
Science - Byron High School
... ex. Think of cutting a piece of aluminum foil into smaller and smaller pieces. How far can it be cut? ...
... ex. Think of cutting a piece of aluminum foil into smaller and smaller pieces. How far can it be cut? ...
Protons, Neutrons and Electrons
... To determine the number of neutrons, you need to do a little subtraction. First round the mass number to the nearest whole number (because you either have a proton or neutron or you do not) Mass Number (A) – Atomic Number (Z) = ...
... To determine the number of neutrons, you need to do a little subtraction. First round the mass number to the nearest whole number (because you either have a proton or neutron or you do not) Mass Number (A) – Atomic Number (Z) = ...
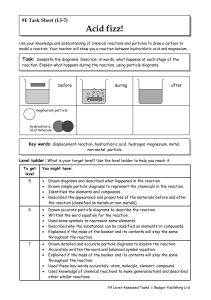
Year 9 Homework Task 9E-5 Reactions 5-7
... Key words: displacement reaction, hydrochloric acid, hydrogen, magnesium, metal, non-metal, particle ...
... Key words: displacement reaction, hydrochloric acid, hydrogen, magnesium, metal, non-metal, particle ...
Do Now - March [4-2], 2009 - stroh
... • An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by physical or chemical means – An element is made of only one type of atom ...
... • An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by physical or chemical means – An element is made of only one type of atom ...
number of protons - Waukee Community School District Blogs
... We have come so far in our understanding of atoms. Centuries of researching and countless scientists devoting their lives to create the understanding of the atom today (textbook concepts). ...
... We have come so far in our understanding of atoms. Centuries of researching and countless scientists devoting their lives to create the understanding of the atom today (textbook concepts). ...
Atomic orbital
... “It was quite the most incredible event that has ever happened to me in my life. It was almost as incredible as if you fired a 15-inch shell at a piece of tissue paper and it came back and hit you. On consideration, I realized that this scattering backward must be the result of a single collision, ...
... “It was quite the most incredible event that has ever happened to me in my life. It was almost as incredible as if you fired a 15-inch shell at a piece of tissue paper and it came back and hit you. On consideration, I realized that this scattering backward must be the result of a single collision, ...
Text Questions from Wilbraham, et. al.
... 34. How do the elements within a group compare? they have similar chemical and physical properties 5.1 35. To explain the chemical properties of elements, we require a model that does what? describes the behavior of electrons within atoms 36. Why did Bohr change Rutherford’s model? to include new di ...
... 34. How do the elements within a group compare? they have similar chemical and physical properties 5.1 35. To explain the chemical properties of elements, we require a model that does what? describes the behavior of electrons within atoms 36. Why did Bohr change Rutherford’s model? to include new di ...
Ch 17 Properties of Atoms - Effingham County Schools
... The organization of elements by their properties is the periodic table. Each small square on the periodic table shows the name of one element and the letter symbol for that element. The elements are arranged based on the number of protons an atom of that element has in its nucleus. Periodic la ...
... The organization of elements by their properties is the periodic table. Each small square on the periodic table shows the name of one element and the letter symbol for that element. The elements are arranged based on the number of protons an atom of that element has in its nucleus. Periodic la ...
Which of the following statements correctly describes the
... If an atom has a mass number of 18, what can be said about the number of protons and neutrons it contains? A ...
... If an atom has a mass number of 18, what can be said about the number of protons and neutrons it contains? A ...
Atomic Structure Past Paper Questions
... line represents electron transitions between energy levels same nuclear charge, fewer electrons (thus more energy required to remove successive electrons)/harder to remove an electron from an ion with increasing positive charge/nucleus has greater effect on smaller number of electrons; large increas ...
... line represents electron transitions between energy levels same nuclear charge, fewer electrons (thus more energy required to remove successive electrons)/harder to remove an electron from an ion with increasing positive charge/nucleus has greater effect on smaller number of electrons; large increas ...
02_Lecture_Presentation_PC
... protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be approximated by the mass number ...
... protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be approximated by the mass number ...
Law of Multiple Proportions
... 400 B.C. – Democritus proposed the existence of fundamental particles of matter that were indivisible and indestructible - “atomos”. Aristotle thought all matter was continuous; he did not believe in atoms. Neither idea was supported by any experimental evidence – speculation only. ...
... 400 B.C. – Democritus proposed the existence of fundamental particles of matter that were indivisible and indestructible - “atomos”. Aristotle thought all matter was continuous; he did not believe in atoms. Neither idea was supported by any experimental evidence – speculation only. ...
CHEM 1405 CHAPTER 4
... lines of specific wavelengths. This is called Atomic Emission Spectrum or the Line Spectrum. This is a discontinuous spectrum. Every element has its own characteristic emission spectrum, which is used to identify the element. Hence, it is called the atomic finger print. When radiations pass through ...
... lines of specific wavelengths. This is called Atomic Emission Spectrum or the Line Spectrum. This is a discontinuous spectrum. Every element has its own characteristic emission spectrum, which is used to identify the element. Hence, it is called the atomic finger print. When radiations pass through ...
Atomic Structure
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with another in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged ...
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with another in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged ...
Atomic Theory and Bonding
... ie. Iron, Fe, loses either 2 (Fe2+) or 3 (Fe3+) electrons Non-metals gain electrons and become negative ions ( = anions) Atoms do this in an attempt to have the same number of valence electrons (electrons furthest from the nucleus) as the nearest noble gas. ...
... ie. Iron, Fe, loses either 2 (Fe2+) or 3 (Fe3+) electrons Non-metals gain electrons and become negative ions ( = anions) Atoms do this in an attempt to have the same number of valence electrons (electrons furthest from the nucleus) as the nearest noble gas. ...
Atomic Theory and Bonding
... ie. Iron, Fe, loses either 2 (Fe2+) or 3 (Fe3+) electrons Non-metals gain electrons and become negative ions ( = anions) Atoms do this in an attempt to have the same number of valence electrons (electrons furthest from the nucleus) as the nearest noble gas. ...
... ie. Iron, Fe, loses either 2 (Fe2+) or 3 (Fe3+) electrons Non-metals gain electrons and become negative ions ( = anions) Atoms do this in an attempt to have the same number of valence electrons (electrons furthest from the nucleus) as the nearest noble gas. ...
Review topics-blog
... (e.g. you might recall the ground state electron configuration of carbon is 1s2 2s2 2p2). ...
... (e.g. you might recall the ground state electron configuration of carbon is 1s2 2s2 2p2). ...
Powerpoint Historical Model
... In 1913, proposed the Bohr Model, which suggests that electrons travel around the nucleus of an atom in orbits or definite paths. Additionally, the electrons can jump from a path in one level to a path in another level (depending on their energy) Won a Nobel Prize Worked with Ernest Rutherford ...
... In 1913, proposed the Bohr Model, which suggests that electrons travel around the nucleus of an atom in orbits or definite paths. Additionally, the electrons can jump from a path in one level to a path in another level (depending on their energy) Won a Nobel Prize Worked with Ernest Rutherford ...
GCSE Radiation - Bishopston Comprehensive School Moodle
... Nuclear Fission Each time a Uranium atom splits up it spits out 2 or 3 neutrons, one of which hits another uranium nucleus, causing it to split. This keeps the chain reaction going. ...
... Nuclear Fission Each time a Uranium atom splits up it spits out 2 or 3 neutrons, one of which hits another uranium nucleus, causing it to split. This keeps the chain reaction going. ...
Radioactive Decay (cont.)
... • Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. ...
... • Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. ...
Subatomic Particles
... • This is the number of protons in an atom • Hydrogen has 1 proton and thus is atomic number 1 • Oxygen has 8 protons and thus atomic number 8 • Every element is different due to its different numbers of protons • So changing the number of protons changes the element! – Some elements may have the sa ...
... • This is the number of protons in an atom • Hydrogen has 1 proton and thus is atomic number 1 • Oxygen has 8 protons and thus atomic number 8 • Every element is different due to its different numbers of protons • So changing the number of protons changes the element! – Some elements may have the sa ...

![Do Now - March [4-2], 2009 - stroh](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008519532_1-cab23fd6aae248311f653b62e7fe2161-300x300.png)




















