Honors Biology I Ch 30 Plant Reproduction Seed Plants *seed
... a) Contain _________parts to their seed b) Vascular bundles are ____________ c) ________________in narrow leaves d) Flower parts in ____________or multiples of _____________ Ex.___________________________________________________________ B. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Early land plants ...
... a) Contain _________parts to their seed b) Vascular bundles are ____________ c) ________________in narrow leaves d) Flower parts in ____________or multiples of _____________ Ex.___________________________________________________________ B. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Early land plants ...
Botany is the study of plants
... What is a Plant? Botany is the study of plants. Without plants life on earth would not exist! The plant kingdom is divided into many groups. There are seeded plants, which are divided into two groups: Angiosperms - flowering plants like deciduous trees, grass and flowers and Gymnosperms - plants tha ...
... What is a Plant? Botany is the study of plants. Without plants life on earth would not exist! The plant kingdom is divided into many groups. There are seeded plants, which are divided into two groups: Angiosperms - flowering plants like deciduous trees, grass and flowers and Gymnosperms - plants tha ...
The New England Carnivorous Plant Society www
... Bladderwort is the common name given to the plants of the genus Utricularia, the largest genus of carnivorous plants. There are over two hundred species found in fresh water and wet soil. Bladderworts are most often cultivated for their flowers, which are often compared with those of snapdragons and ...
... Bladderwort is the common name given to the plants of the genus Utricularia, the largest genus of carnivorous plants. There are over two hundred species found in fresh water and wet soil. Bladderworts are most often cultivated for their flowers, which are often compared with those of snapdragons and ...
Leaves- a plant`s food factory Photosynthesis
... Leaves- a plant’s food factory Animals are Consumers- we have to eat other things to survive. Plants are Producers- they make their own food using Sunlight, Carbon Dioxide and Water to create the sugar (Glucose) they eat. This is called PHOTOSYNTHESIS. ...
... Leaves- a plant’s food factory Animals are Consumers- we have to eat other things to survive. Plants are Producers- they make their own food using Sunlight, Carbon Dioxide and Water to create the sugar (Glucose) they eat. This is called PHOTOSYNTHESIS. ...
basicbotany_tanner
... is transferred to the stigma of another. Self-pollination - the stigma is pollinated by pollen from the same plant. Fertilization - ovule (egg) is fertilized by the sperm from the pollen grain. ...
... is transferred to the stigma of another. Self-pollination - the stigma is pollinated by pollen from the same plant. Fertilization - ovule (egg) is fertilized by the sperm from the pollen grain. ...
Life Functions – Literacy Chart Vocabulary Term Book/internet
... A flowering, fruitbearing plant or tree, the ovules (and therefore seeds) of these plants develop within an enclosed ovary. ...
... A flowering, fruitbearing plant or tree, the ovules (and therefore seeds) of these plants develop within an enclosed ovary. ...
Plants - Back to Basics
... process by which plants make sugars (convert sun’s energy into food) takes place in chloroplasts uses carbon dioxide and water to make sugars and oxygen phloem tissues transport sugars to non-photosynthetic parts of the plant (phloem DOWN) ...
... process by which plants make sugars (convert sun’s energy into food) takes place in chloroplasts uses carbon dioxide and water to make sugars and oxygen phloem tissues transport sugars to non-photosynthetic parts of the plant (phloem DOWN) ...
Chapter 5: Seed Plants
... the time of flowering in many plants. -A plant’s response to these seasonal changes is called ______________________. Winter Dormancy -______________ is a period when an organism’s growth or activity stops. -Dormancy helps plants survive ___________ temperatures and lack of ____________________. -Th ...
... the time of flowering in many plants. -A plant’s response to these seasonal changes is called ______________________. Winter Dormancy -______________ is a period when an organism’s growth or activity stops. -Dormancy helps plants survive ___________ temperatures and lack of ____________________. -Th ...
B - Fort Bend ISD
... Seeds can be dispersed in a number of different ways. They may be carried by wind, water or animals. Some plants even shoot the seeds out explosively. Seed size is an important factor ...
... Seeds can be dispersed in a number of different ways. They may be carried by wind, water or animals. Some plants even shoot the seeds out explosively. Seed size is an important factor ...
Plant reproduction
... potentially develop into a complete plant. This means that it is very easy to clone plants, and many plants can grow from cuttings or broken plant parts. This is asexual reproduction (also called vegetative reproduction). ...
... potentially develop into a complete plant. This means that it is very easy to clone plants, and many plants can grow from cuttings or broken plant parts. This is asexual reproduction (also called vegetative reproduction). ...
rain forest
... chimpanzee. The chimpanzee eats fruit , nuts, leaves, insects ,and eggs. There body size is 68- 94 cm. This animal is endangered it lives in the areas of Africa. ...
... chimpanzee. The chimpanzee eats fruit , nuts, leaves, insects ,and eggs. There body size is 68- 94 cm. This animal is endangered it lives in the areas of Africa. ...
Types of Plants Notes - Teacher Copy
... vi Stores energy as starch B. Plant kingdom is divided into four groups based on: i ...
... vi Stores energy as starch B. Plant kingdom is divided into four groups based on: i ...
Review - Plant Systems 15
... 47. What type of adaptations might a plant have if it lived in a desert? Spines, thick cuticle, deep roots 48. What type of adaptations might a plant have if it lived in the tundra? Short stems 49. What type of plant adaptations might a plant have in the rainforest? Smooth bark, leaf tips pointed d ...
... 47. What type of adaptations might a plant have if it lived in a desert? Spines, thick cuticle, deep roots 48. What type of adaptations might a plant have if it lived in the tundra? Short stems 49. What type of plant adaptations might a plant have in the rainforest? Smooth bark, leaf tips pointed d ...
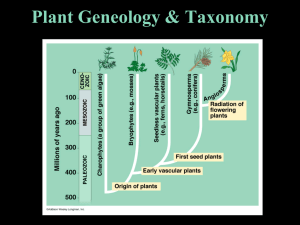
Plant Geneology & Taxonomy
... – Do not produce flowers – Many produce cones to protect seeds - conifers – Seeds not enclosed in fruit – Stems are woody • Example: ...
... – Do not produce flowers – Many produce cones to protect seeds - conifers – Seeds not enclosed in fruit – Stems are woody • Example: ...
Soil Study Guide
... Root – holds the plant in the ground, absorbs water and minerals in soil Stem – holds the plant up, water travels through the stem to the other plant parts Leaves – make the food for the plant, made up of cells Flower – where the seeds are made for the plant Seeds – the first stage of the growth cyc ...
... Root – holds the plant in the ground, absorbs water and minerals in soil Stem – holds the plant up, water travels through the stem to the other plant parts Leaves – make the food for the plant, made up of cells Flower – where the seeds are made for the plant Seeds – the first stage of the growth cyc ...
The Environment and Plant Responses
... plant’s growth is controlled. Hormones are chemical substances which are made by plants and which affect how plant tissue growth by stimulating plant cells to divide, to enlarge, or to stop growing. ...
... plant’s growth is controlled. Hormones are chemical substances which are made by plants and which affect how plant tissue growth by stimulating plant cells to divide, to enlarge, or to stop growing. ...
It grows on palms and can weigh more than a toddler
... The secret behind the world’s largest seed is leaves that serve as good gutters. During rains, they channel lots of water and nutrients right to the plant’s thirsty roots. Coco-de-mer palms (Lodoicea maldivica) produce these monster nuts, which are a type of seed. The biggest can tip the scales at ...
... The secret behind the world’s largest seed is leaves that serve as good gutters. During rains, they channel lots of water and nutrients right to the plant’s thirsty roots. Coco-de-mer palms (Lodoicea maldivica) produce these monster nuts, which are a type of seed. The biggest can tip the scales at ...
General Biology 101 - Linn
... what ancestral forms of all modern plants may have first colonized. Plants are multi-celled photoautotrophs, containing the pigments chlorophyll a and b, similar to the green algae that they share a common ancestor with. There are currently 295,000 species of known plants. Section 23.1 Trends in Pla ...
... what ancestral forms of all modern plants may have first colonized. Plants are multi-celled photoautotrophs, containing the pigments chlorophyll a and b, similar to the green algae that they share a common ancestor with. There are currently 295,000 species of known plants. Section 23.1 Trends in Pla ...
Structures of a seed
... Pollination– the transfer of pollen from the stamen to the pistil. Fertilization– the joining of an egg and sperm Germination– the growth or sprouting of an embryo from a seed. Dormant– the ability of a seed or plant to become inactive, but when conditions are right, the seed or plant will become ac ...
... Pollination– the transfer of pollen from the stamen to the pistil. Fertilization– the joining of an egg and sperm Germination– the growth or sprouting of an embryo from a seed. Dormant– the ability of a seed or plant to become inactive, but when conditions are right, the seed or plant will become ac ...
Answer Key
... grow right on its woody branches which support its large and heavy fruit. How does having fruit that is easily seen help this tree reproduce? Attention: The Theobroma (cacao tree) may not be flowering during your field trip! This may be a good point to bring up with students. Plants are not always i ...
... grow right on its woody branches which support its large and heavy fruit. How does having fruit that is easily seen help this tree reproduce? Attention: The Theobroma (cacao tree) may not be flowering during your field trip! This may be a good point to bring up with students. Plants are not always i ...
Lesson 3 – Explore – Page 261 “Plant Processes”
... maximum amount of light for photosynthesis. The roots of a plant generally exhibit negative phototropism by growing into the soil away from light. By growing into the soil, the roots are able to anchor the plant. Gravitropism – A plant’s response to gravity is called gravitropism. The first root pro ...
... maximum amount of light for photosynthesis. The roots of a plant generally exhibit negative phototropism by growing into the soil away from light. By growing into the soil, the roots are able to anchor the plant. Gravitropism – A plant’s response to gravity is called gravitropism. The first root pro ...
Fiddleleaf Fig - Patty`s Plants
... Patty’s Plants FIDDLELEAF FIG FICUS LYRATA The large leaves are shaped like a Fiddle ...
... Patty’s Plants FIDDLELEAF FIG FICUS LYRATA The large leaves are shaped like a Fiddle ...
Plant physiology
.jpg?width=300)
Plant physiology is a subdiscipline of botany concerned with the functioning, or physiology, of plants. Closely related fields include plant morphology (structure of plants), plant ecology (interactions with the environment), phytochemistry (biochemistry of plants), cell biology, genetics, biophysics and molecular biology.Fundamental processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, plant nutrition, plant hormone functions, tropisms, nastic movements, photoperiodism, photomorphogenesis, circadian rhythms, environmental stress physiology, seed germination, dormancy and stomata function and transpiration, both parts of plant water relations, are studied by plant physiologists.