History of the Atom notes
... He believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible was not based on the scientific method – but just philosophy ...
... He believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible was not based on the scientific method – but just philosophy ...
History of the Atom Power Point Notes
... He believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible was not based on the scientific method – but just philosophy ...
... He believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible was not based on the scientific method – but just philosophy ...
History of Atomic Theory
... evolved over time as a result of their work • To describe how the planetary model and the concept of quantized energy levels explains the atomic emission spectra and phenomena such as fireworks and colored flames ...
... evolved over time as a result of their work • To describe how the planetary model and the concept of quantized energy levels explains the atomic emission spectra and phenomena such as fireworks and colored flames ...
Subject Area Standard Area Organizing Category Course Standard
... 3.2.C.A5: MODELS Recognize discoveries from Dalton (atomic theory), Thomson (the electron), Rutherford (the nucleus), and Bohr (planetary model of atom), and understand how each discovery leads to modern theory. Describe Rutherford’s “gold foil” experiment that led to the discovery of the nuclear at ...
... 3.2.C.A5: MODELS Recognize discoveries from Dalton (atomic theory), Thomson (the electron), Rutherford (the nucleus), and Bohr (planetary model of atom), and understand how each discovery leads to modern theory. Describe Rutherford’s “gold foil” experiment that led to the discovery of the nuclear at ...
Element: a pure, simple substance that can`t be broken down into
... What is the smallest unit of matter that we can find everywhere, even in tuna fish? What charge do electrons have? What are elements? Who organized the atomic elements? What do we call a horizontal row on the periodic table? What do we call the vertical columns on the periodic table? The number of p ...
... What is the smallest unit of matter that we can find everywhere, even in tuna fish? What charge do electrons have? What are elements? Who organized the atomic elements? What do we call a horizontal row on the periodic table? What do we call the vertical columns on the periodic table? The number of p ...
Unit 3 Review Worksheet
... c. The period 6 alkaline earth metal: _____________________________________ d. The metalloid in group 16: _____________________________________ e. The only nonmetal in group 14: _____________________________________ ...
... c. The period 6 alkaline earth metal: _____________________________________ d. The metalloid in group 16: _____________________________________ e. The only nonmetal in group 14: _____________________________________ ...
Chemistry Of Life
... “Atomic Number” = number of protons The atomic number determines what type of element an atom is. All atoms of carbon have six for their atomic number. All atoms of oxygen have eight protons. The atomic number never changes in ...
... “Atomic Number” = number of protons The atomic number determines what type of element an atom is. All atoms of carbon have six for their atomic number. All atoms of oxygen have eight protons. The atomic number never changes in ...
The Atom Part 1 Notes
... • Came up with Dalton’s Atomic Theory • All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms • Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of different ...
... • Came up with Dalton’s Atomic Theory • All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms • Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of different ...
Models of the Atom: A Historical perspective
... All matter is made of atoms Atoms of an element are identical. Each element has different atoms. Atoms of different elements combine in constant ratios to form compounds. • Atoms are rearranged in reactions. ...
... All matter is made of atoms Atoms of an element are identical. Each element has different atoms. Atoms of different elements combine in constant ratios to form compounds. • Atoms are rearranged in reactions. ...
chapter2 2012 (no naming)
... neutrons and mass numbers • Relationships: • Atomic number = # p+ • Charge = p+ - e• Mass # = p+ + n0 ...
... neutrons and mass numbers • Relationships: • Atomic number = # p+ • Charge = p+ - e• Mass # = p+ + n0 ...
Scientists timeline
... modern discovery process about atoms • Transformed Democritus’s theories on atoms into an actual scientific theory ...
... modern discovery process about atoms • Transformed Democritus’s theories on atoms into an actual scientific theory ...
Matter Unit Study Guide Phases of Matter
... Chemical formulas for used to show the different elements that make up a compound. The letters tell you which elements are in the compound. The numbers tell you how many atoms of each element are in one molecule of the compound. Complete the chart with the element name and number of atoms for each e ...
... Chemical formulas for used to show the different elements that make up a compound. The letters tell you which elements are in the compound. The numbers tell you how many atoms of each element are in one molecule of the compound. Complete the chart with the element name and number of atoms for each e ...
Solid - burgess
... 3. the properties of the compound are different from the properties of the elements that make up the compound 4. can be separated only by a chemical reaction 5. two types of compounds a. ionic i. formed by the attraction between two or more elements that transfer electrons known as ions ...
... 3. the properties of the compound are different from the properties of the elements that make up the compound 4. can be separated only by a chemical reaction 5. two types of compounds a. ionic i. formed by the attraction between two or more elements that transfer electrons known as ions ...
DNA
... What are subatomic particles? How do we determine the number of Subatomic Particles in an atom? ...
... What are subatomic particles? How do we determine the number of Subatomic Particles in an atom? ...
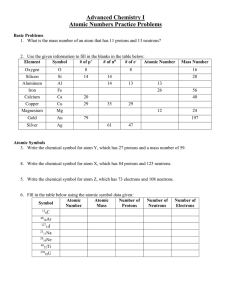
Atomic Numbers Practice Problems
... 3. Write the chemical symbol for atom Y, which has 27 protons and a mass number of 59. ...
... 3. Write the chemical symbol for atom Y, which has 27 protons and a mass number of 59. ...
CHM 103 Lecture 6 S07
... Bohr Model • Bohr noted the line spectra of certain elements and assumed the electrons were confined to specific energy states. These were called orbits. ...
... Bohr Model • Bohr noted the line spectra of certain elements and assumed the electrons were confined to specific energy states. These were called orbits. ...
Classifying Matter
... neutrons. The electrons are always found whizzing around the center in areas called shells or orbitals. Electrons have a negative charge and protons have a positive charge whereas neutrons have no charge. They are neutral. Due to the presence of equal number of negative electrons and positive proton ...
... neutrons. The electrons are always found whizzing around the center in areas called shells or orbitals. Electrons have a negative charge and protons have a positive charge whereas neutrons have no charge. They are neutral. Due to the presence of equal number of negative electrons and positive proton ...
Big History Chemistry Study Guide File
... 5. The atomic mass is equal to the ___________________ plus _____________________. 6. Every atom of _________________ in the universe has 5 protons. The atomic mass of this element is listed as _________ amu, which means that its most common isotopes have masses of _____ and _____. These isotopes ha ...
... 5. The atomic mass is equal to the ___________________ plus _____________________. 6. Every atom of _________________ in the universe has 5 protons. The atomic mass of this element is listed as _________ amu, which means that its most common isotopes have masses of _____ and _____. These isotopes ha ...
UNIT 1 - Grafton Public Schools
... What are the three kinds of subatomic particles? What makes one element different from another? How do isotopes of an element differ? How do you calculate the atomic mass of an element? How do nuclear reactions differ from chemical reactions? What are the three types of nuclear radiation? How much o ...
... What are the three kinds of subatomic particles? What makes one element different from another? How do isotopes of an element differ? How do you calculate the atomic mass of an element? How do nuclear reactions differ from chemical reactions? What are the three types of nuclear radiation? How much o ...
Atoms_and_Elements
... element is found in a molecule, a subscript is used to indicate this in the ...
... element is found in a molecule, a subscript is used to indicate this in the ...
File
... unpaired electron, so they are very reactive. (electrons like to be in pairs). II. Alkali Earth Metals: found in the second column. They are less reactive than the alkali metals, but are pretty reactive. III. Halogens: found in the seventh column, they are very reactive because they have an unpaired ...
... unpaired electron, so they are very reactive. (electrons like to be in pairs). II. Alkali Earth Metals: found in the second column. They are less reactive than the alkali metals, but are pretty reactive. III. Halogens: found in the seventh column, they are very reactive because they have an unpaired ...