Reporting Category 2: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry
... Nuclei often emit gamma rays along with alpha or beta particles. Gamma radiation differs from other types of electromagnetic radiation, such as visible light and radio waves, because it has much higher energy and because it is emitted by the nucleus. The symbol for a gamma ray is the Greek letter ga ...
... Nuclei often emit gamma rays along with alpha or beta particles. Gamma radiation differs from other types of electromagnetic radiation, such as visible light and radio waves, because it has much higher energy and because it is emitted by the nucleus. The symbol for a gamma ray is the Greek letter ga ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical combination of two or more substances on which the identities are retained Nonmetal – is a chemical element that mostly lacks metallic attributes ...
... Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical combination of two or more substances on which the identities are retained Nonmetal – is a chemical element that mostly lacks metallic attributes ...
PHY–309 L. Solutions for homework set # 10. Textbook question Q
... This wikipedia page shows a diagram of a color CRT tube. In any CRT tube — a TV, a monitor, an oscilloscope, or an X-ray tube — a beam of electrons hits the anode (a screen, or just a piece of metal) at high speed. When the atoms in the anode are hit by fast electrons, sometimes the inner electrons ...
... This wikipedia page shows a diagram of a color CRT tube. In any CRT tube — a TV, a monitor, an oscilloscope, or an X-ray tube — a beam of electrons hits the anode (a screen, or just a piece of metal) at high speed. When the atoms in the anode are hit by fast electrons, sometimes the inner electrons ...
Chemistry: Nuclear Reactions Guided Inquiry + n → + + 3 n +
... Nuclear reactions are reactions that affect the nucleus of an atom. In nature, unstable nuclei undergo nuclear reactions to form more stable nuclei. Stable nuclei can also undergo nuclear reactions if ...
... Nuclear reactions are reactions that affect the nucleus of an atom. In nature, unstable nuclei undergo nuclear reactions to form more stable nuclei. Stable nuclei can also undergo nuclear reactions if ...
UC Irvine FOCUS! 5 E Lesson Plan Title: Marble Isotope Lab Grade
... Background Info: Every atom of the same element has the same number of protons. Different atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons. Because the protons and neutrons make up the mass of the atom, different atoms of the same element can have different masses! These are called i ...
... Background Info: Every atom of the same element has the same number of protons. Different atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons. Because the protons and neutrons make up the mass of the atom, different atoms of the same element can have different masses! These are called i ...
Elements and Atoms
... The reason different elements have different properties is because the atoms that make up different elements have different numbers of tiny particles that make them up. The particles that make up atoms are called subatomic particles. There are three types of subatomic particles: 1. protons (positive ...
... The reason different elements have different properties is because the atoms that make up different elements have different numbers of tiny particles that make them up. The particles that make up atoms are called subatomic particles. There are three types of subatomic particles: 1. protons (positive ...
Chemistry Review Answers
... Groups in the Periodic Table- The elements are arranged in the sequence of their increasing atomic numbers into the periodic table, which is arranged in rows and columns, so that elements with similar chemical properties are in the same vertical column. Families- A group or family is a vertical colu ...
... Groups in the Periodic Table- The elements are arranged in the sequence of their increasing atomic numbers into the periodic table, which is arranged in rows and columns, so that elements with similar chemical properties are in the same vertical column. Families- A group or family is a vertical colu ...
Lecture4
... to refer to the subatomic particles themselves. This phenomenon is observed in the heavy elements, like uranium, and unstable isotopes, like carbon-14. For a better understanding of radioactivity, a review of atomic structure is necessary. Atoms are made up of a dense positive core called a nucleus ...
... to refer to the subatomic particles themselves. This phenomenon is observed in the heavy elements, like uranium, and unstable isotopes, like carbon-14. For a better understanding of radioactivity, a review of atomic structure is necessary. Atoms are made up of a dense positive core called a nucleus ...
Radioactivity
... to refer to the subatomic particles themselves. This phenomenon is observed in the heavy elements, like uranium, and unstable isotopes, like carbon-14. For a better understanding of radioactivity, a review of atomic structure is necessary. Atoms are made up of a dense positive core called a nucleus ...
... to refer to the subatomic particles themselves. This phenomenon is observed in the heavy elements, like uranium, and unstable isotopes, like carbon-14. For a better understanding of radioactivity, a review of atomic structure is necessary. Atoms are made up of a dense positive core called a nucleus ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... Since an element has a neutral charge, the atomic number must also represent the number of electrons in a neutral element - Elements have the ability to lose or gain electrons in order to bond with other elements to form molecules. - An element with an imbalance of protons to electrons is called an ...
... Since an element has a neutral charge, the atomic number must also represent the number of electrons in a neutral element - Elements have the ability to lose or gain electrons in order to bond with other elements to form molecules. - An element with an imbalance of protons to electrons is called an ...
25 NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY NOTES __ /__ pts
... ________ 18. Gamma radiation is high-energy electromagnetic radiation. ________ 19. ...
... ________ 18. Gamma radiation is high-energy electromagnetic radiation. ________ 19. ...
UNIT 1 EXAM REVIEW Scientific Method What are the steps in the
... 14. How can you identify the following? Neutral atom, isotope, ion. Neutral atoms have the same number of protons and electrons. Isotopes have a different number of neutrons than protons. Ions have more or less electrons than protons. ...
... 14. How can you identify the following? Neutral atom, isotope, ion. Neutral atoms have the same number of protons and electrons. Isotopes have a different number of neutrons than protons. Ions have more or less electrons than protons. ...
Notes: Structure of matter
... What are the 2 main areas of an atom? What comprises most of an atom's mass? What comprises most of the atom's volume? List the 3 parts to an atom and their electrical property or charge. ...
... What are the 2 main areas of an atom? What comprises most of an atom's mass? What comprises most of the atom's volume? List the 3 parts to an atom and their electrical property or charge. ...
File - Johnson
... • Accidentally discovered that uranium is radioactive • Radioactivity: the spontaneous emission of radiation from an element • Marie and Pierre Curie isolated two other radioactive elements: radium and polonium ...
... • Accidentally discovered that uranium is radioactive • Radioactivity: the spontaneous emission of radiation from an element • Marie and Pierre Curie isolated two other radioactive elements: radium and polonium ...
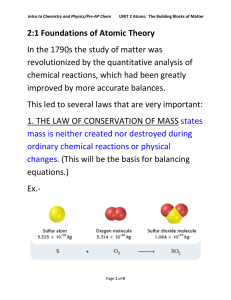
2:1 Foundations of Atomic Theory In the 1790s the study of matter
... The identification of an isotope requires knowing both the name and atomic number of the element and the mass of the isotope. The MASS NUMBER is the total number of protons and neutrons that make up the nucleus of an isotope. The three isotopes of hydrogen mentioned above have mass numbers of 1, 2 a ...
... The identification of an isotope requires knowing both the name and atomic number of the element and the mass of the isotope. The MASS NUMBER is the total number of protons and neutrons that make up the nucleus of an isotope. The three isotopes of hydrogen mentioned above have mass numbers of 1, 2 a ...
Day 2 – Worksheet Atoms and The Periodic Table
... Atoms and The Periodic Table Worksheet 1. Define chemistry. ...
... Atoms and The Periodic Table Worksheet 1. Define chemistry. ...
Isotopes Models
... called Deuterium. Deuterium is not radioactive. Water made from deuterium is called heavy water because the extra neutron makes it heavier. It is used in nuclear reactors. The third isotope of hydrogen is known as Tritium. It has one proton and two neutrons in its nucleus. It is radioactive. It is f ...
... called Deuterium. Deuterium is not radioactive. Water made from deuterium is called heavy water because the extra neutron makes it heavier. It is used in nuclear reactors. The third isotope of hydrogen is known as Tritium. It has one proton and two neutrons in its nucleus. It is radioactive. It is f ...
The Atom - TeacherWeb
... Because protons and neutrons are much larger than electrons, they are the only 2 particles that impact the mass of the atom. ...
... Because protons and neutrons are much larger than electrons, they are the only 2 particles that impact the mass of the atom. ...
Atomic Mass
... It was quite the most incredible event that has ever happened to me in my life. It was almost as incredible as if you fired a 15-inch shell at a piece of tissue paper and it came back and hit you. On consideration, I realized that this scattering backward must be the result of a single collision, a ...
... It was quite the most incredible event that has ever happened to me in my life. It was almost as incredible as if you fired a 15-inch shell at a piece of tissue paper and it came back and hit you. On consideration, I realized that this scattering backward must be the result of a single collision, a ...
Atomic Structure Guided Notes
... The isotopes of an element are virtually identical in their _______________________ reactions because they have the same number of _______________________ and the same number of _______________________. The uncharged _______________________ make little difference to _______________________ propertie ...
... The isotopes of an element are virtually identical in their _______________________ reactions because they have the same number of _______________________ and the same number of _______________________. The uncharged _______________________ make little difference to _______________________ propertie ...
The Periodic Table, Atomic Structure, Isotopes, Ions and Nomenclature
... atom has one proton and one electron, but is only ¼th the mass of a helium atom which has two electrons and two protons. • If all of the mass of an atom comes from its sub-atomic particles, how do we explain the unaccounted for mass? • The answer is neutrons, particles that are equal in mass to prot ...
... atom has one proton and one electron, but is only ¼th the mass of a helium atom which has two electrons and two protons. • If all of the mass of an atom comes from its sub-atomic particles, how do we explain the unaccounted for mass? • The answer is neutrons, particles that are equal in mass to prot ...
CHAPTER 4: ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
... atom: smallest identifiable unit of an element – All matter is made up of atoms. → The properties of specific atoms determine the properties of matter with those atoms. There are currently 91 naturally occurring elements and 20 man-made elements. 4.2 Indivisible: The Atomic Theory Greek philosophers ...
... atom: smallest identifiable unit of an element – All matter is made up of atoms. → The properties of specific atoms determine the properties of matter with those atoms. There are currently 91 naturally occurring elements and 20 man-made elements. 4.2 Indivisible: The Atomic Theory Greek philosophers ...
Name: Midterm Review (Part II) Fill in the blanks (Chapter 6.1 – 6.3
... Atoms of the same kind that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Atomic number = mass number. When an iron nail , its mass stays the same. ...
... Atoms of the same kind that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Atomic number = mass number. When an iron nail , its mass stays the same. ...
All About Isotopes
... All About Isotopes The atomic number of any atom (element) is a whole number and represents the number of protons in the atom, but that’s not true of atomic mass which is not a whole number. Since atomic mass is the number of the protons plus neutrons in the nucleus does that mean the nucleus of ato ...
... All About Isotopes The atomic number of any atom (element) is a whole number and represents the number of protons in the atom, but that’s not true of atomic mass which is not a whole number. Since atomic mass is the number of the protons plus neutrons in the nucleus does that mean the nucleus of ato ...
study guide for atoms/periodic table quiz
... table—just know how to read it. You will need to know that elements in a family have similar properties. You will not need to memorize the family names or tell me specifics about different families, but you will need to be able to tell me if an element is likely to be reactive, based on where its fa ...
... table—just know how to read it. You will need to know that elements in a family have similar properties. You will not need to memorize the family names or tell me specifics about different families, but you will need to be able to tell me if an element is likely to be reactive, based on where its fa ...
Neptunium
.png?width=300)
Neptunium is a chemical element with symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it being named after Neptune, the next planet beyond Uranus. A neptunium atom has 93 protons and 93 electrons, of which seven are valence electrons. Neptunium metal is silvery and tarnishes when exposed to air. The element occurs in three allotropic forms and it normally exhibits five oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +7. It is radioactive, pyrophoric, and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of neptunium dangerous.Although many false claims of its discovery were made over the years, the element was first synthesized by Edwin McMillan and Philip H. Abelson at the Berkeley Radiation Laboratory in 1940. Since then, most neptunium has been and still is produced by neutron irradiation of uranium in nuclear reactors. The vast majority is generated as a by-product in conventional nuclear power reactors. While neptunium itself has no commercial uses at present, it is widely used as a precursor for the formation of plutonium-238, used in radioisotope thermal generators. Neptunium has also been used in detectors of high-energy neutrons.The most stable isotope of neptunium, neptunium-237, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production. It, and the isotope neptunium-239, are also found in trace amounts in uranium ores due to neutron capture reactions and beta decay.