the Program in Occupational Therapy at Washington University School of Medicine in Saint Louis, Missouri, is funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The goal of the threestage research project, "Mobility, Disabilities, Participation and ...
... The project, headed by David B. Gray, PhD, in the Program in Occupational Therapy at Washington University School of Medicine in Saint Louis, Missouri, is funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The goal of the threestage research project, "Mobility, Disabilities, Participation and ...
sms5
... A. The Ia inhibitory interneuron allows higher centers to coordinate opposing muscles at a joint through a single command. This inhibitory interneuron mediates reciprocal innervation in stretch reflex circuits. In addition, it receives inputs from corticospinal descending axons, so that a descending ...
... A. The Ia inhibitory interneuron allows higher centers to coordinate opposing muscles at a joint through a single command. This inhibitory interneuron mediates reciprocal innervation in stretch reflex circuits. In addition, it receives inputs from corticospinal descending axons, so that a descending ...
Control of Movement
... Motor cortex is somatotopically organized (motor homunculus) Motor cortex receives input from Premotor cortex Supplemental motor area Frontal association cortex Primary somatosensory cortex ...
... Motor cortex is somatotopically organized (motor homunculus) Motor cortex receives input from Premotor cortex Supplemental motor area Frontal association cortex Primary somatosensory cortex ...
Final Report
... The generation of rhythmic movements, like breathing and chewing, is one important function of the brain. The brain needs to be able to not only generate these specific motor patterns, but also modify the pattern to adapt to changes in the environment. To further investigate how this mechanism works ...
... The generation of rhythmic movements, like breathing and chewing, is one important function of the brain. The brain needs to be able to not only generate these specific motor patterns, but also modify the pattern to adapt to changes in the environment. To further investigate how this mechanism works ...
CNS Anatomy 2 **You need to study the slide hand in hand with this
... dendrid-axon. This dendrid-axon separates into two processes :1-central process in the spinal cord (function like the axon). 2-perripheral process in the peripheral receptors (function like the dendrites) -The impulse will enter the peripheral process then to the central process without entering the ...
... dendrid-axon. This dendrid-axon separates into two processes :1-central process in the spinal cord (function like the axon). 2-perripheral process in the peripheral receptors (function like the dendrites) -The impulse will enter the peripheral process then to the central process without entering the ...
Chapter 10 - Dr. Eric Schwartz
... integrating information about the nature of an intended movement with information about the surrounding space. • During movement, the cerebellum compares information about what the muscles should be doing with information about what they actually are doing and can send correction signals if needed. ...
... integrating information about the nature of an intended movement with information about the surrounding space. • During movement, the cerebellum compares information about what the muscles should be doing with information about what they actually are doing and can send correction signals if needed. ...