Dalton`s Atomic Theory Atomic Theory II
... negatively charged electrons moved around the nucleus. ...
... negatively charged electrons moved around the nucleus. ...
Chapter 2 Notes
... 1. molecules- 2 or more atoms combined; atoms share electrons in the outermost portion of their electron clouds; example: (H2O) 2. compounds- when 2 or more substances combine chemically; has properties different from the properties of each of the elements in it; example: water (H2O) 3. chemical pro ...
... 1. molecules- 2 or more atoms combined; atoms share electrons in the outermost portion of their electron clouds; example: (H2O) 2. compounds- when 2 or more substances combine chemically; has properties different from the properties of each of the elements in it; example: water (H2O) 3. chemical pro ...
Chemistry - StudyTime NZ
... In order for chemical reac>ons to occur, molecules must collide with each other at the correct orienta>on and with the minimum amount of necessary energy, known as the ‘ac>va>on energy’. ...
... In order for chemical reac>ons to occur, molecules must collide with each other at the correct orienta>on and with the minimum amount of necessary energy, known as the ‘ac>va>on energy’. ...
File
... composed of? What is the structure of material objects? Is there a basic unit from which all objects are made? As early as 400 B.C., some Greek philosophers proposed that matter is made of indivisible building blocks known as atomos. (Atomos in Greek means indivisible.) To these early Greeks, matter ...
... composed of? What is the structure of material objects? Is there a basic unit from which all objects are made? As early as 400 B.C., some Greek philosophers proposed that matter is made of indivisible building blocks known as atomos. (Atomos in Greek means indivisible.) To these early Greeks, matter ...
Document
... • How is an elements atomic number like a person’s fingerprint? • Homework: Calculate the p, n and electrons in the following: tantalum, samarium, uranium ...
... • How is an elements atomic number like a person’s fingerprint? • Homework: Calculate the p, n and electrons in the following: tantalum, samarium, uranium ...
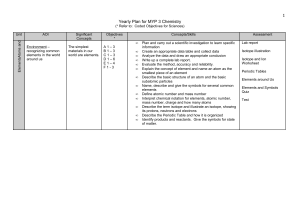
Yearly Plan for MYP 1 Science
... without them - recognizing common chemical reactions in our world - understanding what happens in a chemical change - noticing and identifying common chemicals we use in our everyday lives ...
... without them - recognizing common chemical reactions in our world - understanding what happens in a chemical change - noticing and identifying common chemicals we use in our everyday lives ...
4.2 Structure of the Atom
... Composition of the Nucleus: • A Proton is a – Positively charged subatomic particle that is found in the nucleus of an atom – Mass of 1.673 x 10-24 grams • Approximately 1800 times that of the ...
... Composition of the Nucleus: • A Proton is a – Positively charged subatomic particle that is found in the nucleus of an atom – Mass of 1.673 x 10-24 grams • Approximately 1800 times that of the ...
DIR RD 4-1
... a. Atoms are small, soft particles. b. Atoms are always standing still. c. Atoms are made of a single material. d. Atoms are small particles that can be cut in half again and again. 3. We know that Democritus was right to say that all matter was made up of atoms. So why did people ignore Democritus’ ...
... a. Atoms are small, soft particles. b. Atoms are always standing still. c. Atoms are made of a single material. d. Atoms are small particles that can be cut in half again and again. 3. We know that Democritus was right to say that all matter was made up of atoms. So why did people ignore Democritus’ ...
Atomic Timeline
... The energy of each electron keeps it in motion around the nucleus Atoms must contain some sort of positive charge Atoms are mostly empty space ...
... The energy of each electron keeps it in motion around the nucleus Atoms must contain some sort of positive charge Atoms are mostly empty space ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... elements in which the elements are separated into groups based on a set of repeating properties. A periodic table allows you to easily compare the properties of one element (or a group of elements) to another element (or group of elements). Each horizontal row of the periodic table is called a perio ...
... elements in which the elements are separated into groups based on a set of repeating properties. A periodic table allows you to easily compare the properties of one element (or a group of elements) to another element (or group of elements). Each horizontal row of the periodic table is called a perio ...
Atomic Theory Powerpoint
... In 1913, the Danish scientist Niels Bohr proposed an improvement. He built on the concept that the mass of an atom is contained mostly in the nucleus. He also theorized that electrons move in definite orbits around the nucleus, much like planets circle the sun. These orbits, or energy levels, are lo ...
... In 1913, the Danish scientist Niels Bohr proposed an improvement. He built on the concept that the mass of an atom is contained mostly in the nucleus. He also theorized that electrons move in definite orbits around the nucleus, much like planets circle the sun. These orbits, or energy levels, are lo ...
Chemistry - Beachwood City Schools
... 4. List four physical states of matter. For each physical state, indicate whether the particles are in motion and whether they are close or far apart. 5. List one chemical and one physical property of the element chlorine. (You may use your textbook.) 6. Describe three observations that frequently a ...
... 4. List four physical states of matter. For each physical state, indicate whether the particles are in motion and whether they are close or far apart. 5. List one chemical and one physical property of the element chlorine. (You may use your textbook.) 6. Describe three observations that frequently a ...
File
... Daltons atomic theory was based on the following hypotheses : 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other ele ...
... Daltons atomic theory was based on the following hypotheses : 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other ele ...
Electron Configurations Guided Notes
... The chemical properties of atoms, ions, and molecules are related to the arrangement of ______________________ within them. Over time, the atomic model has evolved regarding where __________________________ are located. Democritus and Dalton: Atom is indivisible—no ___________________________. Thoms ...
... The chemical properties of atoms, ions, and molecules are related to the arrangement of ______________________ within them. Over time, the atomic model has evolved regarding where __________________________ are located. Democritus and Dalton: Atom is indivisible—no ___________________________. Thoms ...
Atom - Images
... (getting smaller) because the positive charge is greater than the smaller negative charges and pulls them in toward the nucleus. • More electrons than protons = radii increases (getting larger) because the electrons are farther away from the positive nucleus. • The Natural state of atoms has protons ...
... (getting smaller) because the positive charge is greater than the smaller negative charges and pulls them in toward the nucleus. • More electrons than protons = radii increases (getting larger) because the electrons are farther away from the positive nucleus. • The Natural state of atoms has protons ...
Atomic Structure Review/Learning Targets KEY
... Identify what determines an atoms identity. The protons identify the element. This number will never change. Explain how to determine what element an atom represents. Count the number protons or electrons to determine the atomic number. Explain what valence electrons are and how to identify them on ...
... Identify what determines an atoms identity. The protons identify the element. This number will never change. Explain how to determine what element an atom represents. Count the number protons or electrons to determine the atomic number. Explain what valence electrons are and how to identify them on ...
CHEMISTRY OLYMPICS 2nd 6 weeks What particles form the
... • A) that electrons orbit the nucleus • B) that atoms are made of positively and negatively charged particles • C) that most of an atom’s mass is concentrated in a relatively small portion of the atom’s entire volume • D) that all neutrons are located in the nucleus ...
... • A) that electrons orbit the nucleus • B) that atoms are made of positively and negatively charged particles • C) that most of an atom’s mass is concentrated in a relatively small portion of the atom’s entire volume • D) that all neutrons are located in the nucleus ...
200 Ways to Pass the Chemistry
... 97. Atoms are most stable when they have 8 valence electrons (an octet) and tend to form ions to obtain such a configuration of electrons. Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl It loses its 1 valence electron leaving 2 below it 98. Covalent ...
... 97. Atoms are most stable when they have 8 valence electrons (an octet) and tend to form ions to obtain such a configuration of electrons. Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl It loses its 1 valence electron leaving 2 below it 98. Covalent ...
History of the Atom
... atom by stating that the exact location of an electron cannot be stated; therefore, it is more accurate to view the electrons in regions called electron clouds; electron clouds are places where the electrons are likely to be found • Did extensive work on the Wave formula Schrodinger equation • Won ...
... atom by stating that the exact location of an electron cannot be stated; therefore, it is more accurate to view the electrons in regions called electron clouds; electron clouds are places where the electrons are likely to be found • Did extensive work on the Wave formula Schrodinger equation • Won ...
Chemistry 1- Final Exam Review
... e. N c. Bi ____ 58. Which of the following has the highest ionization energy? a. K d. N b. Ca e. O c. C ____ 59. For the element whose electron configuration is [Ne] 3s2 3p 3 , how many dots would the Lewis dot diagram have? a. 3 c. 8 b. 5 d. 13 ____ 60. Which of the following bonds is primarily cov ...
... e. N c. Bi ____ 58. Which of the following has the highest ionization energy? a. K d. N b. Ca e. O c. C ____ 59. For the element whose electron configuration is [Ne] 3s2 3p 3 , how many dots would the Lewis dot diagram have? a. 3 c. 8 b. 5 d. 13 ____ 60. Which of the following bonds is primarily cov ...
atomic mass number - Magoffin County Schools
... Because the energy required to maintain the orbit of the more complex sublevels is more than that of more simple orbits, a sublevel will not completely fill before the next higher one begins receiving electron. ...
... Because the energy required to maintain the orbit of the more complex sublevels is more than that of more simple orbits, a sublevel will not completely fill before the next higher one begins receiving electron. ...