Hinduism - Galaxy POD
... Hindus believe the Ganges River to be sacred. Hinduism is one of the oldest known organized religions in the world. It has about 800,000,000 followers today, most of whom are in India. ...
... Hindus believe the Ganges River to be sacred. Hinduism is one of the oldest known organized religions in the world. It has about 800,000,000 followers today, most of whom are in India. ...
GCSE Hinduism Moksha Definition: Liberation from the cycle of birth
... Moksha is a concept that Hindus believe in. It is the leaving of the worldly realm and entering into God’s realm. It is only achieved when you have got enough good karma to free your atman(soul) from the bonds of this world. The release of the soul from the body leads to 2 options 1) re-entrance int ...
... Moksha is a concept that Hindus believe in. It is the leaving of the worldly realm and entering into God’s realm. It is only achieved when you have got enough good karma to free your atman(soul) from the bonds of this world. The release of the soul from the body leads to 2 options 1) re-entrance int ...
gcse religious studies
... Beliefs about the nature of God(s): Hindus have different beliefs about the nature of God as personal or not. Beliefs about the nature of God(s) may come from characteristics of Trimurti, Krishna and Ganesh. Beliefs can also come from characteristics of any Hindu deities. Belief in Gods: Founding st ...
... Beliefs about the nature of God(s): Hindus have different beliefs about the nature of God as personal or not. Beliefs about the nature of God(s) may come from characteristics of Trimurti, Krishna and Ganesh. Beliefs can also come from characteristics of any Hindu deities. Belief in Gods: Founding st ...
oriental perspective - Philosophy of Human Person
... Consequently, the focus of attention must be on the question of morality or ethical conduct. Two forces in the universe that may determine human life: Decree of Heaven and Destiny. The first was originally for the rulers but later extended to everyone. The second seems like fate that is beyond human ...
... Consequently, the focus of attention must be on the question of morality or ethical conduct. Two forces in the universe that may determine human life: Decree of Heaven and Destiny. The first was originally for the rulers but later extended to everyone. The second seems like fate that is beyond human ...
indian history : vedas, upanishads, puranas
... The Rebellion of 1857-58, which sought to restore Indian supremacy, was crushed; and with the subsequent crowning of Victoria as Empress of India, the incorporation of India into the empire was complete. Successive campaigns had the effect of driving the British out of India in 1947. Vedas - Upanish ...
... The Rebellion of 1857-58, which sought to restore Indian supremacy, was crushed; and with the subsequent crowning of Victoria as Empress of India, the incorporation of India into the empire was complete. Successive campaigns had the effect of driving the British out of India in 1947. Vedas - Upanish ...
The Symbol OM The Components of OM
... already an existence, and if by experience, we know that the symbol has expressed that thing many times, then we are sure that there is good relation between them. There must be natural a connection between the symbol and the thing signified: then, when that symbol is pronounced, it recalls the thin ...
... already an existence, and if by experience, we know that the symbol has expressed that thing many times, then we are sure that there is good relation between them. There must be natural a connection between the symbol and the thing signified: then, when that symbol is pronounced, it recalls the thin ...
Samsakaara of Upanayanam/YajnyoPaveetam/MekhalAa Rabinder
... which arises the gross, subtle, and causal, or as speech from which arises Pashyanti, vAc, MadhyamikA vAc and the vaikhari vAc. Which comprises the whole material universe.Then it points to that ultimate reality as the source of all inner light, and pray for filling the individual with that light, h ...
... which arises the gross, subtle, and causal, or as speech from which arises Pashyanti, vAc, MadhyamikA vAc and the vaikhari vAc. Which comprises the whole material universe.Then it points to that ultimate reality as the source of all inner light, and pray for filling the individual with that light, h ...
yogas
... objects in the external world as real. The only true reality is oneness with Brahman, and the only right and true purpose in human life is to realize this oneness. Man's essential duty is to transform his consciousness so that he can become one with Brahman" (Lamb, 27). ...
... objects in the external world as real. The only true reality is oneness with Brahman, and the only right and true purpose in human life is to realize this oneness. Man's essential duty is to transform his consciousness so that he can become one with Brahman" (Lamb, 27). ...
1. - One Bad Ant
... First he [Krishna-dvaipayana Vyasa] divided the Vedas into four, then he explained them in the Puranas, and for less capable people he wrote the Mahabharata. In the Mahabharata there is given the Bhagavad-gita. Then all Vedic literature is summarized in the Vedanta-sutra, and for future guidance he ...
... First he [Krishna-dvaipayana Vyasa] divided the Vedas into four, then he explained them in the Puranas, and for less capable people he wrote the Mahabharata. In the Mahabharata there is given the Bhagavad-gita. Then all Vedic literature is summarized in the Vedanta-sutra, and for future guidance he ...
chapter 4, Hinduism
... In theory, the Hindu can chose from _______ (how many?) deities to worship. All deities tie back to the supreme figure of ________. The most important manifestations of Brahman, the three members of the “Hindu trinity” are _______________. Of these three, the creator spirit is ______, who is often r ...
... In theory, the Hindu can chose from _______ (how many?) deities to worship. All deities tie back to the supreme figure of ________. The most important manifestations of Brahman, the three members of the “Hindu trinity” are _______________. Of these three, the creator spirit is ______, who is often r ...
Ancient and Classical India
... What do Hindus believe? • One impersonal Ultimate Reality – Brahman • Brahman manifests as many personal deities • True essence of life – The soul (atman), is Brahman trapped in matter • Reincarnation – The soul is continually born into this world lifetime after lifetime • Karma – spiritual impurit ...
... What do Hindus believe? • One impersonal Ultimate Reality – Brahman • Brahman manifests as many personal deities • True essence of life – The soul (atman), is Brahman trapped in matter • Reincarnation – The soul is continually born into this world lifetime after lifetime • Karma – spiritual impurit ...
CHAPTER 3: Early Hinduism Chapter Objectives After reading this
... differentiate Indian beliefs from similar concepts in other world cultures. Chapter Summary Hinduism is actually a very diverse family of religions. Modern Hindus when speaking among themselves prefer to use the word dharma which means “way of life and thought.” PreAryan India served as the original ...
... differentiate Indian beliefs from similar concepts in other world cultures. Chapter Summary Hinduism is actually a very diverse family of religions. Modern Hindus when speaking among themselves prefer to use the word dharma which means “way of life and thought.” PreAryan India served as the original ...
WR 401 / Hinduism
... A state of complete numbness or indifference to all things that characterizes nirvana. ...
... A state of complete numbness or indifference to all things that characterizes nirvana. ...
Global I – Test #3 Review – Part II
... Who was it started by? (Mainly the Aryan traditions) What type of religion is Hinduism? What is Brahman? Who are the three main gods? What is atman? Who are the mystics and what do they try to do? What can yoga and other forms of meditation do? What is the ultimate goal in Hinduism? If they do not a ...
... Who was it started by? (Mainly the Aryan traditions) What type of religion is Hinduism? What is Brahman? Who are the three main gods? What is atman? Who are the mystics and what do they try to do? What can yoga and other forms of meditation do? What is the ultimate goal in Hinduism? If they do not a ...
Hinduism - Ms. Paras
... personalities of three different deities: • Depict the three main parts of all human life: ...
... personalities of three different deities: • Depict the three main parts of all human life: ...
gcse religion hinduism
... dharma to follow .Throughout history Hindu teachers have always been both male (rishis) and female (rishikas). Beliefs about Creation and Evolution There are many different stories about creation in the Hindu scriptures. The sacred sound Aum was believed to be the first sound at the start of creatio ...
... dharma to follow .Throughout history Hindu teachers have always been both male (rishis) and female (rishikas). Beliefs about Creation and Evolution There are many different stories about creation in the Hindu scriptures. The sacred sound Aum was believed to be the first sound at the start of creatio ...
File
... Hinduism and Buddhism In the World Religions unit, we will be studying sacred texts as well as fiction related to the religions. Siddhartha is set in India, where both Hinduism and Buddhism originated. A basic understanding of each religion is crucial to understanding the book, as well as the Upanis ...
... Hinduism and Buddhism In the World Religions unit, we will be studying sacred texts as well as fiction related to the religions. Siddhartha is set in India, where both Hinduism and Buddhism originated. A basic understanding of each religion is crucial to understanding the book, as well as the Upanis ...
PDF Version - Bible Teaching Program
... 2. Samaveda – arrangement of mantras for use in offering sacrifice. 3. Yajurveda – instructions for sacrifices 4. Atharvaveda - spells and incarnations to be used against evil. Duties and Spiritual truths. The Brahmanas (commentary on the Vedas) The Upanishads (mystic speculations) Upanishad means ‘ ...
... 2. Samaveda – arrangement of mantras for use in offering sacrifice. 3. Yajurveda – instructions for sacrifices 4. Atharvaveda - spells and incarnations to be used against evil. Duties and Spiritual truths. The Brahmanas (commentary on the Vedas) The Upanishads (mystic speculations) Upanishad means ‘ ...
From the hearth of South Asia
... known through meditation, or a form of deep contemplation. Sikhs believe that everyone has an equal status in the eyes of God Today, there are 16 million Sikhs found mainly in India ...
... known through meditation, or a form of deep contemplation. Sikhs believe that everyone has an equal status in the eyes of God Today, there are 16 million Sikhs found mainly in India ...
Hinduism and Buddhism
... The Four Noble Truths are the heart of Buddhism: 1. All life is full of suffering, pain and sorrow. 2. The cause of suffering is the desire for things that are really illusions, such as riches, power and long life. 3. The only cure for suffering is to overcome desire. 4. The way to overcome desire ...
... The Four Noble Truths are the heart of Buddhism: 1. All life is full of suffering, pain and sorrow. 2. The cause of suffering is the desire for things that are really illusions, such as riches, power and long life. 3. The only cure for suffering is to overcome desire. 4. The way to overcome desire ...
Missionary Encounters with Other Faiths Engaging the Heart of
... lives. It does not necessarily have to be a human life, either; you could come back as a bird or a worm or an insect. Your actions in one life will have automatic repercussions in your follo ...
... lives. It does not necessarily have to be a human life, either; you could come back as a bird or a worm or an insect. Your actions in one life will have automatic repercussions in your follo ...
Hinduism 101
... Brahmin – Education and Knowledge (Priests and Religious Teachers) Kshatriya – Military and Defense (soldiers and warrior kings) Vaishya – Economics and Business (merchants and farmers) ...
... Brahmin – Education and Knowledge (Priests and Religious Teachers) Kshatriya – Military and Defense (soldiers and warrior kings) Vaishya – Economics and Business (merchants and farmers) ...
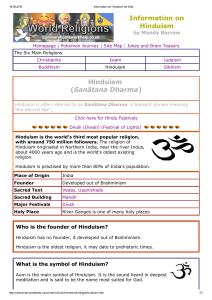
Information on Hinduism Hinduism (Sanātana Dharma)
... About Us | Search | Site Map | Feedback | User Information | Contact Us ...
... About Us | Search | Site Map | Feedback | User Information | Contact Us ...
Om
Om (or Auṃ [ə̃ũ], Sanskrit: ॐ) is a sacred sound and a spiritual icon in Dharmic religions. It is also a mantra in Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism.Om is part of the iconography found in ancient and medieval era manuscripts, temples, monasteries and spiritual retreats in Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism. The symbol has a spiritual meaning in most Indian religions, but the meaning and connotations of Om vary between the diverse schools within and across the various traditions.In Hinduism, Om is one of the most important spiritual symbols (pratima). It refers to Atman (soul, self within) and Brahman (ultimate reality, entirety of the universe, truth, divine, supreme spirit, cosmic principles, knowledge). The syllable is often found at the beginning and the end of chapters in the Vedas, the Upanishads, and other Hindu texts. It is a sacred spiritual incantation made before and during the recitation of spiritual texts, during puja and private prayers, in ceremonies of rites of passages (sanskara) such as weddings, and sometimes during meditative and spiritual activities such as Yoga.The syllable is also referred to as omkara (ओंकार, oṃkāra), aumkara (औंकार, auṃkāra), and pranava (प्रणव, praṇava).