BOX 30.8 THE ROLE OF THE SUBTHALAMIC NUCLEUS IN
... subthalamic nucleus has different territories, including sensorimotor, associative and limbic, which connect to motor/premotor cortical, lateral prefrontal and cingulate/orbital frontal regions, respectively. It is an open question whether the kind of stopping discussed here could extend, for exampl ...
... subthalamic nucleus has different territories, including sensorimotor, associative and limbic, which connect to motor/premotor cortical, lateral prefrontal and cingulate/orbital frontal regions, respectively. It is an open question whether the kind of stopping discussed here could extend, for exampl ...
Chapter 49 and 50 Presentations-Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
... of contraction is controlled by the nervous system. At any given instant, the nervous system can select a large or small numbe of motor neurons to activate. The force of the contraction developed by the muscle is increased/decreased as the number of motor neurons controlling the motor unit ...
... of contraction is controlled by the nervous system. At any given instant, the nervous system can select a large or small numbe of motor neurons to activate. The force of the contraction developed by the muscle is increased/decreased as the number of motor neurons controlling the motor unit ...
BN16 Neural plasticity
... in activity of specific Purkinje cells Climbing fibers may carry error signals corrections parallel fiber influence input specificity only affects active synapses of a parallel fiber ~ ...
... in activity of specific Purkinje cells Climbing fibers may carry error signals corrections parallel fiber influence input specificity only affects active synapses of a parallel fiber ~ ...
Ch. 14 The Peripheral Nervous System
... – Rootlets enter via foramen magnum, exits through jugular foramen ...
... – Rootlets enter via foramen magnum, exits through jugular foramen ...
NEUROSCIENCE Review Questions CHOOSE THE LETTER THAT
... C. there is complete but temporary paralysis. D. there is a complete, but temporary, loss of reflexes below the damage. E. spinal reflexes become hyperactive. 14. Concerning primary motor cortex, area 4: A. lesions in area 4 result in apraxia. B. it has a map of the ipsilateral body with small disc ...
... C. there is complete but temporary paralysis. D. there is a complete, but temporary, loss of reflexes below the damage. E. spinal reflexes become hyperactive. 14. Concerning primary motor cortex, area 4: A. lesions in area 4 result in apraxia. B. it has a map of the ipsilateral body with small disc ...
Module 3 The integration of postural control and selective movement
... 3. Spasticity cannot be exclusively considered a ‘motor disorder’ as afferent activity (cutaneous and proprioceptive) is also involved The European Assembly for Spasticity Measurement (EU SPASM) in 2005 published a new definition of spasticity as: “disordered sensory-motor control, resulting from an ...
... 3. Spasticity cannot be exclusively considered a ‘motor disorder’ as afferent activity (cutaneous and proprioceptive) is also involved The European Assembly for Spasticity Measurement (EU SPASM) in 2005 published a new definition of spasticity as: “disordered sensory-motor control, resulting from an ...
The Motor System of the Cortex and the Brain Stem
... reproduction — but every individual must learn and remember a great deal of motor information during his or her lifetime. Some of that information rises to conscious awareness, but much of it does not. Here we will focus on the motor system of humans, drawing on information from other primates and o ...
... reproduction — but every individual must learn and remember a great deal of motor information during his or her lifetime. Some of that information rises to conscious awareness, but much of it does not. Here we will focus on the motor system of humans, drawing on information from other primates and o ...
Respiratory System
... • Activation of muscles – The extent of control of a muscle depends on the number of muscle fibers within each motor unit. • Muscles that function with great precision may have as few as one muscle fiber per motor neuron. • Muscles that require less precision may have several hundred fibers served b ...
... • Activation of muscles – The extent of control of a muscle depends on the number of muscle fibers within each motor unit. • Muscles that function with great precision may have as few as one muscle fiber per motor neuron. • Muscles that require less precision may have several hundred fibers served b ...
The Graded Motor Imagery Handbook, 2012
... processing speed of CNS & attention to body part Mentally move our own matching limb to mimic the posture of the limb- requires an intact working body schema & it’s integration of premotor processes Confirm or deny the initial judgment –dependent on the processing speed of the CNS ...
... processing speed of CNS & attention to body part Mentally move our own matching limb to mimic the posture of the limb- requires an intact working body schema & it’s integration of premotor processes Confirm or deny the initial judgment –dependent on the processing speed of the CNS ...
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience MIT OpenCourseWare Fall 2007
... • The set of alpha motor neurons that innervates a single muscle. ...
... • The set of alpha motor neurons that innervates a single muscle. ...
DescendSC10
... 2. Prefrontal association areas (maturation and cognition – “get the idea”). 3. Premotor areas “plan of action” 4. 1° motor cortex 5. Corticospinal tract – interneurons motor neurons (grasp the cup) Cerebellum and bg also play a role in feedback control and movement intention – we will discuss s ...
... 2. Prefrontal association areas (maturation and cognition – “get the idea”). 3. Premotor areas “plan of action” 4. 1° motor cortex 5. Corticospinal tract – interneurons motor neurons (grasp the cup) Cerebellum and bg also play a role in feedback control and movement intention – we will discuss s ...
Laboratory Exercise 11: Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain
... center that controls breathing. Medulla oblongata - the most inferior part of the brain, connects brain to spinal cord. Function: It is a control center for vital reflexes through the autonomic nervous system (ANS). For example it regulates heart rate, blood pressure and breathing. Cerebellum - subd ...
... center that controls breathing. Medulla oblongata - the most inferior part of the brain, connects brain to spinal cord. Function: It is a control center for vital reflexes through the autonomic nervous system (ANS). For example it regulates heart rate, blood pressure and breathing. Cerebellum - subd ...
A zebrafish model exemplifies the long preclinical period of motor
... like to highlight recent, important work on a zebrafish model of ALS that contributes to the concept of preclinical change. Specifically, we have developed a sod1 zebrafish model of ALS/motor neuron disease (MND) and demonstrated that zebrafish, like mice and humans, show hallmark features of ALS, sugge ...
... like to highlight recent, important work on a zebrafish model of ALS that contributes to the concept of preclinical change. Specifically, we have developed a sod1 zebrafish model of ALS/motor neuron disease (MND) and demonstrated that zebrafish, like mice and humans, show hallmark features of ALS, sugge ...
1 Principles of structure and functioning of nervous system
... preservation of the brain motor systems is an important term of accidental moves of a person. Motor system abnormalities happen in the damage of nervous system by many different factors and represent great importance for the diagnostics of the nosologic form of a disease. Motor abnormalities represe ...
... preservation of the brain motor systems is an important term of accidental moves of a person. Motor system abnormalities happen in the damage of nervous system by many different factors and represent great importance for the diagnostics of the nosologic form of a disease. Motor abnormalities represe ...
Infant Physical Development2016
... are the same as those experienced by another ◦ Looked longer at novel items than those previously handled ...
... are the same as those experienced by another ◦ Looked longer at novel items than those previously handled ...
AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 2 Week 9/28 – 10/2 The following
... E. Aerobic oxidation will only provide ATP to muscle for the first 6-10 seconds of exercise. 20. Isometric contractions A. can either be eccentric (shortening)or concentric (lengthening) B. maintain the same tension throughout a contraction C. maintain the same rate of extension/contraction througho ...
... E. Aerobic oxidation will only provide ATP to muscle for the first 6-10 seconds of exercise. 20. Isometric contractions A. can either be eccentric (shortening)or concentric (lengthening) B. maintain the same tension throughout a contraction C. maintain the same rate of extension/contraction througho ...
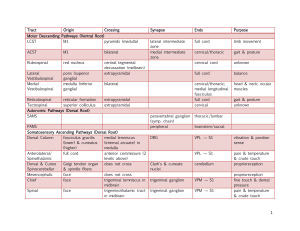
Tract Origin Crossing Synapse Ends Purpose Motor Descending
... peduncle/pontine lesions; hydrocephalus; prefrontal cortex; spinal cord disorder; contralateral ataxia-hemiparesis ...
... peduncle/pontine lesions; hydrocephalus; prefrontal cortex; spinal cord disorder; contralateral ataxia-hemiparesis ...
Neurologic Assessment
... Motor function Pupillary response Vital signs Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) Slide 23-14 ...
... Motor function Pupillary response Vital signs Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) Slide 23-14 ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿 - Shandong University
... Golgi tendon organs help ensure smooth onset and termination of muscle contraction Particularly important in activities involving rapid switching between flexion and extension such as in running ...
... Golgi tendon organs help ensure smooth onset and termination of muscle contraction Particularly important in activities involving rapid switching between flexion and extension such as in running ...
Motor activity induced by disinhibition of the primary motor cortex of
... (APV) in order to block more effectively and locally the transmission through this receptor. Application of APV did not affect the spontaneous EMG activity elicited by bicuculline (Fig. 1B). Application of a non-NMDA receptor antagonist (CNQX), which blocks transmission through the quisqualate and k ...
... (APV) in order to block more effectively and locally the transmission through this receptor. Application of APV did not affect the spontaneous EMG activity elicited by bicuculline (Fig. 1B). Application of a non-NMDA receptor antagonist (CNQX), which blocks transmission through the quisqualate and k ...
stretch reflexes
... in the absence of the cerebellum, a person ordinarily moves the hand or some other moving part of the body considerably beyond the point of intention. This results from the fact that normally the cerebellum initiates most of the motor signal that turns off a movement after it is begun if the cerebel ...
... in the absence of the cerebellum, a person ordinarily moves the hand or some other moving part of the body considerably beyond the point of intention. This results from the fact that normally the cerebellum initiates most of the motor signal that turns off a movement after it is begun if the cerebel ...
Motor System: Reflexes, Pyramidal Tract and Basal Ganglia
... A. control over facial muscles; bilateral input to motor neurons controlling muscles in upper face, but contralateral input to motor neurons controlling lower face (in humans, not sure about rodents) B. control over muscles of mastication: motor trigeminal, and RF C. control over external eye muscle ...
... A. control over facial muscles; bilateral input to motor neurons controlling muscles in upper face, but contralateral input to motor neurons controlling lower face (in humans, not sure about rodents) B. control over muscles of mastication: motor trigeminal, and RF C. control over external eye muscle ...
motor unit
... the cytosolic concentration of Ca2+ remains high The prolonged availability of Ca2+ in the cytosol permits more of the cross bridges to continue participating in the cycling process for a longer time With an increase in the frequency of action potentials, duration of elevated cytosolic Ca2+ concentr ...
... the cytosolic concentration of Ca2+ remains high The prolonged availability of Ca2+ in the cytosol permits more of the cross bridges to continue participating in the cycling process for a longer time With an increase in the frequency of action potentials, duration of elevated cytosolic Ca2+ concentr ...
Motor System II: Brainstem and spinal cord LMN in CNS lesions
... smile, show the teeth, close the eyelid or wrinkle the forehead on the paralyzed (ipsilateral) side. Hyperacusis may result from paralysis of the stapedius. Ipsilateral corneal reflex is also abolished. Unilateral lesion of corticobulbar fibers innervating motor VII. Results in contralateral lower f ...
... smile, show the teeth, close the eyelid or wrinkle the forehead on the paralyzed (ipsilateral) side. Hyperacusis may result from paralysis of the stapedius. Ipsilateral corneal reflex is also abolished. Unilateral lesion of corticobulbar fibers innervating motor VII. Results in contralateral lower f ...