chapter 4: chemical foundations
... J.J. Thomson was given credit for discovering electron although evidence had accumulated for 20 years before his research group’s determination of the electron’s charge and mass. Eugen Goldstein (late 1880s) – carried out experiments on canal rays and found they consisted of positively charged subat ...
... J.J. Thomson was given credit for discovering electron although evidence had accumulated for 20 years before his research group’s determination of the electron’s charge and mass. Eugen Goldstein (late 1880s) – carried out experiments on canal rays and found they consisted of positively charged subat ...
Atomic Number
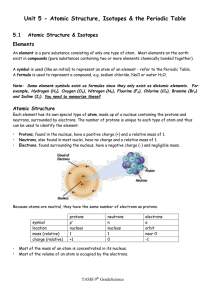
... • Atoms are the building blocks of all materials • An atom is made of 3 parts: – Protons and Neutrons are in the nucleus (center) – Electrons orbit around the nucleus ...
... • Atoms are the building blocks of all materials • An atom is made of 3 parts: – Protons and Neutrons are in the nucleus (center) – Electrons orbit around the nucleus ...
File
... or share electrons so as to have eight electrons in their outer electron shell. Atoms gain or lose electrons so that they have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas. Some metal atoms, depending on the nature of the chemical reaction, can form stable ions with more than one charge. Fo ...
... or share electrons so as to have eight electrons in their outer electron shell. Atoms gain or lose electrons so that they have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas. Some metal atoms, depending on the nature of the chemical reaction, can form stable ions with more than one charge. Fo ...
Powerpoint - Tuskegee University
... Atom and Current Periodic Table In 1913 a young English scientist, Henry Moseley, re-arranged elements based on atomic number instead of atomic mass, which is the current periodic table. Elements in each group (vertical column) have similar properties because they have the same number of valenc ...
... Atom and Current Periodic Table In 1913 a young English scientist, Henry Moseley, re-arranged elements based on atomic number instead of atomic mass, which is the current periodic table. Elements in each group (vertical column) have similar properties because they have the same number of valenc ...
Module 3 - Tuskegee University
... Atom and Current Periodic Table In 1913 a young English scientist, Henry Moseley, re-arranged elements based on atomic number instead of atomic mass, which is the current periodic table. Elements in each group (vertical column) have similar properties because they have the same number of valenc ...
... Atom and Current Periodic Table In 1913 a young English scientist, Henry Moseley, re-arranged elements based on atomic number instead of atomic mass, which is the current periodic table. Elements in each group (vertical column) have similar properties because they have the same number of valenc ...
Atomic Information
... • If electrons are added to the atom, then there are more negative charges than positive charges. The atom becomes negatively charged and is called an anion. • If electrons are removed from the atom, then there are less negative charges than positive charges. The atom becomes positively charged and ...
... • If electrons are added to the atom, then there are more negative charges than positive charges. The atom becomes negatively charged and is called an anion. • If electrons are removed from the atom, then there are less negative charges than positive charges. The atom becomes positively charged and ...
Isotopes - Net Texts
... Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons (same Z), but a different number of neutrons (different N). The chemical properties of the different isotopes of an element are the same, but they might vary in how stable their nucleus is. We can also write elements as E–A where the E is the el ...
... Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons (same Z), but a different number of neutrons (different N). The chemical properties of the different isotopes of an element are the same, but they might vary in how stable their nucleus is. We can also write elements as E–A where the E is the el ...
Unit 2 Lesson 1 - Mrs. Tainter`s Physical Science Class
... proton, found in nuclei of atoms along with protons the center of positive charge called protons – also contains protons (with no charge) the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in a single atom. the number of protons in every atom of an element. atoms of the same element with di ...
... proton, found in nuclei of atoms along with protons the center of positive charge called protons – also contains protons (with no charge) the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in a single atom. the number of protons in every atom of an element. atoms of the same element with di ...
Atomic Structure - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Protons have a charge of +1 and are located in the nucleus with neutrons. Both are 1,840 times larger than electrons. ...
... Protons have a charge of +1 and are located in the nucleus with neutrons. Both are 1,840 times larger than electrons. ...
ATOMS - Greenville Public School District
... very reactive They are very reactive because have 7 valence electrons, this means they are ALMOST full and can combine with many elements. • Nonmetals • Halogen elements combine with metals to form compounds called salts. ...
... very reactive They are very reactive because have 7 valence electrons, this means they are ALMOST full and can combine with many elements. • Nonmetals • Halogen elements combine with metals to form compounds called salts. ...
Distinguishing Among Atoms
... different numbers of neutrons, they also have different mass numbers. ...
... different numbers of neutrons, they also have different mass numbers. ...
1 - Groupfusion.net
... Assume the following three isotopes of element Z exist: Z-248, Z-252, and Z-259. If the atomic mass of Z is 258.63 amu, which of these isotopes is most abundant? Since the atomic mass is the weighted average, the most abundant will be the isotope with the mass number closest to the atomic mass: Z-25 ...
... Assume the following three isotopes of element Z exist: Z-248, Z-252, and Z-259. If the atomic mass of Z is 258.63 amu, which of these isotopes is most abundant? Since the atomic mass is the weighted average, the most abundant will be the isotope with the mass number closest to the atomic mass: Z-25 ...
Unit 1 - Mount St. Mary Catholic High School
... Democritus (460-370 BC) ◦ thought the material world was made up of tiny indivisible particles called atomos ...
... Democritus (460-370 BC) ◦ thought the material world was made up of tiny indivisible particles called atomos ...
Day 10 The Atom - WaylandHighSchoolChemistry
... • They are all C so they all have 6 p+. But they have different mass numbers, meaning they have different #neutrons! ...
... • They are all C so they all have 6 p+. But they have different mass numbers, meaning they have different #neutrons! ...
Topic 3 – Atoms and the Periodic Table – Learning Outcomes
... Group 7 Halogens Group 8 Nobel Gases Between groups 2 and 3 we find the transition metals ...
... Group 7 Halogens Group 8 Nobel Gases Between groups 2 and 3 we find the transition metals ...
Atoms - SD308.org
... He never developed a theory because he did not have experimental support nor did he explain chemical behavior. It took 2000 years after Democritus for the real nature of atoms and events at the atomic level to be established ...
... He never developed a theory because he did not have experimental support nor did he explain chemical behavior. It took 2000 years after Democritus for the real nature of atoms and events at the atomic level to be established ...
Dynamic Earth Unit 2 lesson 3 Absolute Dating
... • Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. • The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus is its mass number and each isotope has a different mass number. • Example: Hydrogen has three natural isotopes: 1H, 2H, and 3H. Each isotope has a differ ...
... • Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. • The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus is its mass number and each isotope has a different mass number. • Example: Hydrogen has three natural isotopes: 1H, 2H, and 3H. Each isotope has a differ ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... 1. Atoms make up all matter. 2. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of another element. 3. Atoms combine in definite ratios to make compounds. 4 Combinations of atoms in compounds can change ...
... 1. Atoms make up all matter. 2. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of another element. 3. Atoms combine in definite ratios to make compounds. 4 Combinations of atoms in compounds can change ...
Atomic Structure of hydrogen
... Cancer treatment – A weak beam of radiation will kill cancer cells more readily than healthy cells. Carbon dating – All living things contain a known proportion of radioactive carbon-14 atoms. When an organism dies it stops taking in new carbon atoms so the proportion of carbon-14 atoms slowly drops ...
... Cancer treatment – A weak beam of radiation will kill cancer cells more readily than healthy cells. Carbon dating – All living things contain a known proportion of radioactive carbon-14 atoms. When an organism dies it stops taking in new carbon atoms so the proportion of carbon-14 atoms slowly drops ...
Chemistry--Chapter 5: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... According to Dalton’s atomic theory, elements are composed of tiny particles called ________________(1). Atoms of each element are ________________(2) from the atoms of all other elements. Atoms of different elements can form ________________(3) by combining in whole-number ratios. Chemical reaction ...
... According to Dalton’s atomic theory, elements are composed of tiny particles called ________________(1). Atoms of each element are ________________(2) from the atoms of all other elements. Atoms of different elements can form ________________(3) by combining in whole-number ratios. Chemical reaction ...
Study Guide: First Page Which particle defines the element?
... • Atomic Mass: mass of a specific isotope of an element • Atomic Number: the number of protons in an element • Mass Number: Protons + Neutrons • Isotopes: forms of elements that have different number of ...
... • Atomic Mass: mass of a specific isotope of an element • Atomic Number: the number of protons in an element • Mass Number: Protons + Neutrons • Isotopes: forms of elements that have different number of ...
Chemistry Review
... a change in matter from one form to another without a change in chemical properties attractive force between two oppositely charged ions that result from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another a change that occurs when a substance changes composition by forming one or more new substances ...
... a change in matter from one form to another without a change in chemical properties attractive force between two oppositely charged ions that result from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another a change that occurs when a substance changes composition by forming one or more new substances ...
Neptunium
.png?width=300)
Neptunium is a chemical element with symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it being named after Neptune, the next planet beyond Uranus. A neptunium atom has 93 protons and 93 electrons, of which seven are valence electrons. Neptunium metal is silvery and tarnishes when exposed to air. The element occurs in three allotropic forms and it normally exhibits five oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +7. It is radioactive, pyrophoric, and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of neptunium dangerous.Although many false claims of its discovery were made over the years, the element was first synthesized by Edwin McMillan and Philip H. Abelson at the Berkeley Radiation Laboratory in 1940. Since then, most neptunium has been and still is produced by neutron irradiation of uranium in nuclear reactors. The vast majority is generated as a by-product in conventional nuclear power reactors. While neptunium itself has no commercial uses at present, it is widely used as a precursor for the formation of plutonium-238, used in radioisotope thermal generators. Neptunium has also been used in detectors of high-energy neutrons.The most stable isotope of neptunium, neptunium-237, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production. It, and the isotope neptunium-239, are also found in trace amounts in uranium ores due to neutron capture reactions and beta decay.