B.F. Skinner - Mr. Hernandez Course Website
... The first response following the interval is reinforced. Produces an overall low rate of responding Ex. I get one pellet of food every 5 minutes when I press the lever ...
... The first response following the interval is reinforced. Produces an overall low rate of responding Ex. I get one pellet of food every 5 minutes when I press the lever ...
Chapter 6 Learning Pwrpt
... Fixed-interval Schedule = in operant conditioning, a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response only after a specific time has elapsed. ...
... Fixed-interval Schedule = in operant conditioning, a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response only after a specific time has elapsed. ...
Chapter 5 Classical and Operant Conditioning
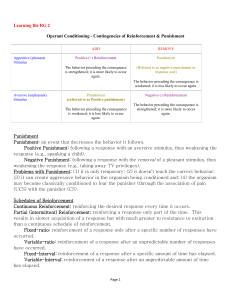
... • Punishment is more effective if it immediately and consistently follows a response ...
... • Punishment is more effective if it immediately and consistently follows a response ...
INTRODUCTION - Pro-Ed
... difficulties for Francine. What started as a few seemingly innocuous remarks by a teacher result in Francine actively avoiding oral reading. In trying to prevent the anxiety associated with oral reading, Francine has made it highly unlikely that she will become fluent in this very important skill. Whe ...
... difficulties for Francine. What started as a few seemingly innocuous remarks by a teacher result in Francine actively avoiding oral reading. In trying to prevent the anxiety associated with oral reading, Francine has made it highly unlikely that she will become fluent in this very important skill. Whe ...
Chapter 8 Review Guide Chapter 8 Review Guide
... Please keep in mind that "learning theory" is associated with the **Remember: During classical conditioning, the neutral psychological perspective of BEHAVIORISM. stimulus (NS) must be presented immediately BEFORE the UCS. After conditioning, the NS will become the conditioned Learning: a relatively ...
... Please keep in mind that "learning theory" is associated with the **Remember: During classical conditioning, the neutral psychological perspective of BEHAVIORISM. stimulus (NS) must be presented immediately BEFORE the UCS. After conditioning, the NS will become the conditioned Learning: a relatively ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... example of Classical Conditioning being applied to practical problems? • A) teaching a dog to wag its tail? • B) using methadone for heroine addicts • C) applying electric shock to depressed ...
... example of Classical Conditioning being applied to practical problems? • A) teaching a dog to wag its tail? • B) using methadone for heroine addicts • C) applying electric shock to depressed ...
Learning - Mr. Hunsaker`s Classes
... used in situation B. • 2. B—Getting a reward in this situation is likely to decrease TV watching. • 3. B—Grounding that is not contingent on a behavior to remove it is less effective than indefinite grounding. Indefinite grounding is punishment whereas grounding with contingencies is negative reinfo ...
... used in situation B. • 2. B—Getting a reward in this situation is likely to decrease TV watching. • 3. B—Grounding that is not contingent on a behavior to remove it is less effective than indefinite grounding. Indefinite grounding is punishment whereas grounding with contingencies is negative reinfo ...
Operant Conditioning - Educational Psychology
... Premack Principle: More desired activity is a positive reinforcer for a less desired activity ...
... Premack Principle: More desired activity is a positive reinforcer for a less desired activity ...
Classical conditioning
... Operant Conditioning behavior strengthened if followed by reinforcement OR diminished (lessened) if followed by punishment Person makes a choice to do something in order to get something or to avoid something Law of Effect Thorndike’s principle: rewarded behaviors are more likely to recur. ...
... Operant Conditioning behavior strengthened if followed by reinforcement OR diminished (lessened) if followed by punishment Person makes a choice to do something in order to get something or to avoid something Law of Effect Thorndike’s principle: rewarded behaviors are more likely to recur. ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... example of Classical Conditioning being applied to practical problems? • A) teaching a dog to wag its tail? • B) using methadone for heroine addicts • C) applying electric shock to depressed ...
... example of Classical Conditioning being applied to practical problems? • A) teaching a dog to wag its tail? • B) using methadone for heroine addicts • C) applying electric shock to depressed ...
Learning Review
... example of Classical Conditioning being applied to practical problems? • A) teaching a dog to wag its tail? • B) using methadone for heroine addicts • C) applying electric shock to depressed ...
... example of Classical Conditioning being applied to practical problems? • A) teaching a dog to wag its tail? • B) using methadone for heroine addicts • C) applying electric shock to depressed ...
The Process of Learning: Skinner`s Scientific Analysis of
... Education” the authors Frank Milhollan and Bill E. Forisha discuss in detail all the aspects of conditioning and operant conditioning. Here is the comprehensive summary of the concepts: Two classes of behavior: ‘Reflex’ or ‘involuntary’ or ‘respondent behavior’ or ‘elicited’ [Spontaneous] Voluntary’ ...
... Education” the authors Frank Milhollan and Bill E. Forisha discuss in detail all the aspects of conditioning and operant conditioning. Here is the comprehensive summary of the concepts: Two classes of behavior: ‘Reflex’ or ‘involuntary’ or ‘respondent behavior’ or ‘elicited’ [Spontaneous] Voluntary’ ...
Handout - personal.kent.edu
... Earning money to buy food, trying to go to bed at the same time each night Secondary reinforcers are originally neutral, but obtain reinforcing value when paired with primary reinforcers Æ money ...
... Earning money to buy food, trying to go to bed at the same time each night Secondary reinforcers are originally neutral, but obtain reinforcing value when paired with primary reinforcers Æ money ...
Ch. 8 - personal.kent.edu
... pairings with the UCS (Bell elicits Salivation) Conditioned Response (CR) a response elicited by some initially neutral stimulus, the (CS) and the (UCS). (Bell elicits Salivation) Experimental Extinction the weakening of the tendency of the CS to elicit the CR by unreinforced presentations of the CS ...
... pairings with the UCS (Bell elicits Salivation) Conditioned Response (CR) a response elicited by some initially neutral stimulus, the (CS) and the (UCS). (Bell elicits Salivation) Experimental Extinction the weakening of the tendency of the CS to elicit the CR by unreinforced presentations of the CS ...
Learning file RG 2
... Cognitive Map: a mental representation of the layout of one's environment. Latent Learning: learning that occurs, but is not apparent, until there is an incentive to demonstrate it Overjustification Effect: the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do. The person may now s ...
... Cognitive Map: a mental representation of the layout of one's environment. Latent Learning: learning that occurs, but is not apparent, until there is an incentive to demonstrate it Overjustification Effect: the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do. The person may now s ...
Unit 6 Study Guide
... 22. Because his football coach frequently yells at him for swearing, Antonio now becomes anxious when he's near his coach. The coach is a(n) ________ for Antonio's anxiety. A) negative reinforcer B) conditioned stimulus C) secondary reinforcer D) unconditioned stimulus E) primary reinforcer. ...
... 22. Because his football coach frequently yells at him for swearing, Antonio now becomes anxious when he's near his coach. The coach is a(n) ________ for Antonio's anxiety. A) negative reinforcer B) conditioned stimulus C) secondary reinforcer D) unconditioned stimulus E) primary reinforcer. ...
Exploring 9e - Forensic Consultation
... Positive does not mean “good” or “desirable” and negative does not mean “bad” or “undesirable.” ...
... Positive does not mean “good” or “desirable” and negative does not mean “bad” or “undesirable.” ...
Psychology – Dr. Saman – Lecture 2
... Change in the individual’s behavior or mental state is in response to something in the environment By controlling the environment, one’s learning can be controlled Only those behaviors we can directly observe are worthy of study ...
... Change in the individual’s behavior or mental state is in response to something in the environment By controlling the environment, one’s learning can be controlled Only those behaviors we can directly observe are worthy of study ...
chapter 8 study test - Mr. Siegerman`s AP Psychology Help Page
... 22. Last evening May-ling ate her first cheeseburger and french fries at an American fast-food restaurant. A few hours later she became ill. It can be expected that: A) May-ling will develop an aversion to the sight of a cheeseburger and french fries. B) May-ling will develop an aversion to the tas ...
... 22. Last evening May-ling ate her first cheeseburger and french fries at an American fast-food restaurant. A few hours later she became ill. It can be expected that: A) May-ling will develop an aversion to the sight of a cheeseburger and french fries. B) May-ling will develop an aversion to the tas ...
Homework Review
... punishment often has a generalized inhibiting effect on the punished individual (they stop doing ANY behavior at all) ...
... punishment often has a generalized inhibiting effect on the punished individual (they stop doing ANY behavior at all) ...
Classical v. Operant Conditioning
... – Sometimes referred to as instrumental conditioning. – Is a method of learning that occurs through rewards and punishments for behavior. – Through operant conditioning, an association is made between a behavior and a consequence for that behavior. • Operant conditioning was coined by behaviorist B. ...
... – Sometimes referred to as instrumental conditioning. – Is a method of learning that occurs through rewards and punishments for behavior. – Through operant conditioning, an association is made between a behavior and a consequence for that behavior. • Operant conditioning was coined by behaviorist B. ...
Operant Conditioning The basic learning process that involves
... • This strategy requires close monitoring of the individual to ensure that a positive reinforcer is delivered only after the behavior has not occurred. For example, reinforce sales clerks for checking identification when people buy alcohol and cigarettes, instead of punishing them when they don’t. ...
... • This strategy requires close monitoring of the individual to ensure that a positive reinforcer is delivered only after the behavior has not occurred. For example, reinforce sales clerks for checking identification when people buy alcohol and cigarettes, instead of punishing them when they don’t. ...
Operant conditioning
... settings when we encounter punishing consequences from actions such as reaching into a fire; in that case, operant conditioning helps us to avoid dangers. Punishment is effective when we try to artificially create punishing consequences for other’s choices; these work best when consequences happen ...
... settings when we encounter punishing consequences from actions such as reaching into a fire; in that case, operant conditioning helps us to avoid dangers. Punishment is effective when we try to artificially create punishing consequences for other’s choices; these work best when consequences happen ...
Learning and Conditioning
... A. Thorndike’s Law of Effect: an animal is more likely to repeat a behavior if it led to favorable consequences even if it doesn’t understand why. ...
... A. Thorndike’s Law of Effect: an animal is more likely to repeat a behavior if it led to favorable consequences even if it doesn’t understand why. ...