Finals Study Guide
... Molar Mass—mass of one mole of a pure substance Mass Number—total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an isotope Nuclear Forces—short-range proton-neutron, proton-proton, and neutron-neutron forces that hold nuclear particles together Law of Conservation of Mass—mass is neither created ...
... Molar Mass—mass of one mole of a pure substance Mass Number—total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an isotope Nuclear Forces—short-range proton-neutron, proton-proton, and neutron-neutron forces that hold nuclear particles together Law of Conservation of Mass—mass is neither created ...
File
... Physical or chemical change? The rain turned to snow… Marty broke a class on the bathroom floor… I burned my bagel! I fried eggs for breakfast… I mixed baking soda and vinegar for science ...
... Physical or chemical change? The rain turned to snow… Marty broke a class on the bathroom floor… I burned my bagel! I fried eggs for breakfast… I mixed baking soda and vinegar for science ...
Unit 3 Rev Pckt - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... d. protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. 23. Scientists have determined that electrons a. move in space around the nucleus. b. have a mass equal to the mass of protons. c. orbit the nucleus in a well-defined path. d. are electrically neutral 24. Atoms of each element contain a unique numb ...
... d. protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. 23. Scientists have determined that electrons a. move in space around the nucleus. b. have a mass equal to the mass of protons. c. orbit the nucleus in a well-defined path. d. are electrically neutral 24. Atoms of each element contain a unique numb ...
1 - Groupfusion.net
... mass of Z is 258.63 amu, which of these isotopes is most abundant? Since the atomic mass is the weighted average, the most abundant will be the isotope with the mass number closest to the atomic mass: Z-259 ...
... mass of Z is 258.63 amu, which of these isotopes is most abundant? Since the atomic mass is the weighted average, the most abundant will be the isotope with the mass number closest to the atomic mass: Z-259 ...
lJr nors ehe mistry -Ato ms fy [-l"me nts
... white light is passed through a prism, what is observed? A) continuous spectrum B) black light C) bright spots and lines D)nothing ...
... white light is passed through a prism, what is observed? A) continuous spectrum B) black light C) bright spots and lines D)nothing ...
The Chemistry of Life
... Atoms of the same Element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. ...
... Atoms of the same Element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. ...
Chapter 5 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Section 5.1
... 78.99% magnesium-24 with a mass of 23.9850 amu, 10.00% magnesium-25 with a mass of 24.9858 amu, and the rest is magnesium-26 with a mass of 25.9826 amu. What is the average atomic mass of magnesium? ...
... 78.99% magnesium-24 with a mass of 23.9850 amu, 10.00% magnesium-25 with a mass of 24.9858 amu, and the rest is magnesium-26 with a mass of 25.9826 amu. What is the average atomic mass of magnesium? ...
Chapter 2 - Chemistry
... 3.) A compound is a type of matter composed of atoms of two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions. 4.) A chemical reaction consists of the rearrangement of the atoms present in the reacting substances to give new chemical combinations present in the substances formed by the react ...
... 3.) A compound is a type of matter composed of atoms of two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions. 4.) A chemical reaction consists of the rearrangement of the atoms present in the reacting substances to give new chemical combinations present in the substances formed by the react ...
Name: _key Date: ______ Period: Unit 3 – Atomic Structure Review
... 4. What subatomic particles have an electrical charge? Electrons 5. ALL neutral atoms contain equal numbers of __protons__ and __electrons_. 6. What do we call atoms that have gained or lost electrons? ions 7. What do we call atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons? isotope ...
... 4. What subatomic particles have an electrical charge? Electrons 5. ALL neutral atoms contain equal numbers of __protons__ and __electrons_. 6. What do we call atoms that have gained or lost electrons? ions 7. What do we call atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons? isotope ...
Chem Notes
... identical; different from atoms of other elements Atoms of different elements can mix or chemically combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form compounds. ...
... identical; different from atoms of other elements Atoms of different elements can mix or chemically combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form compounds. ...
Atoms and elements
... • Today scientists know that electrons do not actually orbit the nucleus as in Bohr's planetary model. • The electron cloud model is now used to describe atoms. • In this model, electrons dart about within an energy level in an ever-changing path. • Most of this path falls into a region called an el ...
... • Today scientists know that electrons do not actually orbit the nucleus as in Bohr's planetary model. • The electron cloud model is now used to describe atoms. • In this model, electrons dart about within an energy level in an ever-changing path. • Most of this path falls into a region called an el ...
What is Organic Chemistry?
... stable, because e- have filled up their orbitals, having very high IE, thus it’s extremely difficult to break an e- away. ...
... stable, because e- have filled up their orbitals, having very high IE, thus it’s extremely difficult to break an e- away. ...
Ch 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... - Atoms of an element all have same Z, but can have different A. - Isotopes are atoms of an element with same Z, but different A’s. (An atom with a particular number of neutrons is called a nuclide.) - The atomic weight on the periodic table is the weighted average of all isotopes. It is the sum of ...
... - Atoms of an element all have same Z, but can have different A. - Isotopes are atoms of an element with same Z, but different A’s. (An atom with a particular number of neutrons is called a nuclide.) - The atomic weight on the periodic table is the weighted average of all isotopes. It is the sum of ...
atom
... All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same mass. Atoms of different elements are different and have different masses. An atom of one element cannot be changed into an atom of a different element. Atoms cannot be created or destroyed in any chemical change, only ...
... All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same mass. Atoms of different elements are different and have different masses. An atom of one element cannot be changed into an atom of a different element. Atoms cannot be created or destroyed in any chemical change, only ...
HistoryWebactivityKey
... American physicist who determined the charge on an electron using charged oil drop experiments in 1909. ...
... American physicist who determined the charge on an electron using charged oil drop experiments in 1909. ...
history of the atom ppt student copy
... form chemical compounds. 5. In chemical reactions, ____________________________________ ________________________________________________________ •Dalton’s theory helped explain the law of conservation of mass because it stated that atoms could not be created or destroyed. •Modifications have been ma ...
... form chemical compounds. 5. In chemical reactions, ____________________________________ ________________________________________________________ •Dalton’s theory helped explain the law of conservation of mass because it stated that atoms could not be created or destroyed. •Modifications have been ma ...
Chapter 9
... 5. The ____________ number on the periodic table tells you the number of protons. The _______ number indicates the number of ____________ and ______________. In a neutral atom, protons always equal ______________. 6. Energy level number (1) in an atom contains a maximum number of __________ electron ...
... 5. The ____________ number on the periodic table tells you the number of protons. The _______ number indicates the number of ____________ and ______________. In a neutral atom, protons always equal ______________. 6. Energy level number (1) in an atom contains a maximum number of __________ electron ...
File
... Mass is created and energy is released. Mass is created and energy is stored. Mass is converted to energy, which is released. Mass is converted to energy, which is stored. ...
... Mass is created and energy is released. Mass is created and energy is stored. Mass is converted to energy, which is released. Mass is converted to energy, which is stored. ...
1. Atoms and Bonding
... Other scans using radioactive tracers A hepatobiliary (HIDA) scan is an imaging procedure used to diagnose problems in the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VDihrC 1RnYE ...
... Other scans using radioactive tracers A hepatobiliary (HIDA) scan is an imaging procedure used to diagnose problems in the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VDihrC 1RnYE ...
File - 7th Grade Science
... – Each object must have a different number of red blocks – Each object must have an equal number of red and blue blocks – Each object must have at least as many yellow blocks as red blocks but can have no more than 2 extra yellow blocks ...
... – Each object must have a different number of red blocks – Each object must have an equal number of red and blue blocks – Each object must have at least as many yellow blocks as red blocks but can have no more than 2 extra yellow blocks ...
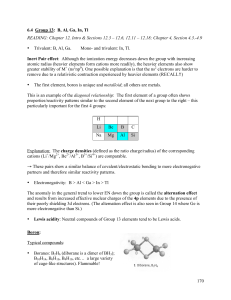
6.5 Main Group
... Inert Pair effect: Although the ionization energy decreases down the group with increasing atomic radius (heavier elements form cations more readily), the heavier elements also show greater stability of M+ (ns2np0). One possible explanation is that the ns2 electrons are harder to remove due to a rel ...
... Inert Pair effect: Although the ionization energy decreases down the group with increasing atomic radius (heavier elements form cations more readily), the heavier elements also show greater stability of M+ (ns2np0). One possible explanation is that the ns2 electrons are harder to remove due to a rel ...