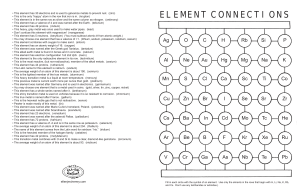
element connections
... • This element has 30 electrons and is used to galvanize metals to prevent rust. (zinc) • This is the only “happy” atom in the row that iron is in. (krypton) • This element is in the same row as silver and the same column as nitrogen. (antimony) • This element has a valence of 4 and was named after ...
... • This element has 30 electrons and is used to galvanize metals to prevent rust. (zinc) • This is the only “happy” atom in the row that iron is in. (krypton) • This element is in the same row as silver and the same column as nitrogen. (antimony) • This element has a valence of 4 and was named after ...
Subatomic Particles
... isotopes, they need an efficient way to specify the number of neutrons in any particular nucleus. The mass number of an atom is the sum of the numbers of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Given the mass number for a nucleus (and knowing the atomic number of that particular atom), you can determi ...
... isotopes, they need an efficient way to specify the number of neutrons in any particular nucleus. The mass number of an atom is the sum of the numbers of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Given the mass number for a nucleus (and knowing the atomic number of that particular atom), you can determi ...
presentation1-elements-atoms-and-isotopes
... How many electrons per shell? Each shell has a maximum number of electrons that it can hold. Electrons will fill the shells nearest the nucleus first. 1st shell holds a maximum of 2 electrons 2nd shell holds a maximum of 8 electrons ...
... How many electrons per shell? Each shell has a maximum number of electrons that it can hold. Electrons will fill the shells nearest the nucleus first. 1st shell holds a maximum of 2 electrons 2nd shell holds a maximum of 8 electrons ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... for elements known to date. The periodic table is base on the similarity of properties and reactivities exhibited by certain elements. Later, Henri Moseley ( England,1887-1915) established that each elements has a unique atomic number, which is how the current periodic table is organized. ...
... for elements known to date. The periodic table is base on the similarity of properties and reactivities exhibited by certain elements. Later, Henri Moseley ( England,1887-1915) established that each elements has a unique atomic number, which is how the current periodic table is organized. ...
Masses of Atoms
... Atomic Number ~ number of protons in the atom of an element Atomic Mass ~ number of neutrons AND number of protons Isotope ~ atoms of the same element, with different numbers of neutrons Carbon - 12 (6 protons, 6 neutrons) Carbon - 14 (6 protons, 8 neutrons) ...
... Atomic Number ~ number of protons in the atom of an element Atomic Mass ~ number of neutrons AND number of protons Isotope ~ atoms of the same element, with different numbers of neutrons Carbon - 12 (6 protons, 6 neutrons) Carbon - 14 (6 protons, 8 neutrons) ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... Finding the Number of Neutrons for an Atom • The protons and neutrons make up the mass of an atom. • If you know the protons (atomic number) then you can find the number of neutrons by subtracting the atomic mass from the # of protons (atomic number). atomic mass - # of protons = # of neutrons ...
... Finding the Number of Neutrons for an Atom • The protons and neutrons make up the mass of an atom. • If you know the protons (atomic number) then you can find the number of neutrons by subtracting the atomic mass from the # of protons (atomic number). atomic mass - # of protons = # of neutrons ...
1 TEST DATE:
... fewer____________________________ than will other atoms of the same element. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called ___________________________ . Hydrogen has three isotopes. A hydrogen atom may contain zero, one, or two___________________________ . Every atom of car ...
... fewer____________________________ than will other atoms of the same element. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called ___________________________ . Hydrogen has three isotopes. A hydrogen atom may contain zero, one, or two___________________________ . Every atom of car ...
Chemical Element
... Bang nucleosynthesis during the first 20 minutes of the universe[9] in a ratio of around 3:1 by mass (approximately 12:1 by number of atoms). Almost all other elements found in nature, including some further hydrogen and helium created since then, were made by various natural or (at times) artificia ...
... Bang nucleosynthesis during the first 20 minutes of the universe[9] in a ratio of around 3:1 by mass (approximately 12:1 by number of atoms). Almost all other elements found in nature, including some further hydrogen and helium created since then, were made by various natural or (at times) artificia ...
Word List
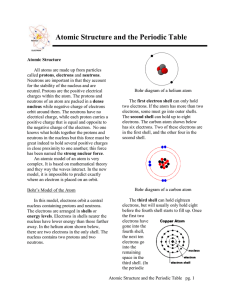
... 1.4 I can describe the charge and location of protons, neutrons, and electrons within the nucleus and shells of an atom. The periodic table is, in many ways, the world’s greatest cheat sheet. The periodic table lists all of the elements (simple substances that make up more complex materials) like go ...
... 1.4 I can describe the charge and location of protons, neutrons, and electrons within the nucleus and shells of an atom. The periodic table is, in many ways, the world’s greatest cheat sheet. The periodic table lists all of the elements (simple substances that make up more complex materials) like go ...
Matching - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... a. Protons, electrons, and neutrons are evenly distributed throughout the volume of the atom. b. The nucleus is made of protons, electrons, and neutrons. c. Electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy almost all the volume of the atom. d. The nucleus is made of electrons and protons. ___ ...
... a. Protons, electrons, and neutrons are evenly distributed throughout the volume of the atom. b. The nucleus is made of protons, electrons, and neutrons. c. Electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy almost all the volume of the atom. d. The nucleus is made of electrons and protons. ___ ...
Modern Physics
... • An atom is stable (not radioactive) if it is in the belt of stability • An atom is unstable (radioactive) if it is outside the belt of stability • All elements beyond number 83, Bismuth are unstable - WHY? ...
... • An atom is stable (not radioactive) if it is in the belt of stability • An atom is unstable (radioactive) if it is outside the belt of stability • All elements beyond number 83, Bismuth are unstable - WHY? ...
The History of the Periodic Table
... other workers had reported. For the rest of the 19th century, atomic masses were continually revised and improved and new elements were rapidly being discovered By 1817, it was recognized that some elements could be placed into groups, using their physical and chemical properties. Elements with clos ...
... other workers had reported. For the rest of the 19th century, atomic masses were continually revised and improved and new elements were rapidly being discovered By 1817, it was recognized that some elements could be placed into groups, using their physical and chemical properties. Elements with clos ...
1b Atomic Structure
... that is used today is called the periodic table. When a property is repeated within a regular interval, that property is said to be periodic. The periodic table consists of both rows and columns. The rows across the table are the periods. They a referred to as the first period second period and so o ...
... that is used today is called the periodic table. When a property is repeated within a regular interval, that property is said to be periodic. The periodic table consists of both rows and columns. The rows across the table are the periods. They a referred to as the first period second period and so o ...
atom - West Ada
... Each element has a unique symbol, based on its name. For some elements, only the first letter of the name is used such as oxygen (O), hydrogen (H) or nitrogen (N). Others use the first letter plus one other letter of the element’s name. The first letter is always capitalized and any other letter is ...
... Each element has a unique symbol, based on its name. For some elements, only the first letter of the name is used such as oxygen (O), hydrogen (H) or nitrogen (N). Others use the first letter plus one other letter of the element’s name. The first letter is always capitalized and any other letter is ...
What`s Inside an Element
... In this activity, students will learn about the elements in the periodic table and how to interpret the information for each element. Students will then choose an element and translate the information from the periodic table into a tri-fold model. The cover of the tri-fold would be a picture of the ...
... In this activity, students will learn about the elements in the periodic table and how to interpret the information for each element. Students will then choose an element and translate the information from the periodic table into a tri-fold model. The cover of the tri-fold would be a picture of the ...
Chapter 4, Lesson 2: The Periodic Table
... The atomic mass of an element is based on the mass of the protons, neutrons, and electrons of the atoms of that element. The mass of the proton and neutron are about the same, but the mass of the electron is much smaller (about 1/2000 the mass of the proton or neutron). The majority of the atomic ma ...
... The atomic mass of an element is based on the mass of the protons, neutrons, and electrons of the atoms of that element. The mass of the proton and neutron are about the same, but the mass of the electron is much smaller (about 1/2000 the mass of the proton or neutron). The majority of the atomic ma ...
Document
... holding the electron to the nucleus • The shells are designated by letters (K, L, M, N …) where K, the shell closest to the nucleus, has the largest binding energy, so the K electron is the most tightly bound • Maximum number of electrons in each shell: 2 in K shell, 8 in L shell … IAEA ...
... holding the electron to the nucleus • The shells are designated by letters (K, L, M, N …) where K, the shell closest to the nucleus, has the largest binding energy, so the K electron is the most tightly bound • Maximum number of electrons in each shell: 2 in K shell, 8 in L shell … IAEA ...
The Periodic Table of the Elements
... weighted according to the natural abundance of each isotope of that element. ...
... weighted according to the natural abundance of each isotope of that element. ...
Chapter 4, Lesson 2: The Periodic Table
... The atomic mass of an element is based on the mass of the protons, neutrons, and electrons of the atoms of that element. The mass of the proton and neutron are about the same, but the mass of the electron is much smaller (about 1/2000 the mass of the proton or neutron). The majority of the atomic ma ...
... The atomic mass of an element is based on the mass of the protons, neutrons, and electrons of the atoms of that element. The mass of the proton and neutron are about the same, but the mass of the electron is much smaller (about 1/2000 the mass of the proton or neutron). The majority of the atomic ma ...
Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table
... In the early 1800’s British scientist John Dalton proposed that each element is made up of tiny particles called atoms. Dalton stated that all of the atoms of a particular element are identical but are different from atoms of all other elements. Daltons theory also assumed that atoms could not be di ...
... In the early 1800’s British scientist John Dalton proposed that each element is made up of tiny particles called atoms. Dalton stated that all of the atoms of a particular element are identical but are different from atoms of all other elements. Daltons theory also assumed that atoms could not be di ...
1 | Page Chemistry Lecture #19: Atomic Number, Isotopes, and
... For now, ignore the 14.0067 (I’ll explain what this number is in another lecture). The number 7 is the atomic number of nitrogen. Thus, nitrogen has 7 protons in the nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of protons in the nucleus is equal to the number of electrons. ...
... For now, ignore the 14.0067 (I’ll explain what this number is in another lecture). The number 7 is the atomic number of nitrogen. Thus, nitrogen has 7 protons in the nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of protons in the nucleus is equal to the number of electrons. ...
Dynamic Earth Unit 2 lesson 3 Absolute Dating
... atom. It differs from a chemical reaction in several ways. • One difference is that chemical reactions do not change the mass of atoms, but nuclear reactions do so by a very small amount by changing the nucleus of an atom. • They can change the number of neutrons • They can change the number of prot ...
... atom. It differs from a chemical reaction in several ways. • One difference is that chemical reactions do not change the mass of atoms, but nuclear reactions do so by a very small amount by changing the nucleus of an atom. • They can change the number of neutrons • They can change the number of prot ...
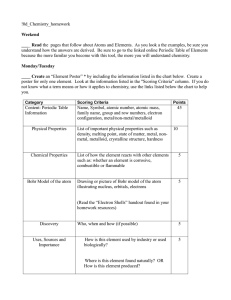
10_Chemistry homework
... Dalton theory described how atoms interacted to form compounds, but never even considered the possibility of subatomic particles. The first of the subatomic particles, the negatively-charged electron, was discovered by J. J. Thomson in 1899. Both Thomson and Ernst Rutherford contributed to the ident ...
... Dalton theory described how atoms interacted to form compounds, but never even considered the possibility of subatomic particles. The first of the subatomic particles, the negatively-charged electron, was discovered by J. J. Thomson in 1899. Both Thomson and Ernst Rutherford contributed to the ident ...
2.4 The Periodic Table
... and the percentage of each must be known. • The atomic weight is calculated as the sum of the masses of the individual isotopes for that element. Atomic weight = [(isotope abundance) × (isotope mass)] • The Greek symbol indicates summing of terms. ...
... and the percentage of each must be known. • The atomic weight is calculated as the sum of the masses of the individual isotopes for that element. Atomic weight = [(isotope abundance) × (isotope mass)] • The Greek symbol indicates summing of terms. ...