
Test #1 Study Guide
... Scientific Theory – A model for nature that explains not only what it does, but why. Formed by one or more well established hypotheses. Experiments – Highly controlled procedures designed to generate observations. ...
... Scientific Theory – A model for nature that explains not only what it does, but why. Formed by one or more well established hypotheses. Experiments – Highly controlled procedures designed to generate observations. ...
Atomic structure
... Bohr refined Rutherford's idea by adding that the electrons were in orbits. Rather like planets orbiting the sun. With each orbit only able to contain a set number of electrons. ...
... Bohr refined Rutherford's idea by adding that the electrons were in orbits. Rather like planets orbiting the sun. With each orbit only able to contain a set number of electrons. ...
CHAPTER 4: ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
... There are 4 fundamental forces: gravity, electromagnetic force, strong force, weak force Let’s focus on the electromagnetic force, which consists of electricity and magnetism. electrostatic force: the force resulting from a charge on an object – Two objects with the same charge (both negative or bot ...
... There are 4 fundamental forces: gravity, electromagnetic force, strong force, weak force Let’s focus on the electromagnetic force, which consists of electricity and magnetism. electrostatic force: the force resulting from a charge on an object – Two objects with the same charge (both negative or bot ...
Final
... pure substances and mixtures Chemical properties and physical properties Density Calculations Temperature Calculations Determine # of sig figs Calculate with sig figs Given a table, fill in #p, #n, #e, symbol, mass#, atomic #and most common charge for neutral atoms and ions Names to formulas, formul ...
... pure substances and mixtures Chemical properties and physical properties Density Calculations Temperature Calculations Determine # of sig figs Calculate with sig figs Given a table, fill in #p, #n, #e, symbol, mass#, atomic #and most common charge for neutral atoms and ions Names to formulas, formul ...
9 19 -1 atomic number mass number charge
... protons. We often use a 1 or 2 letter abbreviation for an element, called the atomic symbol. This is usually fairly self explanatory (C for carbon, H for hydrogen), though in some cases the abbreviation comes from the Latin, Greek or German name for that element. For instance, silver is Ag, which is ...
... protons. We often use a 1 or 2 letter abbreviation for an element, called the atomic symbol. This is usually fairly self explanatory (C for carbon, H for hydrogen), though in some cases the abbreviation comes from the Latin, Greek or German name for that element. For instance, silver is Ag, which is ...
Chapter3 atoms
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different John Dalton elements differ in size, mass, and other properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different John Dalton elements differ in size, mass, and other properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or ...
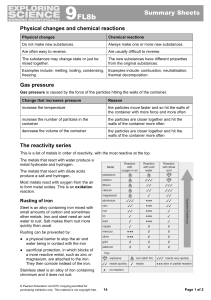
9F Reactivity - Parrs Wood High School
... The metals that react with water produce a metal hydroxide and hydrogen. The metals that react with dilute acids produce a salt and hydrogen. Most metals react with oxygen from the air to form metal oxides. This is an oxidation reaction. ...
... The metals that react with water produce a metal hydroxide and hydrogen. The metals that react with dilute acids produce a salt and hydrogen. Most metals react with oxygen from the air to form metal oxides. This is an oxidation reaction. ...
Chemistry: Nuclear Reactions Guided Inquiry + n → + + 3 n +
... Nuclear reactions are reactions that affect the nucleus of an atom. In nature, unstable nuclei undergo nuclear reactions to form more stable nuclei. Stable nuclei can also undergo nuclear reactions if ...
... Nuclear reactions are reactions that affect the nucleus of an atom. In nature, unstable nuclei undergo nuclear reactions to form more stable nuclei. Stable nuclei can also undergo nuclear reactions if ...
Chapter 3 Review
... 14. Why do nuclei need neutrons to be stable? (ANS: neutrons are like glue that holds positive protons together.) 15. What are the symbols for the three types of radiation? (ANS: 42, 01, and ) 16. Describe two types of nuclear reactions other than radioactive decay. Where do they occur? (ANS: (1 ...
... 14. Why do nuclei need neutrons to be stable? (ANS: neutrons are like glue that holds positive protons together.) 15. What are the symbols for the three types of radiation? (ANS: 42, 01, and ) 16. Describe two types of nuclear reactions other than radioactive decay. Where do they occur? (ANS: (1 ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... 1. All matter consists of indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element have the same shape and mass. 3. Atoms cannot be created or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements may combine with each other in fixed, simple, whole number ratios to form compound atoms. Which of these po ...
... 1. All matter consists of indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element have the same shape and mass. 3. Atoms cannot be created or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements may combine with each other in fixed, simple, whole number ratios to form compound atoms. Which of these po ...
CHEMISTRY FALL FINAL PRACTICE 2016
... How many bonds do each of the following tend to form? C ___ O ____ N ___ H_____ ...
... How many bonds do each of the following tend to form? C ___ O ____ N ___ H_____ ...
Name: Date: ______ Period: Unit 3 – Atomic Structure Review
... 1. Who was the ancient Greek philosopher who first proposed the notion of the atom? Democritus 2. What was Dalton’s atomic model called? Billard ball model 3. Who’s model first introduced the concept of energy levels? Bohr 4. What were the major problems of Dalton’s atomic theory? Did not have an in ...
... 1. Who was the ancient Greek philosopher who first proposed the notion of the atom? Democritus 2. What was Dalton’s atomic model called? Billard ball model 3. Who’s model first introduced the concept of energy levels? Bohr 4. What were the major problems of Dalton’s atomic theory? Did not have an in ...
Atoms, Molecules, Compounds, Elements, and Mixtures
... Electrons • Electrons orbit around an atom. In this picture, they are the small yellow bits. • They have a negative charge. • They are lighter than protons or neutrons. • The number of protons=number of electrons in a neutral atom ...
... Electrons • Electrons orbit around an atom. In this picture, they are the small yellow bits. • They have a negative charge. • They are lighter than protons or neutrons. • The number of protons=number of electrons in a neutral atom ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide-Atomic Structure Define the following terms
... Atomic Mass Unit (amu)-unit of mass of a proton or neutron (1 amu each) Atomic number-number of protons, periodic table Dalton’s Atomic Theory-first theory to relate chemical changes to events at the atomic level Electron-negatively charged subatomic particle, lives outside of the nucleus Group-vert ...
... Atomic Mass Unit (amu)-unit of mass of a proton or neutron (1 amu each) Atomic number-number of protons, periodic table Dalton’s Atomic Theory-first theory to relate chemical changes to events at the atomic level Electron-negatively charged subatomic particle, lives outside of the nucleus Group-vert ...
No Slide Title - boxall.srhs.net
... model of atomic structure, electrons do not travel along fixed paths like planets around the sun. • Instead, electrons can be found most frequently in certain areas around the ...
... model of atomic structure, electrons do not travel along fixed paths like planets around the sun. • Instead, electrons can be found most frequently in certain areas around the ...
Bohr Atomic Model - Flinn Scientific
... lower in energy than electrons that are further away from the nucleus. This idea is called the quantization of energy—electrons can only occupy specific energy levels, they may not have intermediate energy levels between these allowed states. The picture that is often used to describe this idea is t ...
... lower in energy than electrons that are further away from the nucleus. This idea is called the quantization of energy—electrons can only occupy specific energy levels, they may not have intermediate energy levels between these allowed states. The picture that is often used to describe this idea is t ...
File
... Cations have a positive charge Anions have a negative charge Ions usually behave differently than the neutral atom ...
... Cations have a positive charge Anions have a negative charge Ions usually behave differently than the neutral atom ...
ChemChapter_3[1]
... 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are simply combined, separated or rearranged. ...
... 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are simply combined, separated or rearranged. ...
Review Guide: Atomic Theory and Structure (Including the mole
... 1. Identify the three subatomic particles: a. proton b. neutron c. electron 2. The proton and neutron are located in the nucleus of the atom. 3. The electrons are located on the energy levels outside the nucleus. 4. Which subatomic particle(s) make up the majority of the mass of an atom? Proton and ...
... 1. Identify the three subatomic particles: a. proton b. neutron c. electron 2. The proton and neutron are located in the nucleus of the atom. 3. The electrons are located on the energy levels outside the nucleus. 4. Which subatomic particle(s) make up the majority of the mass of an atom? Proton and ...
An atom is an indivisible particle. is chemically indivisible. is the
... is defined by the electrons. ...
... is defined by the electrons. ...
Friday, Feb 3, 2006
... 11) Thomson passed an electric current through sealed glass tubes filled with gases The resulting glowing beam consisted of tiny negatively charged particles moving at high speed. Thomson concluded that electrons must be parts of the atoms of all elements. Millikan determined the charge and mass of ...
... 11) Thomson passed an electric current through sealed glass tubes filled with gases The resulting glowing beam consisted of tiny negatively charged particles moving at high speed. Thomson concluded that electrons must be parts of the atoms of all elements. Millikan determined the charge and mass of ...
Electromagnetic radiation
... ii. 2 gives the probability of finding an electron within a given region in space iii. Contains information about an electron’s position in 3D space defines a volume of space around the nucleus where there is a high probability of finding an electron say nothing about the electron’s path or movemen ...
... ii. 2 gives the probability of finding an electron within a given region in space iii. Contains information about an electron’s position in 3D space defines a volume of space around the nucleus where there is a high probability of finding an electron say nothing about the electron’s path or movemen ...
Atomic Theory
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons, and therefore different atomic masses. While carbon-14 is used in radioactive dating, carbon-12 has a more stable nucleus and therefore is not used in this capacity. ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons, and therefore different atomic masses. While carbon-14 is used in radioactive dating, carbon-12 has a more stable nucleus and therefore is not used in this capacity. ...
















![ChemChapter_3[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000730918_1-e981d4b122189d44b26201a884f03a71-300x300.png)





