Eurasian Watermilfoil - Invasive Species Council of BC
... hairless. Stems become leafless toward the base of the plant. Plants typically grow between 1-4 m but can extend up to 10 m. Leaves: Bright green feathery leaves that are 3 cm long. Leaves occur in whorls of 3 or 4 with 12 or more segments on each side of the rachis. Leaves rarely extend out of wate ...
... hairless. Stems become leafless toward the base of the plant. Plants typically grow between 1-4 m but can extend up to 10 m. Leaves: Bright green feathery leaves that are 3 cm long. Leaves occur in whorls of 3 or 4 with 12 or more segments on each side of the rachis. Leaves rarely extend out of wate ...
Botany Worksheet Maryland Master Gardener Handbook Chapter 3
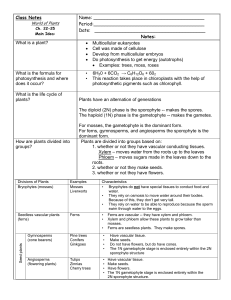
... Plant parts (roots, stems, buds, leaves, flowers and fruits) and their functions The processes of photosynthesis, respiration, and transpiration in plants How the environment (light, temperature, and water) affects plant growth The terminology needs to use keys in the identification of leaves Plant ...
... Plant parts (roots, stems, buds, leaves, flowers and fruits) and their functions The processes of photosynthesis, respiration, and transpiration in plants How the environment (light, temperature, and water) affects plant growth The terminology needs to use keys in the identification of leaves Plant ...
Anatomy of vascular plants notes
... also increase surface area for greater absorption of water SHOOTS = stems + leaves – support; display leaves LEAVES – Photosynthetic organs STOMATA- openings for gas exchange (O2 out/CO2 in) GUARD CELLS- surround and control opening/closing EPIDERMIS- = “plant skin” outer layer made of tightly packe ...
... also increase surface area for greater absorption of water SHOOTS = stems + leaves – support; display leaves LEAVES – Photosynthetic organs STOMATA- openings for gas exchange (O2 out/CO2 in) GUARD CELLS- surround and control opening/closing EPIDERMIS- = “plant skin” outer layer made of tightly packe ...
Hormonal Control in Plants
... prompts that side to grow more, bending the tip towards the light source. ...
... prompts that side to grow more, bending the tip towards the light source. ...
Plants
... Without a vascular system xylem, phloem. No root, stem, leaves quite small (1–2 cm high) They need moist environment to live. They need water for their reproduction. They obtain water by osmosis and Diffusion. Ex: Moss, Liverworts, Hornworts ...
... Without a vascular system xylem, phloem. No root, stem, leaves quite small (1–2 cm high) They need moist environment to live. They need water for their reproduction. They obtain water by osmosis and Diffusion. Ex: Moss, Liverworts, Hornworts ...
Introduction to Plant Reproduction: Sexual vs
... • Compare a human with a plant – We don’t have leaves or roots and a plants do not have a heart or brain – BUT we are alike in many ways ...
... • Compare a human with a plant – We don’t have leaves or roots and a plants do not have a heart or brain – BUT we are alike in many ways ...
Cellular respiration
... a. Spores use both male and female sex cells to form a new organism. b. A spore is a diploid cell and begins ...
... a. Spores use both male and female sex cells to form a new organism. b. A spore is a diploid cell and begins ...
Name - Humble ISD
... 3) How does this affect their ability to conduct water? Water is conducted through the process of osmosis. 4) Because bryophytes lack vascular tissue how does this affect the habitat is which they can grow and survive? They must live in a wet, moist environment which affects their ability to grow ta ...
... 3) How does this affect their ability to conduct water? Water is conducted through the process of osmosis. 4) Because bryophytes lack vascular tissue how does this affect the habitat is which they can grow and survive? They must live in a wet, moist environment which affects their ability to grow ta ...
Ethnobotany Winter Term 2008
... Ethnobotany is the study of the interactions of plants and people, including the influence of plants on human culture. ...
... Ethnobotany is the study of the interactions of plants and people, including the influence of plants on human culture. ...
Plant Adaptations WebQuest-key
... Wildflowers grow earlier in season before tree leaves spread out Light-weight leaves to capture sunlight Thick bark on trees to protect from winter Plants can photosynthesize quickly due to trees being coniferous Needle-like leaves lose less water and shed snow Dark colored needles to absorb more su ...
... Wildflowers grow earlier in season before tree leaves spread out Light-weight leaves to capture sunlight Thick bark on trees to protect from winter Plants can photosynthesize quickly due to trees being coniferous Needle-like leaves lose less water and shed snow Dark colored needles to absorb more su ...
Plant Structures
... Plants contain vascular tissue, made up of cells that form tubes through which water and food move in the plants. These tubes form a continuous system in the plant. Water enters the plant at the roots, moves up through the root and the stem, and into the leaves. Food made in the leaves moves down t ...
... Plants contain vascular tissue, made up of cells that form tubes through which water and food move in the plants. These tubes form a continuous system in the plant. Water enters the plant at the roots, moves up through the root and the stem, and into the leaves. Food made in the leaves moves down t ...
Cool Things that Plants Do
... Victoria amazonica Leaves can grow to over 2.5 m across Network of protruding ribs on underside of leaf for buoyancy and stability ...
... Victoria amazonica Leaves can grow to over 2.5 m across Network of protruding ribs on underside of leaf for buoyancy and stability ...
Larrea tridentata
... Regulated by ABA Hydropassive closure – second line of defense Regulated by general loss of turgor ...
... Regulated by ABA Hydropassive closure – second line of defense Regulated by general loss of turgor ...
THINGS TO STUDY FOR THE FINAL EXAM
... 1. What organs do plants possess? Tissues? Cells? a. Compare and contrast the structures and functions of each. 2. How is the dependence (or lack thereof) on water reflected in the plants’ structures? 3. Compare and contrast pollination in the seed plants. 4. What are the organs of the embryo? a. Wh ...
... 1. What organs do plants possess? Tissues? Cells? a. Compare and contrast the structures and functions of each. 2. How is the dependence (or lack thereof) on water reflected in the plants’ structures? 3. Compare and contrast pollination in the seed plants. 4. What are the organs of the embryo? a. Wh ...
Life Cycles of Plants and Animals
... *Plants and animals are among those things that change. *They go through many different stages as they grow, just like you! ...
... *Plants and animals are among those things that change. *They go through many different stages as they grow, just like you! ...
06-PlantsCN
... Seeds are dispersed by fruit, sticking to the fur of animals, or spread by the wind. ...
... Seeds are dispersed by fruit, sticking to the fur of animals, or spread by the wind. ...
Botany: the study of plants Botanical: of or relating to plants
... Evolution: Cumulative changes in a population as a result of: • variation in a population (often caused by mutation), • selection for or against the survival of certain individuals in the population • reproduction passing on of the selected characteristic that allowed for survival. ...
... Evolution: Cumulative changes in a population as a result of: • variation in a population (often caused by mutation), • selection for or against the survival of certain individuals in the population • reproduction passing on of the selected characteristic that allowed for survival. ...
Name
... 18) Which one of the following statements is false? A) A pea pod develops from the ovary wall. B) In peas, the seeds each develop from separate ovules. C) An entire pea pod represents an aggregate fruit. D) The tip of a pea pod corresponds to the tip of the carpel. E) Each ovary in a pea plant conta ...
... 18) Which one of the following statements is false? A) A pea pod develops from the ovary wall. B) In peas, the seeds each develop from separate ovules. C) An entire pea pod represents an aggregate fruit. D) The tip of a pea pod corresponds to the tip of the carpel. E) Each ovary in a pea plant conta ...
Anthuriums - Bellevue Nursery
... sunlight. Lower levels of light may slow down or cease flower production. The foliage type species will tolerate lower light levels as they grow in some of the shadiest areas in their natural habitat. Leaves emerging under lower light may stretch and/or become distorted Anthuriums are tropical plant ...
... sunlight. Lower levels of light may slow down or cease flower production. The foliage type species will tolerate lower light levels as they grow in some of the shadiest areas in their natural habitat. Leaves emerging under lower light may stretch and/or become distorted Anthuriums are tropical plant ...
`Nun`s Orchid` - Aussie Winners
... Phaius australe is a local native orchid showing up in nature from the coastal areas of Northern New South Wales and through Southern Queensland and the off shore islands. Being blessed with such showy flowers the plants were collected by gardeners from early times. Now they are rare and not often s ...
... Phaius australe is a local native orchid showing up in nature from the coastal areas of Northern New South Wales and through Southern Queensland and the off shore islands. Being blessed with such showy flowers the plants were collected by gardeners from early times. Now they are rare and not often s ...
Plant Science HL
... there as a food reserve in the endosperm). • Maltose then further hydrolyses into glucose that can be used for cellular respiration or converted into cellulose by condensation reactions. • The cellulose is necessary to produce the cell walls of new cells being produced. ...
... there as a food reserve in the endosperm). • Maltose then further hydrolyses into glucose that can be used for cellular respiration or converted into cellulose by condensation reactions. • The cellulose is necessary to produce the cell walls of new cells being produced. ...
Ch 21 Guided Notes
... Carrying Out Photosynthesis -The _________ grows from a stem and is where photosynthesis occurs Putting Down Roots -Plants depend on _________ as their primary source of __________ & nutrients -a _________ is the organ that absorbs water & minerals -contain tissues that transport nutrient to the ___ ...
... Carrying Out Photosynthesis -The _________ grows from a stem and is where photosynthesis occurs Putting Down Roots -Plants depend on _________ as their primary source of __________ & nutrients -a _________ is the organ that absorbs water & minerals -contain tissues that transport nutrient to the ___ ...
Honors Biology I Ch 30 Plant Reproduction Seed Plants *seed
... a) Contain _________parts to their seed b) Vascular bundles are ____________ c) ________________in narrow leaves d) Flower parts in ____________or multiples of _____________ Ex.___________________________________________________________ B. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Early land plants ...
... a) Contain _________parts to their seed b) Vascular bundles are ____________ c) ________________in narrow leaves d) Flower parts in ____________or multiples of _____________ Ex.___________________________________________________________ B. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Early land plants ...
Plant physiology
.jpg?width=300)
Plant physiology is a subdiscipline of botany concerned with the functioning, or physiology, of plants. Closely related fields include plant morphology (structure of plants), plant ecology (interactions with the environment), phytochemistry (biochemistry of plants), cell biology, genetics, biophysics and molecular biology.Fundamental processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, plant nutrition, plant hormone functions, tropisms, nastic movements, photoperiodism, photomorphogenesis, circadian rhythms, environmental stress physiology, seed germination, dormancy and stomata function and transpiration, both parts of plant water relations, are studied by plant physiologists.