Theories in Environmental Psychology The steps in the scientific
... These propositions include sets of concepts and how they are related to each other Models are often more complex than theories but the term is used in much the same way e.g., Moos Integrative Model of Crowding Purpose or Function 1. Theories explain environmental behavior Why don’t people help as mu ...
... These propositions include sets of concepts and how they are related to each other Models are often more complex than theories but the term is used in much the same way e.g., Moos Integrative Model of Crowding Purpose or Function 1. Theories explain environmental behavior Why don’t people help as mu ...
Reasoning and learning by analogy: Introduction.
... areas that are more distant cousins, such as categorization and decision making. Modern views of analogy can be traced to such pioneering influences as the philosopher Mary Hesse (1966), whose treatise on analogy in science argued that analogies are powerful forces in discovery and conceptual chang ...
... areas that are more distant cousins, such as categorization and decision making. Modern views of analogy can be traced to such pioneering influences as the philosopher Mary Hesse (1966), whose treatise on analogy in science argued that analogies are powerful forces in discovery and conceptual chang ...
behaviorism and classical conditioning
... psychology was too based in theoretical concepts that could not be supported by research. “The brain is not always the best way to understand behavior.” ...
... psychology was too based in theoretical concepts that could not be supported by research. “The brain is not always the best way to understand behavior.” ...
What Is Psychology - Methacton School District
... Behaviorism originated with the work of John B. Watson, an American psychologist. Watson claimed that psychology was not concerned with the mind or with human consciousness. Instead, psychology would be concerned only with behavior. Today it is associated with the name of B.F. Skinner, who made his ...
... Behaviorism originated with the work of John B. Watson, an American psychologist. Watson claimed that psychology was not concerned with the mind or with human consciousness. Instead, psychology would be concerned only with behavior. Today it is associated with the name of B.F. Skinner, who made his ...
Module 5.1 Classical Conditioning
... B. Involves unobserved mental process II. Insight Learning A. Wolfgang Kohler studied this by having a chimp try and obtain bananas outside of his cage; eventually the chimp used a cage to reach the fruit B. Insight learning is a mental process in which the restructuring of a problem into its compon ...
... B. Involves unobserved mental process II. Insight Learning A. Wolfgang Kohler studied this by having a chimp try and obtain bananas outside of his cage; eventually the chimp used a cage to reach the fruit B. Insight learning is a mental process in which the restructuring of a problem into its compon ...
GX Learning Approach presentation
... setting out his ideas of science based learning. Watson argued that psychology should focus more on observation and measurement to come to conclusions on learning and behaviour. The learning approach is also known as the umbrella term for a group of theories which highlight the importance of learnin ...
... setting out his ideas of science based learning. Watson argued that psychology should focus more on observation and measurement to come to conclusions on learning and behaviour. The learning approach is also known as the umbrella term for a group of theories which highlight the importance of learnin ...
RHCh7 - HomePage Server for UT Psychology
... Early behaviorists believed that learned behaviors of various animals could be reduced to mindless mechanisms. However, later behaviorists suggested that animals learn the predictability of a stimulus, meaning they learn expectancy or awareness of a stimulus (Rescorla & Wagner, 1972). ...
... Early behaviorists believed that learned behaviors of various animals could be reduced to mindless mechanisms. However, later behaviorists suggested that animals learn the predictability of a stimulus, meaning they learn expectancy or awareness of a stimulus (Rescorla & Wagner, 1972). ...
Learning Theories
... An approach to the study of learning that emphasizes abstract mental processes and previous knowledge. – Helps explain more complex examples of learning. – Focus on how knowledge is… • Obtained • Processed • Organized ...
... An approach to the study of learning that emphasizes abstract mental processes and previous knowledge. – Helps explain more complex examples of learning. – Focus on how knowledge is… • Obtained • Processed • Organized ...
Operant Conditioning and Gagne`s Conditions of Learning Ryan P
... What are this theory's major strengths/weaknesses? The major issue with operant conditioning and behaviorism in general, is its lack of including cognitive skill sets into the learning environment (Hill, 2001). Because the mind is ignored, feelings are often ignored as being too ambiguous (Gredler, ...
... What are this theory's major strengths/weaknesses? The major issue with operant conditioning and behaviorism in general, is its lack of including cognitive skill sets into the learning environment (Hill, 2001). Because the mind is ignored, feelings are often ignored as being too ambiguous (Gredler, ...
5 Behavioural - WordPress.com
... • Observational Learning – learning of a new behaviour through the observation of a model (watching someone else who is doing that behaviour) • Children observe adults’ behaviours at home, during social ceremonies and functions etc. • Children learn and develop various personality characteristics th ...
... • Observational Learning – learning of a new behaviour through the observation of a model (watching someone else who is doing that behaviour) • Children observe adults’ behaviours at home, during social ceremonies and functions etc. • Children learn and develop various personality characteristics th ...
AP Psychology - School District of Clayton
... 2. Professor Jackson believes that frustration increases the need for achievement. She decides to test her hypothesis with her introductory psychology class of about 100 students. The first 50 students who arrive for class one day are taken to a separate room and given a series of easy puzzles to co ...
... 2. Professor Jackson believes that frustration increases the need for achievement. She decides to test her hypothesis with her introductory psychology class of about 100 students. The first 50 students who arrive for class one day are taken to a separate room and given a series of easy puzzles to co ...
- W.W. Norton
... a. Remember the key terms about learning. Write the definition for each key term. (Complete this activity below.) learning: habituation: sensitization: b. Understand the three main types of learning. Describe these three types of learning using your own words. (Complete this activity below.) c. Appl ...
... a. Remember the key terms about learning. Write the definition for each key term. (Complete this activity below.) learning: habituation: sensitization: b. Understand the three main types of learning. Describe these three types of learning using your own words. (Complete this activity below.) c. Appl ...
IntroSyl.Complete.doc
... Critical thinking embraces methods for applying both qualitative and quantitative skills analytically and creatively to subject matter in order to evaluate arguments and to construct alternative strategies. Problem solving is one of the applications of critical thinking used to address an identified ...
... Critical thinking embraces methods for applying both qualitative and quantitative skills analytically and creatively to subject matter in order to evaluate arguments and to construct alternative strategies. Problem solving is one of the applications of critical thinking used to address an identified ...
Test Bank 1
... one of the theoretical perspectives described in this chapter (biological, psychodynamic, behavioral, learning, humanistic, and cognitive). Using a case from the text, or one from your own experience, have each group attempt to explain the "client's" behavior from the theoretical perspective they ha ...
... one of the theoretical perspectives described in this chapter (biological, psychodynamic, behavioral, learning, humanistic, and cognitive). Using a case from the text, or one from your own experience, have each group attempt to explain the "client's" behavior from the theoretical perspective they ha ...
The Behavioral Approach
... Behavior therapy was well suited to the Boulder model because clinical psychology training was designed to emphasize both the science and practice. The behavioral approach was well suited to the social and political influences of the time. It was an optimistic notion that we could create a more perf ...
... Behavior therapy was well suited to the Boulder model because clinical psychology training was designed to emphasize both the science and practice. The behavioral approach was well suited to the social and political influences of the time. It was an optimistic notion that we could create a more perf ...
AP Psychology Syllabus Syllabus The purpose of AP Psychology is
... B. Modes of Therapy (e.g., individual, group) C. Community and Preventive Approaches Objectives • Discuss the aims and methods of psychoanalysis. • Identify the basic characteristics of the humanistic therapies. • Identify the basic assumptions of behavior therapy. • Describe the assumptions and goa ...
... B. Modes of Therapy (e.g., individual, group) C. Community and Preventive Approaches Objectives • Discuss the aims and methods of psychoanalysis. • Identify the basic characteristics of the humanistic therapies. • Identify the basic assumptions of behavior therapy. • Describe the assumptions and goa ...
LEARNING
... if he is unwilling to learn. It warns us not make the child learn till he is ready to learn and also not to miss any opportunity of providing learning experience if the child is already ...
... if he is unwilling to learn. It warns us not make the child learn till he is ready to learn and also not to miss any opportunity of providing learning experience if the child is already ...
Psychological Foundations
... 5. How should the concept of learning styles influence the thinking of those responsible for curriculum development and delivery? 6. How should an educator use the information about various types of thinking? 7. How would you define humanistic learning in schools? 8. In what ways can addressing emot ...
... 5. How should the concept of learning styles influence the thinking of those responsible for curriculum development and delivery? 6. How should an educator use the information about various types of thinking? 7. How would you define humanistic learning in schools? 8. In what ways can addressing emot ...
The Behaviorist Revolution: Pavlov and Watson
... position here no better than by saying that I should like to bring my students up in the same ignorance of such hypotheses as one finds among the students of other branches of science.” ...
... position here no better than by saying that I should like to bring my students up in the same ignorance of such hypotheses as one finds among the students of other branches of science.” ...
Honors Psychology Syllabus - Bremen High School District 228
... AP Psychology Syllabus Instructor: Mr. Augustine Course Description: AP Psychology is a full year course covering the content matter and taught at the difficulty level of a regular General Psychology college course following AP guidelines. It stresses basic facts, concepts and generally accepted pri ...
... AP Psychology Syllabus Instructor: Mr. Augustine Course Description: AP Psychology is a full year course covering the content matter and taught at the difficulty level of a regular General Psychology college course following AP guidelines. It stresses basic facts, concepts and generally accepted pri ...
AP Psychology Syllabus - Bremen High School District 228
... AP Psychology Syllabus Instructor: Mrs. Hausken Course Description: AP Psychology is a full year course covering the content matter and taught at the difficulty level of a regular General Psychology college course following AP guidelines. It stresses basic facts, concepts and generally accepted prin ...
... AP Psychology Syllabus Instructor: Mrs. Hausken Course Description: AP Psychology is a full year course covering the content matter and taught at the difficulty level of a regular General Psychology college course following AP guidelines. It stresses basic facts, concepts and generally accepted prin ...
An Introduction to Lifespan Development
... • Scientific, developmental approach that focuses on continuous human development • Every period of life contains potential for growth and decline in abilities • Process of development persists throughout every part of people's lives • Neither heredity nor environment alone can account for the full ...
... • Scientific, developmental approach that focuses on continuous human development • Every period of life contains potential for growth and decline in abilities • Process of development persists throughout every part of people's lives • Neither heredity nor environment alone can account for the full ...
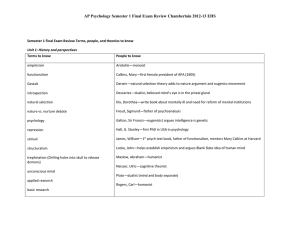
Semester 1 Final Exam Review Terms, people, and
... Semester 1 Final Exam Review Terms, people, and theories to know Unit 1: History and perspectives Terms to know ...
... Semester 1 Final Exam Review Terms, people, and theories to know Unit 1: History and perspectives Terms to know ...
Skinner`s Radical Behaviorism vs. Piaget`s Cognitive Development
... So much for similarities. Differences between the two are much more obvious. The most significant difference is that the two theories are based on entirely different premises. Radical behaviorism is defined by a refusal to work with the unobservable. Piaget worked with cognitive structures – a theo ...
... So much for similarities. Differences between the two are much more obvious. The most significant difference is that the two theories are based on entirely different premises. Radical behaviorism is defined by a refusal to work with the unobservable. Piaget worked with cognitive structures – a theo ...