Name - Aurora City Schools
... 9. __ __ any charged particle, an atom that has gained or lost electrons ...
... 9. __ __ any charged particle, an atom that has gained or lost electrons ...
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements
... •Dmitri Mendeleev and Lothar Meyer (~1869) independently came to the same conclusion about how elements should be grouped in the periodic table. •Henry Moseley (1913) developed the concept of atomic numbers (the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom) ...
... •Dmitri Mendeleev and Lothar Meyer (~1869) independently came to the same conclusion about how elements should be grouped in the periodic table. •Henry Moseley (1913) developed the concept of atomic numbers (the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom) ...
ChemFinalgeocities
... Which of the following has the greatest density? a. a rock c. oil b. oxygen d. ice A 26.0-g sample of a liquid was found to have a volume of 13.0 mL. What is the density of the liquid? a. 0.500 g/mL c. 39.0 g/mL b. 2.00 g/mL d. 338 g/mL Coal burns in a furnace, producing light and heat. This reactio ...
... Which of the following has the greatest density? a. a rock c. oil b. oxygen d. ice A 26.0-g sample of a liquid was found to have a volume of 13.0 mL. What is the density of the liquid? a. 0.500 g/mL c. 39.0 g/mL b. 2.00 g/mL d. 338 g/mL Coal burns in a furnace, producing light and heat. This reactio ...
1. I can define valence electron and use the periodic
... #2. I can make a Lewis dot drawing of an element. 5. Make Lewis Dot structures for all the elements listed above (a-j). #3. I can explain how valence electrons are related to chemical reactivity. 6. Which elements react violently with water? 7. Which anions are most reactive? 8. Why are these atoms ...
... #2. I can make a Lewis dot drawing of an element. 5. Make Lewis Dot structures for all the elements listed above (a-j). #3. I can explain how valence electrons are related to chemical reactivity. 6. Which elements react violently with water? 7. Which anions are most reactive? 8. Why are these atoms ...
Atoms pg. 102
... Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons. Isotopes are identified by its mass. ...
... Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons. Isotopes are identified by its mass. ...
Atomic Structure Video Guide
... 12. If Carbon has 6 electrons then it has 6 _________________________. 13. Atomic Mass is the number of _______________________ and _____________________ in an atom. 14. Silicon (Si) is a major element that makes up ____________. It has ___________ Protons and _____________ Neutrons which makes up a ...
... 12. If Carbon has 6 electrons then it has 6 _________________________. 13. Atomic Mass is the number of _______________________ and _____________________ in an atom. 14. Silicon (Si) is a major element that makes up ____________. It has ___________ Protons and _____________ Neutrons which makes up a ...
Chapter 2 part 1
... • Each additional shell can contain eight electrons • Each lower shell is filled with electrons before the next higher level contains any electrons. ...
... • Each additional shell can contain eight electrons • Each lower shell is filled with electrons before the next higher level contains any electrons. ...
Chemistry
... • About 110 known at this point • Organized on the Periodic Table • Made of atoms • Each type of element has a unique atomic structure • Basic structure includes p+, n, and e- ...
... • About 110 known at this point • Organized on the Periodic Table • Made of atoms • Each type of element has a unique atomic structure • Basic structure includes p+, n, and e- ...
Matter Review
... • In your notes, use your periodic tables to determine the following for the elements at the bottom. – The number of protons – The number of neutrons – The number of shells – The number of electrons on the outer most shell (valence electrons) – Draw the atoms for each ...
... • In your notes, use your periodic tables to determine the following for the elements at the bottom. – The number of protons – The number of neutrons – The number of shells – The number of electrons on the outer most shell (valence electrons) – Draw the atoms for each ...
Trends in the Periodic Table
... • The positive charge of the nucleus is increasing with each element in the period. • The nucleus is pulling the electrons closer. • At the point where atomic radius levels off the electrons begin repelling each other because they are close together. ...
... • The positive charge of the nucleus is increasing with each element in the period. • The nucleus is pulling the electrons closer. • At the point where atomic radius levels off the electrons begin repelling each other because they are close together. ...
Ch. 2-1 Nature of Matter
... by Miller and Levine, © 2007. These images have been produced from the originals by permission of the publisher. These illustrations may not be reproduced in any format for any purpose without express written permission from the publisher. ...
... by Miller and Levine, © 2007. These images have been produced from the originals by permission of the publisher. These illustrations may not be reproduced in any format for any purpose without express written permission from the publisher. ...
Practice Test #2 - smhs
... The masses of these three isotopes are 148.1010 amu, 149.2005 amu, and 152.4107 amu, respectively. If the lightest isotope is three times as abundant as the heaviest, and the middle isotope is known to be 16.00% abundant, what is the percent abundance of the heaviest isotope? The average atomic mass ...
... The masses of these three isotopes are 148.1010 amu, 149.2005 amu, and 152.4107 amu, respectively. If the lightest isotope is three times as abundant as the heaviest, and the middle isotope is known to be 16.00% abundant, what is the percent abundance of the heaviest isotope? The average atomic mass ...
So where did all the matter on Earth come from - Bennatti
... atomic number of helium is two. Each helium atom has two protons. No other element is made of atoms with two protons in the nucleus. Each element is represented with a chemical symbol. Most chemical symbols are one or two letters. The first letter is always capitalized. If it has two or three letter ...
... atomic number of helium is two. Each helium atom has two protons. No other element is made of atoms with two protons in the nucleus. Each element is represented with a chemical symbol. Most chemical symbols are one or two letters. The first letter is always capitalized. If it has two or three letter ...
1) - Kurt Niedenzu
... 32) The increase in atomic radius of each successive element within a group is primarily due to an increase in the number of a) neutrons in the nucleus b) electrons in the outermost shell c) unpaired electrons d) occupied principal energy levels 33) Elements that have properties of both metals and n ...
... 32) The increase in atomic radius of each successive element within a group is primarily due to an increase in the number of a) neutrons in the nucleus b) electrons in the outermost shell c) unpaired electrons d) occupied principal energy levels 33) Elements that have properties of both metals and n ...
Adv review key
... B) Valence electrons- outer shell electrons C) Metals a. Lend valence electrons b. 1 – 4 valence electrons c. Form positive ions ( more protons than electrons) D) Nonmetals a. Borrow valence electrons b. 4 - 8 valence electrons c. Form negative ions (more electrons than protons) E) Metals lend and n ...
... B) Valence electrons- outer shell electrons C) Metals a. Lend valence electrons b. 1 – 4 valence electrons c. Form positive ions ( more protons than electrons) D) Nonmetals a. Borrow valence electrons b. 4 - 8 valence electrons c. Form negative ions (more electrons than protons) E) Metals lend and n ...
APS 1st semester exam review 2016
... B) Valence electrons- outer shell electrons C) Metals a. Lend valence electrons b. 1 – 4 valence electrons c. Form positive ions ( more protons than electrons) D) Nonmetals a. Borrow valence electrons b. 4 - 8 valence electrons c. Form negative ions (more electrons than protons) E) Metals lend and n ...
... B) Valence electrons- outer shell electrons C) Metals a. Lend valence electrons b. 1 – 4 valence electrons c. Form positive ions ( more protons than electrons) D) Nonmetals a. Borrow valence electrons b. 4 - 8 valence electrons c. Form negative ions (more electrons than protons) E) Metals lend and n ...
Gr 10 Review sheet chemistry
... 1. Change of________________ 2. Formation of a ________________ 3. Formation of _____________ 4. Release or absorption of_____________ ...
... 1. Change of________________ 2. Formation of a ________________ 3. Formation of _____________ 4. Release or absorption of_____________ ...
Types of Chemical Reactions - Celebrity Examples
... y Reaction with oxygen gas and ALWAYS forms water ...
... y Reaction with oxygen gas and ALWAYS forms water ...
Honors Chemistry Chapter 6 Student Notes
... Also have found use in deep sea diving suits and smoke alarms. f block elements are called inner transition elements - they were put into their current position by Glenn Seaborg - the only living person ever to have an element named after himself. ...
... Also have found use in deep sea diving suits and smoke alarms. f block elements are called inner transition elements - they were put into their current position by Glenn Seaborg - the only living person ever to have an element named after himself. ...
Chap 1-3 Review
... Covalent - electrons are shared between the two nuclei Ionic - one or more electrons are transferred from the metal atom to the ...
... Covalent - electrons are shared between the two nuclei Ionic - one or more electrons are transferred from the metal atom to the ...
document
... 5. Ionic Bond I E. States that all elements want either a full outer shell or eight 6. Subscript H electrons in their outer electron shell. 7. Polyatomic Ion J F. A multiplier. It is used to balance equations. 8. Synthesis Reaction L G. A reaction in which two reactant compounds switch ions. 9. Deco ...
... 5. Ionic Bond I E. States that all elements want either a full outer shell or eight 6. Subscript H electrons in their outer electron shell. 7. Polyatomic Ion J F. A multiplier. It is used to balance equations. 8. Synthesis Reaction L G. A reaction in which two reactant compounds switch ions. 9. Deco ...
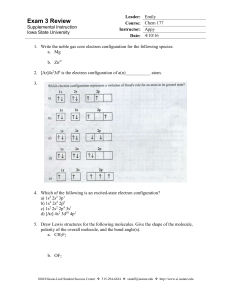
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... 11. Based on their positions in the periodic table, select the atom of each pair that has the larger value of the indicated atomic property. a. Ionization energy, Na or Mg b. Ionization energy, Mg or Cl c. Electron affinity, Cl or Br d. Atomic radius, K or Cs e. Atomic radius, Se or Br 12. List thr ...
... 11. Based on their positions in the periodic table, select the atom of each pair that has the larger value of the indicated atomic property. a. Ionization energy, Na or Mg b. Ionization energy, Mg or Cl c. Electron affinity, Cl or Br d. Atomic radius, K or Cs e. Atomic radius, Se or Br 12. List thr ...