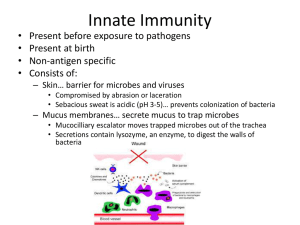
Innate Immunity - Santa Susana High School
... – Antigens (foreign particles) elicit the immune response • Epitote… small part of the antigen molecule that is recognized by a specific lymphocyte – Each lymphocyte may contain up to 100,000 identical epitote recognition sites ...
... – Antigens (foreign particles) elicit the immune response • Epitote… small part of the antigen molecule that is recognized by a specific lymphocyte – Each lymphocyte may contain up to 100,000 identical epitote recognition sites ...
Immunology_IX__immunity_against_infections
... • Tc lymphocytes – elimination of virus-infected cells ...
... • Tc lymphocytes – elimination of virus-infected cells ...
The Immune System
... dysentery from contaminated water and Salmonella from eggs, turkey, etc. › Animal Bites are also concern for the transmission of disease, because of the fact that animals can be a vector for many viruses, i.e. bubonic plague was spread by fleas, Lyme disease is spread by ticks, rabies is spread in t ...
... dysentery from contaminated water and Salmonella from eggs, turkey, etc. › Animal Bites are also concern for the transmission of disease, because of the fact that animals can be a vector for many viruses, i.e. bubonic plague was spread by fleas, Lyme disease is spread by ticks, rabies is spread in t ...
January 29, 2002 - wvhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... 6) Describe the various mechanisms of antigen disposal: ● neutralization: ● opsonization: ● complement activation & pore formation: ...
... 6) Describe the various mechanisms of antigen disposal: ● neutralization: ● opsonization: ● complement activation & pore formation: ...
IMMUNOPROPHYLAXIS: Vaccines and Immunotherapy 2014
... – Secondary exposure does not protect against disease. • Induction of protection can be achieved with vaccine if able to sustain high long‐term antibody titer. • Achievable by giving several immunizations in a shorter time frame to raise sustained titer. ...
... – Secondary exposure does not protect against disease. • Induction of protection can be achieved with vaccine if able to sustain high long‐term antibody titer. • Achievable by giving several immunizations in a shorter time frame to raise sustained titer. ...
Purposes and uses of epidemiology The ultimate purpose of
... Live vaccines (not used currently due to infection risk). Live, attenuated vaccines Killed or inactivated vaccines Toxoid vaccines Others Conjugate vaccines DNA vaccines Recombinant vector vaccines Live, attenuated vaccines: Live, attenuated vaccines contain a version of the living mi ...
... Live vaccines (not used currently due to infection risk). Live, attenuated vaccines Killed or inactivated vaccines Toxoid vaccines Others Conjugate vaccines DNA vaccines Recombinant vector vaccines Live, attenuated vaccines: Live, attenuated vaccines contain a version of the living mi ...
Development of Advanced Adjuvants and Immune Modulators
... Adjuvants and Immunity Adaptive immunity is antigen-specific, requires gene rearrangements and thus is slow to develop (days to weeks) and can discriminate between self and non self. Exploited with Vaccines Innate immunity fast acting and relatively non-specific. Exploited using immune modul ...
... Adjuvants and Immunity Adaptive immunity is antigen-specific, requires gene rearrangements and thus is slow to develop (days to weeks) and can discriminate between self and non self. Exploited with Vaccines Innate immunity fast acting and relatively non-specific. Exploited using immune modul ...
Topic 6: Infection, immunity and forensics Microorganisms
... immunity (natural, artificial, active, reinforcement sheet to solve passive). to make a link between he previous and the current topic. Focusing event: Students will be divided in four groups and they will be assigned a specific topic G1. Natural immunity G2. Artificial Immunity G3. Active Immunity ...
... immunity (natural, artificial, active, reinforcement sheet to solve passive). to make a link between he previous and the current topic. Focusing event: Students will be divided in four groups and they will be assigned a specific topic G1. Natural immunity G2. Artificial Immunity G3. Active Immunity ...
Chapter 11 Immune
... 3. 3-14 days are required to generate enough antibody. 4. Memory cells are produced; don’t produce as much antibody, but respond more quickly to the same antigen. 5. Secondary response is triggered. 6. This prevents an animal from developing the infectious disease a second time. Can come from natura ...
... 3. 3-14 days are required to generate enough antibody. 4. Memory cells are produced; don’t produce as much antibody, but respond more quickly to the same antigen. 5. Secondary response is triggered. 6. This prevents an animal from developing the infectious disease a second time. Can come from natura ...
The Immune System
... • You don’t become ill because there is such a small amount of weakened disease • But some antibodies remain… – They can be reactivated if the antigen enters your body in the future ...
... • You don’t become ill because there is such a small amount of weakened disease • But some antibodies remain… – They can be reactivated if the antigen enters your body in the future ...
Lecture 26. Prevention and Control -
... Deliberately infected the child with smallpox. The boy survived (Today, Jenner would be majorly sued, would lose his license, be put on trial, get a good lawyer, write a book, and do the talk ...
... Deliberately infected the child with smallpox. The boy survived (Today, Jenner would be majorly sued, would lose his license, be put on trial, get a good lawyer, write a book, and do the talk ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... b. Elucidate various steps in processing and presentation of antigens by cytosolic pathway. 19. a. Mention the evidences that implicate CD4+ , T cells, MHC and TCR in autoimmunity. b. What are the modern methods used in the treatment of autoimmune disease? 20. a. Give an account of the different typ ...
... b. Elucidate various steps in processing and presentation of antigens by cytosolic pathway. 19. a. Mention the evidences that implicate CD4+ , T cells, MHC and TCR in autoimmunity. b. What are the modern methods used in the treatment of autoimmune disease? 20. a. Give an account of the different typ ...
Third Semester M.Sc. Degree Examination (CSS)
... Give an account on the applications of monoclonal antibodies. Describe the role of cytokines in immunogenic reactions. Explain the immune responses shown to viral, bacterial and parasitic infections. Discuss the role of secondary lymphoid organs in immunity. Give an account on HAT medium and its app ...
... Give an account on the applications of monoclonal antibodies. Describe the role of cytokines in immunogenic reactions. Explain the immune responses shown to viral, bacterial and parasitic infections. Discuss the role of secondary lymphoid organs in immunity. Give an account on HAT medium and its app ...
BIOL 432_532 Sp 17 Syllabus
... sources (including internet), including copying or paraphrasing with slight change of wording. Disability Support Services: Reasonable accomodations are made for students who have documented temporary or permanent disabilities All accommodations must be approved through Disability Support Services ...
... sources (including internet), including copying or paraphrasing with slight change of wording. Disability Support Services: Reasonable accomodations are made for students who have documented temporary or permanent disabilities All accommodations must be approved through Disability Support Services ...
assembly floor analysis
... vaccinated, and this provides protection for unprotected individuals. The larger the number of people who are vaccinated in a population, the lower the likelihood that a susceptible (unvaccinated) person will physically come into contact with the infection. It is more difficult for diseases to sprea ...
... vaccinated, and this provides protection for unprotected individuals. The larger the number of people who are vaccinated in a population, the lower the likelihood that a susceptible (unvaccinated) person will physically come into contact with the infection. It is more difficult for diseases to sprea ...
دانلود
... • Pathogen-associated molecular patterns(PAMP):dsRNA,Nformylmethionine,LPS,teichoic acid ,mannose • Toll Like receptors ...
... • Pathogen-associated molecular patterns(PAMP):dsRNA,Nformylmethionine,LPS,teichoic acid ,mannose • Toll Like receptors ...
Section 3.3. Maintaining Healthy Systems
... infection in a manner that is more safe than being exposed to the pathogen without vaccination. ...
... infection in a manner that is more safe than being exposed to the pathogen without vaccination. ...
Immune System
... 1. Natural active immunity occurs when lymphocytes produce antibodies in response to the body becoming infected with a pathogen from the environment. 2. Artificial active immunity occurs when lymphocytes produce antibodies in response to the pathogen being administered through vaccination. ...
... 1. Natural active immunity occurs when lymphocytes produce antibodies in response to the body becoming infected with a pathogen from the environment. 2. Artificial active immunity occurs when lymphocytes produce antibodies in response to the pathogen being administered through vaccination. ...
P-selective Sets and the Power of One Bit
... all x ≤ b are in A. The b are easily computable. f(x,y)=if |x|=|y| then the lexicographically least. o.w. the smaller length is computable in linear time in the larger length. So decide which is the case and then return the most likely candidate. ...
... all x ≤ b are in A. The b are easily computable. f(x,y)=if |x|=|y| then the lexicographically least. o.w. the smaller length is computable in linear time in the larger length. So decide which is the case and then return the most likely candidate. ...
IMMUNOLOGY 2010™ Poster Symposia Schedule
... Effector Cells and Tissue Damage in Autoimmunity Host Defense: Innate Immune Receptors and Signal Transduction Immune Regulation of Host Immunity during Viral Infection Immune System Regulation iTreg, Th17, and CD4 CTL Differentiation Leukocyte Activation, Adhesion, and Recruitment Mechanisms of Dis ...
... Effector Cells and Tissue Damage in Autoimmunity Host Defense: Innate Immune Receptors and Signal Transduction Immune Regulation of Host Immunity during Viral Infection Immune System Regulation iTreg, Th17, and CD4 CTL Differentiation Leukocyte Activation, Adhesion, and Recruitment Mechanisms of Dis ...
Chapter 16 Supplement
... It has been stated that “boosting your immune system is the single most important thing you can do for your health.” Students interested in learning how to improve their immune system should read The Immune Advantage: The Powerful, Natural Immune-Boosting Program to Help You Prevent Disease, Enhance ...
... It has been stated that “boosting your immune system is the single most important thing you can do for your health.” Students interested in learning how to improve their immune system should read The Immune Advantage: The Powerful, Natural Immune-Boosting Program to Help You Prevent Disease, Enhance ...
Herd immunity

Herd immunity (also called herd effect, community immunity, population immunity, or social immunity) is a form of indirect protection from infectious disease that occurs when a large percentage of a population has become immune to an infection, thereby providing a measure of protection for individuals who are not immune. In a population in which a large number of individuals are immune, chains of infection are likely to be disrupted, which stops or slows the spread of disease. The greater the proportion of individuals in a community who are immune, the smaller the probability that those who are not immune will come into contact with an infectious individual.Individual immunity can be gained through recovering from a natural infection or through artificial means such as vaccination. Some individuals cannot become immune due to medical reasons and in this group herd immunity is an important method of protection. Once a certain threshold has been reached, herd immunity will gradually eliminate a disease from a population. This elimination, if achieved worldwide, may result in the permanent reduction in the number of infections to zero, called eradication. This method was used for the eradication of smallpox in 1977 and for the regional elimination of other diseases. Herd immunity does not apply to all diseases, just those that are contagious, meaning that they can be transmitted from one individual to another. Tetanus, for example, is infectious but not contagious, so herd immunity does not apply.The term herd immunity was first used in 1923. It was recognized as a naturally occurring phenomenon in the 1930s when it was observed that after a significant number of children had become immune to measles, the number of new infections temporarily decreased, including among susceptible children. Mass vaccination to induce herd immunity has since become common and proved successful in preventing the spread of many infectious diseases. Opposition to vaccination has posed a challenge to herd immunity, allowing preventable diseases to persist in or return to communities that have inadequate vaccination rates.