Physical Science 1st Semester final Review
... 35.A material that is malleable and conducts electricity well is most likely a __________________________________. ...
... 35.A material that is malleable and conducts electricity well is most likely a __________________________________. ...
03 Atoms – Nuclides
... a positively charged alpha particle (α), which is the same as a helium nuclei consisting of two neutrons and two protons a negatively charged beta minus particle (β-), which is the same as an electron a positively charged beta plus particle (β+), which is the same as a positron, a particle of equal ...
... a positively charged alpha particle (α), which is the same as a helium nuclei consisting of two neutrons and two protons a negatively charged beta minus particle (β-), which is the same as an electron a positively charged beta plus particle (β+), which is the same as a positron, a particle of equal ...
8.1 Atoms and Their Parts Assignment
... Electrons are negatively charged and are located in shells or orbits spinning around the nucleus. The number of protons and electrons are usually equal. This equality is important so that the atom as a whole is neither positively nor negatively charged. It is said to be neutral. Electrons have nearl ...
... Electrons are negatively charged and are located in shells or orbits spinning around the nucleus. The number of protons and electrons are usually equal. This equality is important so that the atom as a whole is neither positively nor negatively charged. It is said to be neutral. Electrons have nearl ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Polyatomic ions – ______________________________________________________ 1. Same as writing formulas for binary ionic compounds (see above) but use the charge of the cation and the polyatomic anion. 2. You may need to use parentheses to prevent confusion! Example: Barium phosphate ...
... Polyatomic ions – ______________________________________________________ 1. Same as writing formulas for binary ionic compounds (see above) but use the charge of the cation and the polyatomic anion. 2. You may need to use parentheses to prevent confusion! Example: Barium phosphate ...
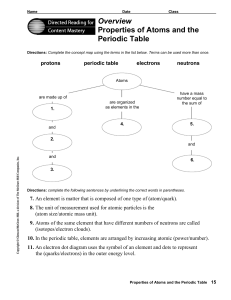
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. Terms can be used more than once. ...
... Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. Terms can be used more than once. ...
Document
... 38) Elements that are shiny conductive solids at room temperature are likely to be classified as which of the following? a) metals b) nonmetals c) inert gases ...
... 38) Elements that are shiny conductive solids at room temperature are likely to be classified as which of the following? a) metals b) nonmetals c) inert gases ...
The Periodic Table HL Page 1 of 3 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... 3. Mendeleev: Arranged the elements in order of increasing weight. Defn: Mendeleev’s Periodic Law: When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic weight, the properties of the elements recur periodically, i.e. the properties displayed by the element are repeated at regular intervals in oth ...
... 3. Mendeleev: Arranged the elements in order of increasing weight. Defn: Mendeleev’s Periodic Law: When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic weight, the properties of the elements recur periodically, i.e. the properties displayed by the element are repeated at regular intervals in oth ...
Atomic Structure - s3.amazonaws.com
... The smallest part of an element that still has the element’s properties ◦ Remember that elements are on the Periodic Table and are represented by a capital letter or a capital letter and lower case letter ...
... The smallest part of an element that still has the element’s properties ◦ Remember that elements are on the Periodic Table and are represented by a capital letter or a capital letter and lower case letter ...
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. Terms can be used more than once. ...
... Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. Terms can be used more than once. ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... may not all have the same _________ (due to differences in nuclear structure), any natural sample of the element will have a definite __________________that is characteristic of that element as compared to any other element. ...
... may not all have the same _________ (due to differences in nuclear structure), any natural sample of the element will have a definite __________________that is characteristic of that element as compared to any other element. ...
COS 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3
... atoms of same element do but has a different number of neutrons. Some are more common than others. If you know the atomic number and mass number of an atom, you can calculate the number of neutrons it has. ...
... atoms of same element do but has a different number of neutrons. Some are more common than others. If you know the atomic number and mass number of an atom, you can calculate the number of neutrons it has. ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... Using the periodic table on page 10 of this study guide, answer the following questions: 1. Which element stands alone in its family? _______________ 2. Which element has a larger atomic radius O or Ca? _____________ 3. Which element has a larger atomic radius Ca or Ba? _____________ 4. Which elemen ...
... Using the periodic table on page 10 of this study guide, answer the following questions: 1. Which element stands alone in its family? _______________ 2. Which element has a larger atomic radius O or Ca? _____________ 3. Which element has a larger atomic radius Ca or Ba? _____________ 4. Which elemen ...
GOB 3ed Chapter 2 part 1
... •An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by a chemical reaction. •Each element is identified by a one- or two-letter symbol. •Elements are arranged in the periodic table. •The position of an element in the periodic table tells us much about its chemical prop ...
... •An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by a chemical reaction. •Each element is identified by a one- or two-letter symbol. •Elements are arranged in the periodic table. •The position of an element in the periodic table tells us much about its chemical prop ...
I. The Atomic Concept:
... a. Natural radioactivity: ______________________________________________________________ ...
... a. Natural radioactivity: ______________________________________________________________ ...
Name______________________ Making - Science
... one neutron in its nucleus is called Deuterium. Deuterium is not radioactive. Water made from deuterium is called heavy water because the extra neutron makes it heavier. It is used in nuclear reactors. The third isotope of hydrogen is known as Tritium. It has one proton and two neutrons in its nucle ...
... one neutron in its nucleus is called Deuterium. Deuterium is not radioactive. Water made from deuterium is called heavy water because the extra neutron makes it heavier. It is used in nuclear reactors. The third isotope of hydrogen is known as Tritium. It has one proton and two neutrons in its nucle ...
PowerPoint - Models of the Atom
... 1. The Atomic Number of an atom = number of protons in the nucleus. 2. The Atomic Mass of an atom = number of Protons + Neutrons in the nucleus 3. The number of Protons = Number of Electrons. 4. Electrons orbit the nucleus in shells. 5. Each shell can only carry a set number of electrons. ...
... 1. The Atomic Number of an atom = number of protons in the nucleus. 2. The Atomic Mass of an atom = number of Protons + Neutrons in the nucleus 3. The number of Protons = Number of Electrons. 4. Electrons orbit the nucleus in shells. 5. Each shell can only carry a set number of electrons. ...
protons and neutrons
... Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons Electrons have so little mass that a ...
... Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons Electrons have so little mass that a ...
Average Atomic Mass
... particles called atoms. (atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical and physical properties of that element.) 2. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. 3. Atoms canno ...
... particles called atoms. (atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical and physical properties of that element.) 2. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. 3. Atoms canno ...
Atomic Model Power Point
... retains its identity in a chemical reaction. Democritus believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible. Dalton’s atomic theory states that ...
... retains its identity in a chemical reaction. Democritus believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible. Dalton’s atomic theory states that ...
Atomic History - Wylie High School Advanced Chemistry
... Look at any glowing neon sign and you are looking at the modern descendants of the cathode ray tube. Do atoms have parts? J.J. Thomson suggested that they do. He advanced the idea that cathode rays are really streams of very small pieces of atoms. Three experiments led him to this. Thomson built a c ...
... Look at any glowing neon sign and you are looking at the modern descendants of the cathode ray tube. Do atoms have parts? J.J. Thomson suggested that they do. He advanced the idea that cathode rays are really streams of very small pieces of atoms. Three experiments led him to this. Thomson built a c ...
Chemistry Study Guide What is matter made of? Matter is anything
... Elements are unique, pure substances. Elements and the Periodic Table Elements are arranged in order of their atomic number. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element. Every element has its own atomic number. The periodic table has horizontal ...
... Elements are unique, pure substances. Elements and the Periodic Table Elements are arranged in order of their atomic number. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element. Every element has its own atomic number. The periodic table has horizontal ...
Ch:2
... nucleus. Must be equivalent to the number of electrons around the atom’s nucleus. Mass Number (A): The sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in an atom’s nucleus. Isotope: Atoms with identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers (due to differing number of neutrons). ...
... nucleus. Must be equivalent to the number of electrons around the atom’s nucleus. Mass Number (A): The sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in an atom’s nucleus. Isotope: Atoms with identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers (due to differing number of neutrons). ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical combination of two or more substances on which the identities are retained Nonmetal – is a chemical element that mostly lacks metallic attributes ...
... Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical combination of two or more substances on which the identities are retained Nonmetal – is a chemical element that mostly lacks metallic attributes ...
Neptunium
.png?width=300)
Neptunium is a chemical element with symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it being named after Neptune, the next planet beyond Uranus. A neptunium atom has 93 protons and 93 electrons, of which seven are valence electrons. Neptunium metal is silvery and tarnishes when exposed to air. The element occurs in three allotropic forms and it normally exhibits five oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +7. It is radioactive, pyrophoric, and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of neptunium dangerous.Although many false claims of its discovery were made over the years, the element was first synthesized by Edwin McMillan and Philip H. Abelson at the Berkeley Radiation Laboratory in 1940. Since then, most neptunium has been and still is produced by neutron irradiation of uranium in nuclear reactors. The vast majority is generated as a by-product in conventional nuclear power reactors. While neptunium itself has no commercial uses at present, it is widely used as a precursor for the formation of plutonium-238, used in radioisotope thermal generators. Neptunium has also been used in detectors of high-energy neutrons.The most stable isotope of neptunium, neptunium-237, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production. It, and the isotope neptunium-239, are also found in trace amounts in uranium ores due to neutron capture reactions and beta decay.