Atomic Structure
... ◦ all the positive charge and almost all the mass are concentrated in a small region that has enough positive charge to account for the great deflection of some of the alpha particles ◦ Nucleus: tiny, central core of an atom that is composed of neutrons and protons ◦ Electron are distributed around ...
... ◦ all the positive charge and almost all the mass are concentrated in a small region that has enough positive charge to account for the great deflection of some of the alpha particles ◦ Nucleus: tiny, central core of an atom that is composed of neutrons and protons ◦ Electron are distributed around ...
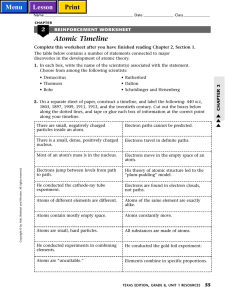
Atomic Timeline
... along the dotted lines, and tape or glue each box of information at the correct point along your timeline. There are small, negatively charged particles inside an atom. 1897 (Thomson) There is a small, dense, positively charged nucleus. 1911 (Rutherford) ...
... along the dotted lines, and tape or glue each box of information at the correct point along your timeline. There are small, negatively charged particles inside an atom. 1897 (Thomson) There is a small, dense, positively charged nucleus. 1911 (Rutherford) ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... compound, the masses of one element combined with a fixed mass of the second are in the ratio of small whole numbers. Same elements to combine in different ratios to give different substances. ...
... compound, the masses of one element combined with a fixed mass of the second are in the ratio of small whole numbers. Same elements to combine in different ratios to give different substances. ...
Chem Reactions (and Balancing Equations)
... 4. aluminum sulfate and calcium hydroxide become aluminum hydroxide and calcium sulfate. 5. copper metal and silver nitrate react to form silver metal and copper (II) nitrate. 6. sodium metal and chlorine react to make sodium chloride. ...
... 4. aluminum sulfate and calcium hydroxide become aluminum hydroxide and calcium sulfate. 5. copper metal and silver nitrate react to form silver metal and copper (II) nitrate. 6. sodium metal and chlorine react to make sodium chloride. ...
Atoms Development of the Atomic Theory
... Beta radiation consists of fast-moving electrons. The symbol for a beta particle is B or 0B or 0e. They are small and fairly penetrating. The relative mass is 0 and the charge is -1. Gamma radiation (or gamma rays) is not particles but extremely high-energy electromagnetic radiation. They are very p ...
... Beta radiation consists of fast-moving electrons. The symbol for a beta particle is B or 0B or 0e. They are small and fairly penetrating. The relative mass is 0 and the charge is -1. Gamma radiation (or gamma rays) is not particles but extremely high-energy electromagnetic radiation. They are very p ...
chapter 2 - Scranton Prep Biology
... An atom's electronconfigurationdeterminesits chemicalbehavior. ' Electron conJiguration= Distributionof electronsin an atom's electron shells The first l8 elementsof a periodicchartare arrangedsequentially by atomic numberinto threerows (periods).In referenceto theserepresentotive elements, note the ...
... An atom's electronconfigurationdeterminesits chemicalbehavior. ' Electron conJiguration= Distributionof electronsin an atom's electron shells The first l8 elementsof a periodicchartare arrangedsequentially by atomic numberinto threerows (periods).In referenceto theserepresentotive elements, note the ...
Basic Atomic Structure
... Protons- positive charge, in the nucleus, has a mass of 1 amu Neutron- neutral/no charge, in the nucleus, has a mass of 1 amu Electron- negative charge, towards the outside of the atom, has no mass ...
... Protons- positive charge, in the nucleus, has a mass of 1 amu Neutron- neutral/no charge, in the nucleus, has a mass of 1 amu Electron- negative charge, towards the outside of the atom, has no mass ...
Aristotle, Dalton, Thomson to Rutherford, Bohr and Schrödinger
... (Law of Conservation of Mass) 3) Atoms of an element have identical ...
... (Law of Conservation of Mass) 3) Atoms of an element have identical ...
1.3 History of the Atom Notes
... different components: Earth, Wind, Water, and Fire. Even then, this theory was starting to lose followers and sink the pit of theories that did not last. The rise of Alchemy brought on a new type of process to create scientific theories. Before the Alcehmists, the way people devised theories was to ...
... different components: Earth, Wind, Water, and Fire. Even then, this theory was starting to lose followers and sink the pit of theories that did not last. The rise of Alchemy brought on a new type of process to create scientific theories. Before the Alcehmists, the way people devised theories was to ...
The only sure evidence that a chemical reaction has occured is
... TEST CHEMICAL REACTIONS 2011 Practice Questions 1. The only sure evidence that a chemical reaction has occurred is 2. CaCO3 represents a chemical _____. 3. A shorter, easier way to show chemical reactions, using symbols instead of words, is called a _____. 4. The substances on the left of the arrow ...
... TEST CHEMICAL REACTIONS 2011 Practice Questions 1. The only sure evidence that a chemical reaction has occurred is 2. CaCO3 represents a chemical _____. 3. A shorter, easier way to show chemical reactions, using symbols instead of words, is called a _____. 4. The substances on the left of the arrow ...
Chapter 4 and 5 study guide 2016-2017
... Filtering or straining can be used to separate mixtures based on __________________________ ...
... Filtering or straining can be used to separate mixtures based on __________________________ ...
Unit 3C Standards for Quiz
... calculators are allowed on the standards exam that we will be modeling this in this assessment of progress. Atomic and Molecular Structure 1. The Periodic Table displays the elements in increasing atomic number and shows how periodicity of the physical and chemical properties of the elements relates ...
... calculators are allowed on the standards exam that we will be modeling this in this assessment of progress. Atomic and Molecular Structure 1. The Periodic Table displays the elements in increasing atomic number and shows how periodicity of the physical and chemical properties of the elements relates ...
THE ATOM
... • Isotopes – different atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons • some isotopes are radioactive – they emit energy when the nucleus of the atom breaks down spontaneously • most radioactive isotopes are not dangerous • to determine if an isotope ...
... • Isotopes – different atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons • some isotopes are radioactive – they emit energy when the nucleus of the atom breaks down spontaneously • most radioactive isotopes are not dangerous • to determine if an isotope ...
Chapter Three: Atoms and Atomic Masses
... We symbolize this ion as Al3+. Note that losing electrons is indicated with +, and gaining electrons is indicated with -. ...
... We symbolize this ion as Al3+. Note that losing electrons is indicated with +, and gaining electrons is indicated with -. ...
PHYSICS E09 11
... Unit Statement: In essential unit nine, the student will also learn that certain elements radiate particles and turn into other elements. The student will also learn that nuclear fission and nuclear fusion reactions release huge amounts of energy. Essential Outcomes: (must be assessed) 1. The Studen ...
... Unit Statement: In essential unit nine, the student will also learn that certain elements radiate particles and turn into other elements. The student will also learn that nuclear fission and nuclear fusion reactions release huge amounts of energy. Essential Outcomes: (must be assessed) 1. The Studen ...
Unit 3 Review
... It tells us that electrons exist in 3-D space around the nucleus, it can tell us the probability of where an electron is about 90% of the time ...
... It tells us that electrons exist in 3-D space around the nucleus, it can tell us the probability of where an electron is about 90% of the time ...
Answers - Dr Terry Dwyer National Curriculum mathematics and
... 1 Briefly describe the chemical properties of group 17 - the halogens. The group 17 halogens are reactive and dangerous (Chlorine was used as a poisonous gas during World War I). The halogens react with metals to form salts. The halogens become less reactive the further down the group. 2 Briefly ...
... 1 Briefly describe the chemical properties of group 17 - the halogens. The group 17 halogens are reactive and dangerous (Chlorine was used as a poisonous gas during World War I). The halogens react with metals to form salts. The halogens become less reactive the further down the group. 2 Briefly ...
50 Frequently Forgotten Facts
... c) Name an element that exists in a crystal lattice at STP:_________________________________ d) Name an element that has no definite volume or shape at STP:______________________________ 22) Electronegativity is an atom’s attraction to electrons in a chemical bond. [Table S] a) Which element, when b ...
... c) Name an element that exists in a crystal lattice at STP:_________________________________ d) Name an element that has no definite volume or shape at STP:______________________________ 22) Electronegativity is an atom’s attraction to electrons in a chemical bond. [Table S] a) Which element, when b ...
Chapter 3 - cloudfront.net
... Mass (not weight) of atoms is very, very small, i.e. around ____________ Better to use a relative scale to compare mass of atoms to each other, but you need a standard. Choose ______, which has 6 protons & 6 neutrons, 126C, also ...
... Mass (not weight) of atoms is very, very small, i.e. around ____________ Better to use a relative scale to compare mass of atoms to each other, but you need a standard. Choose ______, which has 6 protons & 6 neutrons, 126C, also ...