ExamView - chemistry chapter 6 test.tst
... ____ 15. What is the element with the highest electronegativity value? a. helium c. calcium b. cesium d. fluorine ____ 16. Of the elements Fe, Hg, U, and Te, which is a representative element? a. Te c. Fe b. U d. Hg ____ 17. Which statement about noble gases is correct? a. They form compounds with v ...
... ____ 15. What is the element with the highest electronegativity value? a. helium c. calcium b. cesium d. fluorine ____ 16. Of the elements Fe, Hg, U, and Te, which is a representative element? a. Te c. Fe b. U d. Hg ____ 17. Which statement about noble gases is correct? a. They form compounds with v ...
Notes 3-2
... Ductile – a term used to describe a material that can be pulled out into a long wire. Conductor – a substance that transmits heat or electricity easily. Magnetic – a characteristic of metals in which it is attracted to magnets or can be made into a magnet. Chemical Properties of Metals Reactivity – ...
... Ductile – a term used to describe a material that can be pulled out into a long wire. Conductor – a substance that transmits heat or electricity easily. Magnetic – a characteristic of metals in which it is attracted to magnets or can be made into a magnet. Chemical Properties of Metals Reactivity – ...
Matter: Building Blocks of the Universe Chapter 5 Classification of
... the same number of valence electrons Family 1—Alkali—soft, silver, white, shiny—react or combine with other elements easily—never found alone in nature Family 2—Alkaline—Earth metals—very reactive Between Family 2 and 13 are the transition metals—these are the metals you are most familiar with ...
... the same number of valence electrons Family 1—Alkali—soft, silver, white, shiny—react or combine with other elements easily—never found alone in nature Family 2—Alkaline—Earth metals—very reactive Between Family 2 and 13 are the transition metals—these are the metals you are most familiar with ...
C3 The Periodic Table
... element . • Mendeleev ordered the elements based on their atomic weights and arranged them so there was a pattern. • He left GAPS because he predicted new elements would fit in, as they were discovered. He was right! ...
... element . • Mendeleev ordered the elements based on their atomic weights and arranged them so there was a pattern. • He left GAPS because he predicted new elements would fit in, as they were discovered. He was right! ...
Grouping of Elements in the Periodic Table
... 7. Which elements are most likely to lose electrons and form cations? a) transition metals b) noble gases c) elements in the last two periods d) metals in the first two periods 8. What is another name for semimetals? a) alkaline earth metals b) alkali metals c) transition metals d) metalloids 9. How ...
... 7. Which elements are most likely to lose electrons and form cations? a) transition metals b) noble gases c) elements in the last two periods d) metals in the first two periods 8. What is another name for semimetals? a) alkaline earth metals b) alkali metals c) transition metals d) metalloids 9. How ...
How is an Atoms Structure Related to its Position on the Periodic
... How is an Atoms Structure Related to its Position on the Periodic Table? http://goo.gl/Cf5SvM ...
... How is an Atoms Structure Related to its Position on the Periodic Table? http://goo.gl/Cf5SvM ...
How is the periodic table organized?
... highly reactive. This group includes the elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), and potassium (K). ...
... highly reactive. This group includes the elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), and potassium (K). ...
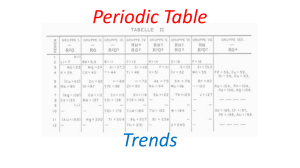
Periodic Table Trends
... added to the outermost shell. For example, sodium has one electron in shell 3, followed by magnesium which has two electrons in shell 3. ...
... added to the outermost shell. For example, sodium has one electron in shell 3, followed by magnesium which has two electrons in shell 3. ...
STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 8 TEST AND ELEMENT SYMBOLS
... ACROSS EACH PERIOD Diamond and soot are very different, yet both are natural forms of When a halogen reacts with a metal, what is formed? Periodic means? ...
... ACROSS EACH PERIOD Diamond and soot are very different, yet both are natural forms of When a halogen reacts with a metal, what is formed? Periodic means? ...
PERIODIC TRENDS PRACTICE QUIZ
... 8. Of the following elements, which one would have the smallest ionization energy? a. Neon b. Lithium c. Boron d. Nitrogen 9. As one moves from left to right within a period, the ionization energy of the elements tends to a. Increase. b. Decrease. c. Stay the Same. 10. The measure of the attraction ...
... 8. Of the following elements, which one would have the smallest ionization energy? a. Neon b. Lithium c. Boron d. Nitrogen 9. As one moves from left to right within a period, the ionization energy of the elements tends to a. Increase. b. Decrease. c. Stay the Same. 10. The measure of the attraction ...
PERIODIC TRENDS PRACTICE QUIZ
... 8. Of the following elements, which one would have the smallest ionization energy? a. Neon b. Lithium c. Boron d. Nitrogen 9. As one moves from left to right within a period, the ionization energy of the elements tends to a. Increase. b. Decrease. c. Stay the Same. 10. The measure of the attraction ...
... 8. Of the following elements, which one would have the smallest ionization energy? a. Neon b. Lithium c. Boron d. Nitrogen 9. As one moves from left to right within a period, the ionization energy of the elements tends to a. Increase. b. Decrease. c. Stay the Same. 10. The measure of the attraction ...
Chapter 5 - Geocities
... atomic number, elements with similar properties appear at regular intervals. Periodic table: Arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column, or group Lanthanides: 14 elements with atomic numbers from 58 to 71 Actinides: 1 ...
... atomic number, elements with similar properties appear at regular intervals. Periodic table: Arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column, or group Lanthanides: 14 elements with atomic numbers from 58 to 71 Actinides: 1 ...
The Periodic Table Notes
... Very good at stealing an electron from other compounds which make them great oxidizers Known as halogens because they react with metals to create salts At room temperature, fluorine and chlorine are gases, bromine is a liquid, and iodine is a solid ...
... Very good at stealing an electron from other compounds which make them great oxidizers Known as halogens because they react with metals to create salts At room temperature, fluorine and chlorine are gases, bromine is a liquid, and iodine is a solid ...
Unit 2 Overview
... Explain how elements are arranged in order of atomic number, usually in rows, so that elements with similar atomic structure (and hence similar chemical properties) appear in vertical columns. Define & describe how periods and groups are also used to organize the periodic table. Define atomic number ...
... Explain how elements are arranged in order of atomic number, usually in rows, so that elements with similar atomic structure (and hence similar chemical properties) appear in vertical columns. Define & describe how periods and groups are also used to organize the periodic table. Define atomic number ...
OBETA CHINONSO FAVOUR. 16/SCI14/018. GEOLOGY. CHM 221
... 3. Metals can be extracted from their metal ores by: I. Electrolysis of their molten chlorides for metals like sodium, magnesium, calcium and potassium. ii. Reduction of oxides using carbons for metals like zinc, iron, tin, lead and copper. iii. Roasting of the ore by heating alone for metals like m ...
... 3. Metals can be extracted from their metal ores by: I. Electrolysis of their molten chlorides for metals like sodium, magnesium, calcium and potassium. ii. Reduction of oxides using carbons for metals like zinc, iron, tin, lead and copper. iii. Roasting of the ore by heating alone for metals like m ...
Periodic Table
... They are also harder than group 1 metals and have higher melting points. How many valence e- do they have? Differences in their reactivity is how they react with water. They are good conductors of electricity. Mg can be as hard as steel when mixed with other metals but is extremely light. How could ...
... They are also harder than group 1 metals and have higher melting points. How many valence e- do they have? Differences in their reactivity is how they react with water. They are good conductors of electricity. Mg can be as hard as steel when mixed with other metals but is extremely light. How could ...
2- Periodic Trends
... • unique properties different from group 1 and 2 metals (make coloured compounds, speed up chemical reactions…) ...
... • unique properties different from group 1 and 2 metals (make coloured compounds, speed up chemical reactions…) ...
Periodic Table[1]
... to increasing Atomic Number When elements are arranged according to increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical ...
... to increasing Atomic Number When elements are arranged according to increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical ...
More Chemistry!
... Mendeleev grouped elements that had similar chemical and physical properties. Within these groups, he listed the elements top to bottom by their atomic masses; The elements also line up in rows across the table by bonding power; this is the number of chemical bonds an element can form by attachi ...
... Mendeleev grouped elements that had similar chemical and physical properties. Within these groups, he listed the elements top to bottom by their atomic masses; The elements also line up in rows across the table by bonding power; this is the number of chemical bonds an element can form by attachi ...
Chapter 22- Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... ii. Neutrons do not have an electrical charge. iii. Electrons have electrical charge of 1-. iv. Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom; electrons surround the nucleus. c. i. Protons and neutrons are made up of smaller particles called quarks. ii. Six quarks are known to exist; the sixth ...
... ii. Neutrons do not have an electrical charge. iii. Electrons have electrical charge of 1-. iv. Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom; electrons surround the nucleus. c. i. Protons and neutrons are made up of smaller particles called quarks. ii. Six quarks are known to exist; the sixth ...
Periodic Table cloze activity.
... atom, atomic number, column, element, gold, inert, Mendeleev, metals, nonmetals, periodic, properties, symbol All matter is composed of various elements. An _________________ is a form of matter that is composed of a single type of _________________. In 1869, Dmitri _________________ created the ___ ...
... atom, atomic number, column, element, gold, inert, Mendeleev, metals, nonmetals, periodic, properties, symbol All matter is composed of various elements. An _________________ is a form of matter that is composed of a single type of _________________. In 1869, Dmitri _________________ created the ___ ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... Noble Gases - Helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon are all noble gases. They are unique in that the outer shell of their atoms is full of electrons. This means they don't react much with other elements. They are often used in signs as they glow in bright colors when an electrical current i ...
... Noble Gases - Helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon are all noble gases. They are unique in that the outer shell of their atoms is full of electrons. This means they don't react much with other elements. They are often used in signs as they glow in bright colors when an electrical current i ...
2.5-The Periodic Table
... The periodic table is arranged into: - rows – called periods. The trend within a period is increasing atomic mass. - Columns – called groups or families. The trend within a group is the elements ...
... The periodic table is arranged into: - rows – called periods. The trend within a period is increasing atomic mass. - Columns – called groups or families. The trend within a group is the elements ...
Periodic Table Notes Odysseyware Vocabulary the average relative
... In the late ______________the sixty-three known elements had been classified according to their properties, but they hadn’t been organized. Then, he (Mendeleev) began to lay the cards out according to increasing ________________ ____________________. The Modern Periodic Table Notice that the element ...
... In the late ______________the sixty-three known elements had been classified according to their properties, but they hadn’t been organized. Then, he (Mendeleev) began to lay the cards out according to increasing ________________ ____________________. The Modern Periodic Table Notice that the element ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.















![Periodic Table[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003104404_1-7138f0e5d3dcc06b9019743402d7e0ca-300x300.png)