Outline14 Efferent NS
... - axon terminals secrete ACh into the synaptic cleft nicotinic cholinergic receptors at the motor end plate binding of ACh open cation channels → strong EPSP → exceeds threshold → muscle AP B. Autonomic Division (ANS) - involuntary control of autonomic effectors (visceral organs, blood vessels, etc. ...
... - axon terminals secrete ACh into the synaptic cleft nicotinic cholinergic receptors at the motor end plate binding of ACh open cation channels → strong EPSP → exceeds threshold → muscle AP B. Autonomic Division (ANS) - involuntary control of autonomic effectors (visceral organs, blood vessels, etc. ...
Commentary on slides Lecture 16
... directed towards the deep cerebellar nuclei: the globose, embolliform (these two make up the interpositus nucleus), fastigial and dentate. These nuclei also receive excitatory input from the collaterals of afferent fibers; Purkinje cell outputs thus modify discharges of the deep cerebellar nuclei. T ...
... directed towards the deep cerebellar nuclei: the globose, embolliform (these two make up the interpositus nucleus), fastigial and dentate. These nuclei also receive excitatory input from the collaterals of afferent fibers; Purkinje cell outputs thus modify discharges of the deep cerebellar nuclei. T ...
56 Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia
... all its input from the motor cortex, adjacent pre-motor and somatic sensory cortices of the brain. Transmits its output information back to the brain. Functions in a “feedback” manner with all of the cortical sensory-motor system to plan sequential voluntary body and limb movements, ...
... all its input from the motor cortex, adjacent pre-motor and somatic sensory cortices of the brain. Transmits its output information back to the brain. Functions in a “feedback” manner with all of the cortical sensory-motor system to plan sequential voluntary body and limb movements, ...
Objectives 34
... distal hand muscles (direct control); motor cortex has a specialized function for fine finger movement control because: 1. Humans have skilled hand functions 2. The hand is complicated and has a flexibility of actions ...
... distal hand muscles (direct control); motor cortex has a specialized function for fine finger movement control because: 1. Humans have skilled hand functions 2. The hand is complicated and has a flexibility of actions ...
Document
... • Mossy fiber (+) granule cells (axon: parallel fibers, +) Purkinje cells (-) deep nuclei • each parallel fiber projects to thousands of Purkinje cells (high divergence) • each Purkinje cell receives input from ~200,000 parallel fibers (high convergence) • Weak excitatory connection, spatiotem ...
... • Mossy fiber (+) granule cells (axon: parallel fibers, +) Purkinje cells (-) deep nuclei • each parallel fiber projects to thousands of Purkinje cells (high divergence) • each Purkinje cell receives input from ~200,000 parallel fibers (high convergence) • Weak excitatory connection, spatiotem ...
A study on the general visceral sensory and motor systems in fish
... Afferent information from the visceral organs is carried through the general visceral sensory system while efferent information from the central nervous system is sent through the general visceral motor system. The motor system belongs to a parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous systems. ...
... Afferent information from the visceral organs is carried through the general visceral sensory system while efferent information from the central nervous system is sent through the general visceral motor system. The motor system belongs to a parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous systems. ...
Practice Questions for Neuro Anatomy Lectures 1 and 10 White
... 20. If a patient performs an act with unexpected and irrelevant movements then they could likely have a: a. Cerebellar lesion b. Cerebral lesion c. Basal ganglia lesion 21. Broadman’s area 4 is the ________ area and is located _______ to the central sulcus and generates neural impulses that control ...
... 20. If a patient performs an act with unexpected and irrelevant movements then they could likely have a: a. Cerebellar lesion b. Cerebral lesion c. Basal ganglia lesion 21. Broadman’s area 4 is the ________ area and is located _______ to the central sulcus and generates neural impulses that control ...
Motor Units and Motor Neuron Disease
... studies showed that the active channel for the G93A mutant is larger than that of the wildtype, thus it’s more accessible to peroxide. b) Is it a good model? Why? It is a good model because it successfully represents the gain-of-function of SOD1 found in some familial cases of ALS. However since thi ...
... studies showed that the active channel for the G93A mutant is larger than that of the wildtype, thus it’s more accessible to peroxide. b) Is it a good model? Why? It is a good model because it successfully represents the gain-of-function of SOD1 found in some familial cases of ALS. However since thi ...
Descending Spinal Tracts
... Receptors - also called hair cells encode location and movement relative to gravity ...
... Receptors - also called hair cells encode location and movement relative to gravity ...
Purkinje cells
... (GABA) first to the external segment of the globus pallidus (GABA) and then to the subthalamic nucleus (Glu), before finally reaching the internal segment of the globus pallidus or the substantia nigra pars reticulata. The isgp and the snpr project inhibitory (GABA) synapses to the thalamus. Result: ...
... (GABA) first to the external segment of the globus pallidus (GABA) and then to the subthalamic nucleus (Glu), before finally reaching the internal segment of the globus pallidus or the substantia nigra pars reticulata. The isgp and the snpr project inhibitory (GABA) synapses to the thalamus. Result: ...
Pathways - Orange Coast College
... Sensory pathways utilize a series of two or three neurons to transmit stimulus information from the body periphery to the brain. The first neuron is the primary (first-order) neuron The dendrites are part of the receptor that detects a ...
... Sensory pathways utilize a series of two or three neurons to transmit stimulus information from the body periphery to the brain. The first neuron is the primary (first-order) neuron The dendrites are part of the receptor that detects a ...
Basic Structure and Function of Neurons
... to a ventral root .They form excitatory synaptic contacts with interneurons located in the ventromedial region of the ventral horn . The axons of these Renshaw cells establish inhibitory synaptic contacts with the same and interneurons in an overlapping and diffuse fashion. Since the Renshaw cells p ...
... to a ventral root .They form excitatory synaptic contacts with interneurons located in the ventromedial region of the ventral horn . The axons of these Renshaw cells establish inhibitory synaptic contacts with the same and interneurons in an overlapping and diffuse fashion. Since the Renshaw cells p ...
7 - smw15.org
... • Rapid, ballistic movements, sequences that require accurate aiming and timing • Finger-to-nose task: initial rapid movement may strike face or hold segment of task may waver, as when intoxicated • Judging differences in delay in pairs of tones ...
... • Rapid, ballistic movements, sequences that require accurate aiming and timing • Finger-to-nose task: initial rapid movement may strike face or hold segment of task may waver, as when intoxicated • Judging differences in delay in pairs of tones ...
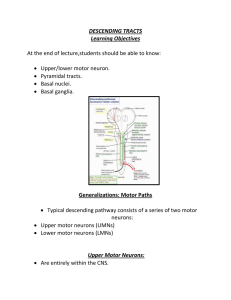
DESCENDING TRACTS Learning Objectives At the end of lecture
... Originates in various regions of reticular formation. Descends in anterior portion of lateral funiculus (column). Thought to mediate larger movements of trunk and limbs that do not require balance or fine movements of upper limbs. ...
... Originates in various regions of reticular formation. Descends in anterior portion of lateral funiculus (column). Thought to mediate larger movements of trunk and limbs that do not require balance or fine movements of upper limbs. ...
Anatomy Questions 3/2/16 1. The dorsal gray horns of the spinal
... i. It is part of the limbic system ii. It plays a role in controlling circadian rhythms iii. It regulates body temperature iv. It controls specific involuntary somatic motor activities a. 1 and 3 b. 2 and 4 c. 1, 2, and 3 d. All of the above e. None of the above 4. Non-fluent aphasia is a condition ...
... i. It is part of the limbic system ii. It plays a role in controlling circadian rhythms iii. It regulates body temperature iv. It controls specific involuntary somatic motor activities a. 1 and 3 b. 2 and 4 c. 1, 2, and 3 d. All of the above e. None of the above 4. Non-fluent aphasia is a condition ...
presentation5
... Premotor cortex, parietal areas and the superior temporal sulcus (STS) neurons are activated during action observation ...
... Premotor cortex, parietal areas and the superior temporal sulcus (STS) neurons are activated during action observation ...
Lecture 26 revised 03/10 Upper Motor Control Last lecture we
... somatosensory ctx motor and premotor axons terminate on ventral horn and intermediate zone of spinal cord somatosensory ctx axons terminate in dorsal horn; thought to regulate influx of somatosensory info There is somatotopic organization of descending projections in internal capsule, cerebral pedun ...
... somatosensory ctx motor and premotor axons terminate on ventral horn and intermediate zone of spinal cord somatosensory ctx axons terminate in dorsal horn; thought to regulate influx of somatosensory info There is somatotopic organization of descending projections in internal capsule, cerebral pedun ...
Organization of the Nervous System and Motor unit BY
... 3 Axon hillock بروزat which nerve impulses begin &pass in one direction from soma to the axon( nerve fiber) then to axon terminal. 4-Axon and axon terminal end on skeletal muscle via neuromuscular junction Nerve cell axons are very thin, about 1 micrometer. However, they are extraordinarily long. ...
... 3 Axon hillock بروزat which nerve impulses begin &pass in one direction from soma to the axon( nerve fiber) then to axon terminal. 4-Axon and axon terminal end on skeletal muscle via neuromuscular junction Nerve cell axons are very thin, about 1 micrometer. However, they are extraordinarily long. ...
CranialN11
... B. Cortical areas involved in eye movement control. Rapid and slow eye movements: Rapid: saccades: quick movements of eyes in tandem to bring the fovea to an image. Slow: smooth pursuit: eyes in tandem to track a moving object Slow: convergence: disconjugate eye movement for viewing an object at a ...
... B. Cortical areas involved in eye movement control. Rapid and slow eye movements: Rapid: saccades: quick movements of eyes in tandem to bring the fovea to an image. Slow: smooth pursuit: eyes in tandem to track a moving object Slow: convergence: disconjugate eye movement for viewing an object at a ...
Cerebellar system and diseases
... Loss of ability to gauge • the distance • Speed • Power of movement The act may be carried out with too little or too much power. The act may stop before the goal is reached or overshoot. ...
... Loss of ability to gauge • the distance • Speed • Power of movement The act may be carried out with too little or too much power. The act may stop before the goal is reached or overshoot. ...
Final review quiz
... Which brain structure is implicated in procedural learning? _______________________________ A rat is trained to run a T-maze. When the maze is rotated 180º, will the rat go to the specific place or make the same turn as it was trained to get the reward? When the maze is flipped early in training (in ...
... Which brain structure is implicated in procedural learning? _______________________________ A rat is trained to run a T-maze. When the maze is rotated 180º, will the rat go to the specific place or make the same turn as it was trained to get the reward? When the maze is flipped early in training (in ...
bulbar pseudobulbar
... If a lesion occurs in the brain stem and damages both the nucleus of a cranial nerve and one side of the upper motor neurons of the pyramidal tract, a condition known as alternating hemiplegia may result. This involves paralysis of different structures on each side of the body. The lesion on the nu ...
... If a lesion occurs in the brain stem and damages both the nucleus of a cranial nerve and one side of the upper motor neurons of the pyramidal tract, a condition known as alternating hemiplegia may result. This involves paralysis of different structures on each side of the body. The lesion on the nu ...