Another look at chemical reactions HYDROGEN PEROXIDE WATER
... Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every helium atom has two protons in its nucleus. - MASS NUMBER: The number of protons PLUS the number of neutrons in the atomic nucleus, Atoms of the same element may have DIFFERENT mass numbers. - ISOTOPES: are atoms of the same element with different mas ...
... Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every helium atom has two protons in its nucleus. - MASS NUMBER: The number of protons PLUS the number of neutrons in the atomic nucleus, Atoms of the same element may have DIFFERENT mass numbers. - ISOTOPES: are atoms of the same element with different mas ...
Parts of an Atom
... The period an element is in is equal to the number of energy levels it has. (see the column of numbers in the upper right hand corner of each box) Properties change slowly from one end of each row to the other. Groups: Vertical columns of elements All elements in a group have similar propertie ...
... The period an element is in is equal to the number of energy levels it has. (see the column of numbers in the upper right hand corner of each box) Properties change slowly from one end of each row to the other. Groups: Vertical columns of elements All elements in a group have similar propertie ...
The parts of Dalton`s theory Matter is composed of small, chemically
... Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every helium atom has two protons in its nucleus. - MASS NUMBER: The number of protons PLUS the number of neutrons in the atomic nucleus, Atoms of the same element may have DIFFERENT mass numbers. - ISOTOPES: are atoms of the same element with different mas ...
... Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every helium atom has two protons in its nucleus. - MASS NUMBER: The number of protons PLUS the number of neutrons in the atomic nucleus, Atoms of the same element may have DIFFERENT mass numbers. - ISOTOPES: are atoms of the same element with different mas ...
1st Semester Review - Moore Public Schools
... 16. How many sublevels would the energy level represented by n = 4 be broken up into? 17. How many orbitals does a p sublevel contain? 18. How many total electrons can the second energy level hold? 19. Explain the following, which determine electron configuration: a. Hund's rule b. Aufbau principle ...
... 16. How many sublevels would the energy level represented by n = 4 be broken up into? 17. How many orbitals does a p sublevel contain? 18. How many total electrons can the second energy level hold? 19. Explain the following, which determine electron configuration: a. Hund's rule b. Aufbau principle ...
Development of atomic theory
... acceptance of the nuclear atom, however. According to classical theory, as the electrons orbit about the nucleus, they are continuously being accelerated (see acceleration), and all accelerated charges radiate electromagnetic energy. Thus, they should lose their energy and spiral into the nucleus. T ...
... acceptance of the nuclear atom, however. According to classical theory, as the electrons orbit about the nucleus, they are continuously being accelerated (see acceleration), and all accelerated charges radiate electromagnetic energy. Thus, they should lose their energy and spiral into the nucleus. T ...
File - Ingolstadt Academy
... Density (definition and equation) Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
... Density (definition and equation) Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
Chemistry Fall-2016 Final
... J. the difference between the number of protons and the number of electrons in an atom or ion; if there are more protons than electrons, the net charge is positive; if there are more ...
... J. the difference between the number of protons and the number of electrons in an atom or ion; if there are more protons than electrons, the net charge is positive; if there are more ...
General Chemistry First Semester Review General
... - read given information carefully. Water vapor is noted with a (g) because it is a gas, not a liquid. Double replacement reactions are between two aqueous solutions that produce an insoluble precipitate. Solubility rules can predict which substance is the solid. The solubility table is on p. 178 in ...
... - read given information carefully. Water vapor is noted with a (g) because it is a gas, not a liquid. Double replacement reactions are between two aqueous solutions that produce an insoluble precipitate. Solubility rules can predict which substance is the solid. The solubility table is on p. 178 in ...
Review of the Atom
... Ground state: electrons in lowest possible energy levels Excited state: one or more electrons move up to a higher energy level ...
... Ground state: electrons in lowest possible energy levels Excited state: one or more electrons move up to a higher energy level ...
I. Chemistry
... The 1st energy level contains 1 orbital and therefore holds a maximum of 2 electrons. It is called the 1s orbital and it is spherical The second energy level contains a maximum of 4 orbitals. A spherical 2s and 3 dumbbell shaped orbitals in the X, Y, and Z axis called the P1, P2 and P3 orbitals ...
... The 1st energy level contains 1 orbital and therefore holds a maximum of 2 electrons. It is called the 1s orbital and it is spherical The second energy level contains a maximum of 4 orbitals. A spherical 2s and 3 dumbbell shaped orbitals in the X, Y, and Z axis called the P1, P2 and P3 orbitals ...
Ch. 2 Chemical Basis of the Body (pp. 26-33)
... Radioisotopes *By losing subatomic particles, energy is released called radioactive decay. *This energy can penetrate and destroy tissues *Since rapidly dividing cells are more sensitive to destructive effects of radiation, this is why radiation is good on cancer. ...
... Radioisotopes *By losing subatomic particles, energy is released called radioactive decay. *This energy can penetrate and destroy tissues *Since rapidly dividing cells are more sensitive to destructive effects of radiation, this is why radiation is good on cancer. ...
Periodic Table
... Columns also have names for their families. On your periodic table, write the names above each column. Rows are called ___________ There are ____ rows. But there are two rows that seem to be out of place. They are the ______________ and _____________ series ...
... Columns also have names for their families. On your periodic table, write the names above each column. Rows are called ___________ There are ____ rows. But there are two rows that seem to be out of place. They are the ______________ and _____________ series ...
Section 2.1
... • All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, but atoms of an element are unique to that element only. • Atoms of an element are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions; they are neither created nor destroyed. • Compounds are fo ...
... • All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, but atoms of an element are unique to that element only. • Atoms of an element are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions; they are neither created nor destroyed. • Compounds are fo ...
Nature of Matter
... that consists entirely of one type of atom. -Over 100 elements are known, but only about 24 are found in living organisms. -Elements are represented by symbols, Ex : C = Carbon, H = Hydrogen, etc. -An element’s atomic number = # protons in an atom of the element. ...
... that consists entirely of one type of atom. -Over 100 elements are known, but only about 24 are found in living organisms. -Elements are represented by symbols, Ex : C = Carbon, H = Hydrogen, etc. -An element’s atomic number = # protons in an atom of the element. ...
Notes - Organization of Matter
... • Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically combined • Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes ...
... • Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically combined • Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes ...
Chapter 3
... 3. Atoms of different elements have different properties. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. 5. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed when they are combined, separated, or rearranged in chemical reactions. ...
... 3. Atoms of different elements have different properties. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. 5. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed when they are combined, separated, or rearranged in chemical reactions. ...
Atomic Structure
... Reasoned that electrons could not be random Reasoned that they were in set orbits, set distances away from nucleus. Planetary orbital model ...
... Reasoned that electrons could not be random Reasoned that they were in set orbits, set distances away from nucleus. Planetary orbital model ...
Review for Midyear - 1 KEY - Ms. Robbins` PNHS Science Classes
... HS-PS1-1. Use the periodic table as a model to predict the relative properties of main group elements, including ionization energy and relative sizes of atoms and ions, based on the patterns of electrons in the outermost energy level of each element. Use the patterns of valence electron configuratio ...
... HS-PS1-1. Use the periodic table as a model to predict the relative properties of main group elements, including ionization energy and relative sizes of atoms and ions, based on the patterns of electrons in the outermost energy level of each element. Use the patterns of valence electron configuratio ...
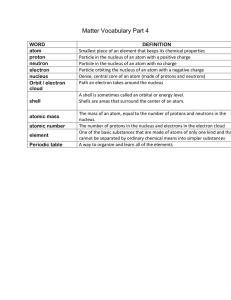
Matter Vocab Part 4
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
Early Models of the Atom
... emission of radiation of the nucleus of an atom Discovered polonium and radium, amount of energy based on amount of starting material; Marie won two Nobel prizes Marie died from radiation; curie = unit of radiation proved the existence of neutrons – atomic nuclei had neutral particles as well no ele ...
... emission of radiation of the nucleus of an atom Discovered polonium and radium, amount of energy based on amount of starting material; Marie won two Nobel prizes Marie died from radiation; curie = unit of radiation proved the existence of neutrons – atomic nuclei had neutral particles as well no ele ...