Chapter 2 Review
... A.All matter is made up of atoms. B.Atoms are made up of smaller particles. C.Atoms are indestructible. D.All atoms of one element are exactly alike, but they are different from atoms of other elements. ...
... A.All matter is made up of atoms. B.Atoms are made up of smaller particles. C.Atoms are indestructible. D.All atoms of one element are exactly alike, but they are different from atoms of other elements. ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Elements, Orbitals, and Electron Configurations
... Questions about the fundamental nature of matter can be traced as far back as the Greek philosophers. • Aristotle believed that matter could be divided indefinitely. • Democritus argued that there was a limit. John Dalton proposed atomic theory in 1808. − The work atom literally means "uncuttable." ...
... Questions about the fundamental nature of matter can be traced as far back as the Greek philosophers. • Aristotle believed that matter could be divided indefinitely. • Democritus argued that there was a limit. John Dalton proposed atomic theory in 1808. − The work atom literally means "uncuttable." ...
PHY–309 L. Solutions for homework set # 10. Textbook question Q
... But the natural sources (ores, etc.) for many chemical elements provide mixtures of different isotopes, and since the isotopes of the same element have similar chemical properties, they don’t get separated when the element is refined from its ore or participates in chemical reactions. Although there ...
... But the natural sources (ores, etc.) for many chemical elements provide mixtures of different isotopes, and since the isotopes of the same element have similar chemical properties, they don’t get separated when the element is refined from its ore or participates in chemical reactions. Although there ...
File - Cynthia Campbell
... In printed tables, each element is usually listed with its element symbol and atomic number; many versions of the table also list the element's atomic mass and other information, such as its abbreviated electron configuration, electronegativity and most common valence numbers. As of 2010, the table ...
... In printed tables, each element is usually listed with its element symbol and atomic number; many versions of the table also list the element's atomic mass and other information, such as its abbreviated electron configuration, electronegativity and most common valence numbers. As of 2010, the table ...
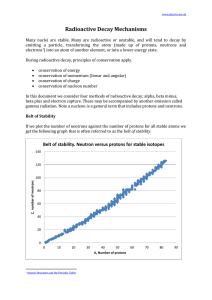
Radioactive Decay Mechanisms
... 2. for smaller atoms the ratio neutrons:protons is 1:1 3. for larger atoms the ratio of neutrons:protons approaches about 1.5:1 Since the strong nuclear force weakens significantly with distance, as the atom gets bigger. If the number protons to neutrons remained in the ratio of 1:1 for larger atoms ...
... 2. for smaller atoms the ratio neutrons:protons is 1:1 3. for larger atoms the ratio of neutrons:protons approaches about 1.5:1 Since the strong nuclear force weakens significantly with distance, as the atom gets bigger. If the number protons to neutrons remained in the ratio of 1:1 for larger atoms ...
In 1869, Russia`s Dmitri Mendeleev and Germany`s Lothar Meyer
... element - this can only happen in a ...
... element - this can only happen in a ...
Getting to Know: Periodic Table
... element do not have the same number of neutrons. For example, most atoms of the element carbon, C, have 6 neutrons in their nucleus. There are some atoms of carbon that have 7 or even 8 neutrons in their nucleus. Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. ...
... element do not have the same number of neutrons. For example, most atoms of the element carbon, C, have 6 neutrons in their nucleus. There are some atoms of carbon that have 7 or even 8 neutrons in their nucleus. Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. ...
Atom/Elements Study Guide
... Protons and neutrons so the charge of the nucleus is positive 3. The atom is composed mostly of empty space. 4. Where is most of the mass of the atom located? In the nucleus 5. How many electrons can exist in the first shell? The second? 2, 8, 8,18 6. Which two subatomic particles have approximatel ...
... Protons and neutrons so the charge of the nucleus is positive 3. The atom is composed mostly of empty space. 4. Where is most of the mass of the atom located? In the nucleus 5. How many electrons can exist in the first shell? The second? 2, 8, 8,18 6. Which two subatomic particles have approximatel ...
PS 2.2 - S2TEM Centers SC
... Introduction to the lesson: Isotopes have the same atomic number and hence nearly identical chemical behavior but different atomic masses. Most elements found in nature are mixtures of several isotopes; tin, for example, has 10 isotopes. In most cases, only stable isotopes of elements are found in n ...
... Introduction to the lesson: Isotopes have the same atomic number and hence nearly identical chemical behavior but different atomic masses. Most elements found in nature are mixtures of several isotopes; tin, for example, has 10 isotopes. In most cases, only stable isotopes of elements are found in n ...
Trends in the Periodic Table
... Name: _________________________________ Period: ____ Date: ___ / ___ / ___ ...
... Name: _________________________________ Period: ____ Date: ___ / ___ / ___ ...
Periodic Table Trends
... These particles have different properties Electrons are tiny, very light and have a negative charge ...
... These particles have different properties Electrons are tiny, very light and have a negative charge ...
atomic number.
... 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios YES! Called the Law of Definite Proportions 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new compounds; they are not created, destroyed, or changed into atoms of any other elements. Yes, except for nuclear reactions that can change at ...
... 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios YES! Called the Law of Definite Proportions 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new compounds; they are not created, destroyed, or changed into atoms of any other elements. Yes, except for nuclear reactions that can change at ...
Chemistry--Chapter 5: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... According to Dalton’s atomic theory, elements are composed of tiny particles called ________________(1). Atoms of each element are ________________(2) from the atoms of all other elements. Atoms of different elements can form ________________(3) by combining in whole-number ratios. Chemical reaction ...
... According to Dalton’s atomic theory, elements are composed of tiny particles called ________________(1). Atoms of each element are ________________(2) from the atoms of all other elements. Atoms of different elements can form ________________(3) by combining in whole-number ratios. Chemical reaction ...
atomic mass number - Magoffin County Schools
... The ELECTRON is the smallest of the subatomic particles. It takes 1834 electrons to have about the same mass as ONE proton! ...
... The ELECTRON is the smallest of the subatomic particles. It takes 1834 electrons to have about the same mass as ONE proton! ...
IPS Unit 2 Worksheet Packet
... ____ 11. An atom has a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large region in which scientists can predict where an electron is likely to be found. ____ 12. An atom is made of positively charged, pudding like material through which negatively charged particles are scattered. ____ 13. In a ...
... ____ 11. An atom has a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large region in which scientists can predict where an electron is likely to be found. ____ 12. An atom is made of positively charged, pudding like material through which negatively charged particles are scattered. ____ 13. In a ...
Parts of the Atom - Dalton Local Schools
... 14. What is true about the number of electrons and protons in an element? a. There is always twice the number of electrons than protons in the nucleus. b. The numbers of protons and electrons are always changing. c. The number of electrons in an atom always equals the number of protons in the nucle ...
... 14. What is true about the number of electrons and protons in an element? a. There is always twice the number of electrons than protons in the nucleus. b. The numbers of protons and electrons are always changing. c. The number of electrons in an atom always equals the number of protons in the nucle ...
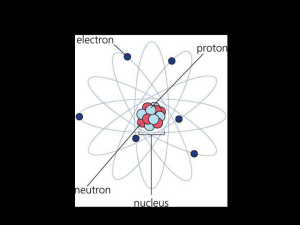
The atomic number tells how many protons Protons make an atom
... p+ and no, but some rare atoms will have only 196. They ALL have 79 p+. Most have 118no, but a few may have 117 no. ...
... p+ and no, but some rare atoms will have only 196. They ALL have 79 p+. Most have 118no, but a few may have 117 no. ...
03.03a Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Isotopes
... ATOMS: All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons: the number of protons determines the identity of the atom. For example, a carbon atom always has six protons. If it has seven protons, it’s nitrogen, not carbon. The number of protons is called the atomic number (Z). ISOTOPES: Alt ...
... ATOMS: All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons: the number of protons determines the identity of the atom. For example, a carbon atom always has six protons. If it has seven protons, it’s nitrogen, not carbon. The number of protons is called the atomic number (Z). ISOTOPES: Alt ...
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table Part 1: The Atomic Model
... gaps the for next elements 7 in a new thatrow, I and predicted filled restwould of thebetable discovered. like that. ...
... gaps the for next elements 7 in a new thatrow, I and predicted filled restwould of thebetable discovered. like that. ...
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table Part 1: The Atomic Model
... gaps the for next elements 7 in a new thatrow, I and predicted filled restwould of thebetable discovered. like that. ...
... gaps the for next elements 7 in a new thatrow, I and predicted filled restwould of thebetable discovered. like that. ...
The Modern Atomic Model
... • A Proton and a Neutron have about the same mass (1 amu). • Electrons mass are around 2,000 times less than protons and neutrons. • Protons and Neutrons contribute to most of the atom’s mass. ...
... • A Proton and a Neutron have about the same mass (1 amu). • Electrons mass are around 2,000 times less than protons and neutrons. • Protons and Neutrons contribute to most of the atom’s mass. ...
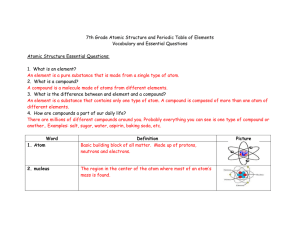
7th Grade Atomic Structure and Periodic Table of Elements
... A compound is a molecule made of atoms from different elements. 3. What is the difference between and element and a compound? An element is a substance that contains only one type of atom. A compound is composed of more than one atom of different elements. 4. How are compounds a part of our daily li ...
... A compound is a molecule made of atoms from different elements. 3. What is the difference between and element and a compound? An element is a substance that contains only one type of atom. A compound is composed of more than one atom of different elements. 4. How are compounds a part of our daily li ...
6.1 Atoms and Elements
... 2. Elements of the same column (group) of the periodic table have similar properties. 3. Atoms consist of protons and neutrons in the central core surrounded by electrons. Parts of the Atom Proton: a positively charged particle in an atom. Neutron: a particle in an atom that has no electrical charge ...
... 2. Elements of the same column (group) of the periodic table have similar properties. 3. Atoms consist of protons and neutrons in the central core surrounded by electrons. Parts of the Atom Proton: a positively charged particle in an atom. Neutron: a particle in an atom that has no electrical charge ...