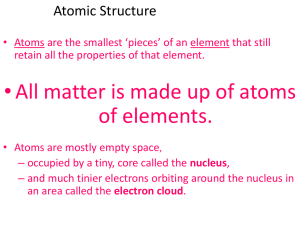
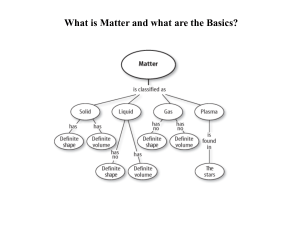
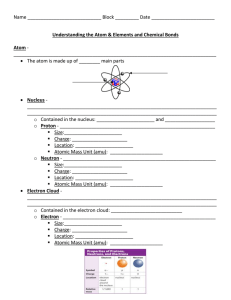
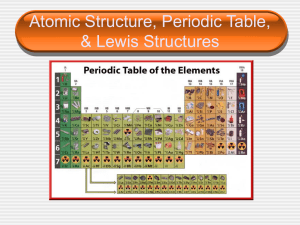
3-ELEMENTS AND THE ATOMIC MODEL. C4.8A Identify the
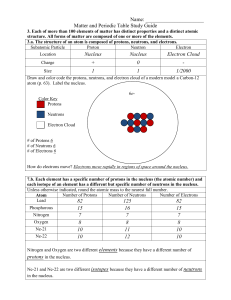
... C4.8A Identify the location, relative mass, and charge for electrons, protons, and neutrons. C4.8B Describe the atom as mostly empty space with an extremely small, dense nucleus consisting of the protons and neutrons and an electron cloud surrounding the nucleus. C4.8C Recognize that protons repel e ...
... C4.8A Identify the location, relative mass, and charge for electrons, protons, and neutrons. C4.8B Describe the atom as mostly empty space with an extremely small, dense nucleus consisting of the protons and neutrons and an electron cloud surrounding the nucleus. C4.8C Recognize that protons repel e ...
Quiz review
... Horizontal rows of the periodic table are called this. Vertical columns of the periodic table are called ‘groups’ or this. Which element in period 3 has 6 valence electrons? Which element in period 5 has only 1 electron in its 5s sublevel? Which element in period 3 has a full octet? What family of e ...
... Horizontal rows of the periodic table are called this. Vertical columns of the periodic table are called ‘groups’ or this. Which element in period 3 has 6 valence electrons? Which element in period 5 has only 1 electron in its 5s sublevel? Which element in period 3 has a full octet? What family of e ...
Atomic Structure - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... So, what’s up with all these isotopes anyway? In nature elements are not made up of atoms that are all exactly the same! Some will be heavier than others, even though they are still the same type of atom. C-12 and C-14 are both Carbon, with all the usual Carbon properties, but the C-14 has two more ...
... So, what’s up with all these isotopes anyway? In nature elements are not made up of atoms that are all exactly the same! Some will be heavier than others, even though they are still the same type of atom. C-12 and C-14 are both Carbon, with all the usual Carbon properties, but the C-14 has two more ...
element - Mrs. Phillips` Physical Science Webpage
... things together in a way that makes sense, so that like are with like – makes it easier to find things if you know where to look. • The periodic table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, as a way of classifying elements according to their properties. ...
... things together in a way that makes sense, so that like are with like – makes it easier to find things if you know where to look. • The periodic table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, as a way of classifying elements according to their properties. ...
Matter and the Periodic Table
... Groups: Also known as families, the 18 vertical rows The elements in each group have similar characteristics. ...
... Groups: Also known as families, the 18 vertical rows The elements in each group have similar characteristics. ...
Power point on the Periodic Table
... Vertical columns in the periodic table: group Numbered from 1 to 18 Elements in the same family (group) share similar physical and chemical properties The group also tells you the amount of valence electrons ...
... Vertical columns in the periodic table: group Numbered from 1 to 18 Elements in the same family (group) share similar physical and chemical properties The group also tells you the amount of valence electrons ...
Understanding the Atom GN
... When atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons they are called ____________________. Isotope – ________________________________________________________________________ Most elements have ______________________ isotopes. Mass Number - ________________________________________ ...
... When atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons they are called ____________________. Isotope – ________________________________________________________________________ Most elements have ______________________ isotopes. Mass Number - ________________________________________ ...
Ch. 6 Vocabulary
... • atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons ...
... • atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons ...
Periodic Table Vocab page 7
... Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. This number identifies the atom. Mass number: the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Mass number = protons + neutrons Valence #: The number of outermost electrons in an atom. Periodic Table: An arrangement of elem ...
... Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. This number identifies the atom. Mass number: the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Mass number = protons + neutrons Valence #: The number of outermost electrons in an atom. Periodic Table: An arrangement of elem ...
Periodic Table Quiz
... 11. Which element is in Period 4, Group 13? a) Na b) Al c) Ga d) K 12. How many electrons does Sulfur contain? a) 15 b) 16 c) 17 d) 18 13. Which elements below are ALL nonmetals? a) K, Ca, Sc b) Be, Br, Kr c) V, Cr, Mn d) Ne, Cl, Br ...
... 11. Which element is in Period 4, Group 13? a) Na b) Al c) Ga d) K 12. How many electrons does Sulfur contain? a) 15 b) 16 c) 17 d) 18 13. Which elements below are ALL nonmetals? a) K, Ca, Sc b) Be, Br, Kr c) V, Cr, Mn d) Ne, Cl, Br ...
Periodic Table
... Atoms of one element are converted into another element May involve protons, neutrons, or electrons Have large energy changes Reaction rates are not affected ...
... Atoms of one element are converted into another element May involve protons, neutrons, or electrons Have large energy changes Reaction rates are not affected ...
Matter and the Periodic Table Study Guide Answer Key
... Semimetals/Metalloids have properties of both metals and non-metals. 3.b. Compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 3.f. Use the periodic table to identify elements in simple compounds. Compound ...
... Semimetals/Metalloids have properties of both metals and non-metals. 3.b. Compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 3.f. Use the periodic table to identify elements in simple compounds. Compound ...
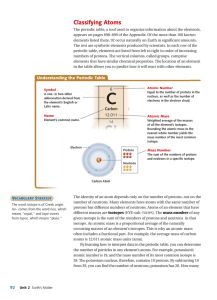
Classifying Atoms
... appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the periodic table, elements are listed from left to right in order of increasing num ...
... appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the periodic table, elements are listed from left to right in order of increasing num ...
Exam III Review
... Atomic Theory, History of the Atom, and Nuclear Chemistry 1. These 6 scientists were influential to atomic history. Draw and name their atomic models (if they had one) and what part of the atom they are credited with discovering. Include important experiments (such as the cathode ray tube, gold foil ...
... Atomic Theory, History of the Atom, and Nuclear Chemistry 1. These 6 scientists were influential to atomic history. Draw and name their atomic models (if they had one) and what part of the atom they are credited with discovering. Include important experiments (such as the cathode ray tube, gold foil ...
Atomic Structure Power Point
... is a form of an element that has the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass on the periodic table reflects the average mass of all of the known isotopes of an element. Each isotope may have different characteristics. ...
... is a form of an element that has the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass on the periodic table reflects the average mass of all of the known isotopes of an element. Each isotope may have different characteristics. ...
Chemistry lecture notes
... different number of neutrons). Isotopes behave the same chemically, because they are the same element. The only difference is that one is heavier than the other, because of the additional neutrons. For example, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are both isotopes of carbon. Carbon-12 has 6 neutrons; carbon ...
... different number of neutrons). Isotopes behave the same chemically, because they are the same element. The only difference is that one is heavier than the other, because of the additional neutrons. For example, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are both isotopes of carbon. Carbon-12 has 6 neutrons; carbon ...
Chapter 11 and 12-2 Review/Study Guide for Test
... 1. List the major discovery or accomplishment associated with of each of the following scientists: a. Democritus – named the atom, stated it was indivisible b. Dalton – atom is positively charged sphere - said atoms of different elements are different, atoms of the same element are the same c. Thoms ...
... 1. List the major discovery or accomplishment associated with of each of the following scientists: a. Democritus – named the atom, stated it was indivisible b. Dalton – atom is positively charged sphere - said atoms of different elements are different, atoms of the same element are the same c. Thoms ...
Chap 7: Around the Room Review
... 1. The central part of an atom is called the _____ 2. A proton has a _____ charge. 3. The atomic number tells us __________. 4. Nitrogen’s atomic number is 7. An isotope of nitrogen containing 7 neutrons would be nitrogen_____. 5. How does the size of a negative ion compare to the size of the atom t ...
... 1. The central part of an atom is called the _____ 2. A proton has a _____ charge. 3. The atomic number tells us __________. 4. Nitrogen’s atomic number is 7. An isotope of nitrogen containing 7 neutrons would be nitrogen_____. 5. How does the size of a negative ion compare to the size of the atom t ...
Atomic Structure/Electrons
... 6. An atom is defined as the smallest part of an element that: a. contains at least one proton, neutron and electron. b. retains the chemical identity of the element. c. can carry an electrical charge. d. is affected in a cathode ray tube. 7. The electrical charges in an atom are located: a. only in ...
... 6. An atom is defined as the smallest part of an element that: a. contains at least one proton, neutron and electron. b. retains the chemical identity of the element. c. can carry an electrical charge. d. is affected in a cathode ray tube. 7. The electrical charges in an atom are located: a. only in ...
Atomic Structure/Electrons
... 10. He discovered the electron and developed the “plum pudding” model. B 11. His five postulates make up atomic theory. A 12. His gold foil experiment led to his discovery of the nucleus. C 13. He developed the planetary model of the atom, which described the light spectrum. D 14. What is the shape ...
... 10. He discovered the electron and developed the “plum pudding” model. B 11. His five postulates make up atomic theory. A 12. His gold foil experiment led to his discovery of the nucleus. C 13. He developed the planetary model of the atom, which described the light spectrum. D 14. What is the shape ...
Vocabulary for Periodic Table
... 3) Nucleus: the central region of an atom where most of the atom’s mass is found in protons and neutrons. 4) Electron: a negatively charged particle located outside an atom’s nucleus. 5) Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. 6) Atomic mass number: the total number of proton ...
... 3) Nucleus: the central region of an atom where most of the atom’s mass is found in protons and neutrons. 4) Electron: a negatively charged particle located outside an atom’s nucleus. 5) Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. 6) Atomic mass number: the total number of proton ...
Atoms and Molecules
... • Elements are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom ...
... • Elements are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom ...
Introduction to the Periodic Table
... The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. ...
... The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. ...