What is Hinduism?
... there is no eternal, unchanging self (“no soul” – no atman) Suffering is a state of mind – achieve a balanced, peaceful, detached state of mind and suffering can be extinguished (Nirvana) ...
... there is no eternal, unchanging self (“no soul” – no atman) Suffering is a state of mind – achieve a balanced, peaceful, detached state of mind and suffering can be extinguished (Nirvana) ...
Buddhism/Hinduism Notes - Troup County School System
... Vedas = collections of hymns and ceremonies passed down orally by Aryan priests and later written down knowledge comes from the Vedas Key Beliefs: Henotheistic – recognize existence of many gods but believe in only one supreme god Atman o the duty of the individual self o to seek to know thi ...
... Vedas = collections of hymns and ceremonies passed down orally by Aryan priests and later written down knowledge comes from the Vedas Key Beliefs: Henotheistic – recognize existence of many gods but believe in only one supreme god Atman o the duty of the individual self o to seek to know thi ...
Hinduism
... Hindus believe in the concept of many reincarnations. The ultimate goal is to unite with the Supreme Being, Brahman. They also belief in Karma, and tend to be fatalistic. The general belief is that one's present status and condition is a result of existence in the previous birth and is, therefore, d ...
... Hindus believe in the concept of many reincarnations. The ultimate goal is to unite with the Supreme Being, Brahman. They also belief in Karma, and tend to be fatalistic. The general belief is that one's present status and condition is a result of existence in the previous birth and is, therefore, d ...
adhva vedanta - WordPress.com
... (Jiva), matter, etc. exist with their own separate reality. The distinguishing factor of this philosophy as opposed to Advaita Vedanta (monistic conclusion of Vedas) is that God takes on a personal role and is seen as a real eternal entity that governs and controls the universe. Five fundamental, et ...
... (Jiva), matter, etc. exist with their own separate reality. The distinguishing factor of this philosophy as opposed to Advaita Vedanta (monistic conclusion of Vedas) is that God takes on a personal role and is seen as a real eternal entity that governs and controls the universe. Five fundamental, et ...
File
... Teacher’s notes and background information Hinduism is a way of life and a philosophy where Hindus endeavour to seek the Divinity within, this divine essence is known as Atman. Hindus call their religion Sanatana dharma meaning “eternal spiritual path”. Hindus believe in one Supreme Being, Brahman, ...
... Teacher’s notes and background information Hinduism is a way of life and a philosophy where Hindus endeavour to seek the Divinity within, this divine essence is known as Atman. Hindus call their religion Sanatana dharma meaning “eternal spiritual path”. Hindus believe in one Supreme Being, Brahman, ...
Hinduism Definition Sanathana Dharma
... It has two parts: the Vedas and the Upanishads. There are four Vedas:, Rig,Sama, Yajur, and Atharva. There are 108 extant Upanishads, of which 10 are most important: Isa, Kena, Katha, Prashna, Mundaka, Mandukya, Taitiriya, Aitareya, Chandogya, Brihadaranyaka. The Vedas are a large body of texts orig ...
... It has two parts: the Vedas and the Upanishads. There are four Vedas:, Rig,Sama, Yajur, and Atharva. There are 108 extant Upanishads, of which 10 are most important: Isa, Kena, Katha, Prashna, Mundaka, Mandukya, Taitiriya, Aitareya, Chandogya, Brihadaranyaka. The Vedas are a large body of texts orig ...
03--Hinduism and Buddhism - Park Cities Baptist Church
... 13% of the world follows the Hindu faith, more than 800 million people. 6% of the world, more than 360 million people, are Buddhists. Hinduism has existed as long as history has been recorded. Buddhism was founded in 523 B.C. The two religions have much in common, and present a similar challenge to ...
... 13% of the world follows the Hindu faith, more than 800 million people. 6% of the world, more than 360 million people, are Buddhists. Hinduism has existed as long as history has been recorded. Buddhism was founded in 523 B.C. The two religions have much in common, and present a similar challenge to ...
Hinduism: World Civilizations Jefferson High School: 2012
... Vedas; the Vedas are a collection of prayers, chants, incantations, and meditative musings. They were initially written as instructions for priests as to how believers should perform the rituals of the religion, however, as a result of the Upanishads, they have become a more “personal” document – th ...
... Vedas; the Vedas are a collection of prayers, chants, incantations, and meditative musings. They were initially written as instructions for priests as to how believers should perform the rituals of the religion, however, as a result of the Upanishads, they have become a more “personal” document – th ...
Document
... Deities. Early Hindus worshiped gods that represented powers in nature, such as rain and the sun. Some Hindus came to believe that, though deities appear in many separate forms, these forms are part of one universal spirit called Brahman. Individual Hindus often focus on just a few of the many deiti ...
... Deities. Early Hindus worshiped gods that represented powers in nature, such as rain and the sun. Some Hindus came to believe that, though deities appear in many separate forms, these forms are part of one universal spirit called Brahman. Individual Hindus often focus on just a few of the many deiti ...
Introduction to HINDUISM keighan
... •A philosophy and a way of life - focused both on this world and beyond. Hindu Concept of God Polytheistic but some say monotheistic - It is often believed that Hindus worship many Gods; (330 million gods) but in reality their faith is ultimately directed to the belief in the universal Soul or God ...
... •A philosophy and a way of life - focused both on this world and beyond. Hindu Concept of God Polytheistic but some say monotheistic - It is often believed that Hindus worship many Gods; (330 million gods) but in reality their faith is ultimately directed to the belief in the universal Soul or God ...
Chapter 5 Section 2
... • Guru is Sanskrit for teacher • He blended Hinduism and Islam, his teaching were later expanded upon by nine other gurus. ...
... • Guru is Sanskrit for teacher • He blended Hinduism and Islam, his teaching were later expanded upon by nine other gurus. ...
It is a way of life which shapes and unifies much of Indian
... shapes and unifies much of Indian culture. Om—symbol of Hinduism ...
... shapes and unifies much of Indian culture. Om—symbol of Hinduism ...
Chapter 5: Ancient India Section 2: Origins of Hinduism Big Idea
... Mahavira was raised as a Hindu, but he thought that Hinduism put too much emphasis on ritual. His teaching emphasize four basic principles: ...
... Mahavira was raised as a Hindu, but he thought that Hinduism put too much emphasis on ritual. His teaching emphasize four basic principles: ...
Hindu
... Brahma is the creator of the universe and the universal spirit, found in everything. Brahma created all other gods as helpers. 2 chief helpers: Shiva and Vishnu ...
... Brahma is the creator of the universe and the universal spirit, found in everything. Brahma created all other gods as helpers. 2 chief helpers: Shiva and Vishnu ...
IndianPhilosophyUpanishadsSP13
... and moral goodness (Svetasvatara Upanishad, VI.1-23). • Some passages in Mundaka Upanishad subordinate imperishable Brahman to the supreme “Purusha” (person). • Other later Upanishads emphasize personal theism (e.g. Katha, Isa, and Svetasvatara). ...
... and moral goodness (Svetasvatara Upanishad, VI.1-23). • Some passages in Mundaka Upanishad subordinate imperishable Brahman to the supreme “Purusha” (person). • Other later Upanishads emphasize personal theism (e.g. Katha, Isa, and Svetasvatara). ...
Hinduism 101
... HINDU GODS AND GODDESSES—The gods and goddesses of Hinduism stand for different parts of brahman. An ancient Hindu saying expresses this idea: “God is one, but wise people know it by many names.” The most important Hindu gods are Brahma, the Creator; Vishnu, the Preserver: and Shiva, the Destroyer. ...
... HINDU GODS AND GODDESSES—The gods and goddesses of Hinduism stand for different parts of brahman. An ancient Hindu saying expresses this idea: “God is one, but wise people know it by many names.” The most important Hindu gods are Brahma, the Creator; Vishnu, the Preserver: and Shiva, the Destroyer. ...
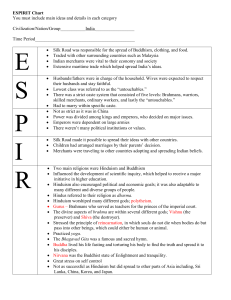
SPRITE Chart - BMcFeeleyAPWHP4
... many different and diverse groups of people. Hindus referred to their religion as dharma. Hinduism worshiped many different gods; polytheism. Gurus – Brahmans who served as teachers for the princes of the imperial court. The divine aspects of brahma are within several different gods; Vishnu ...
... many different and diverse groups of people. Hindus referred to their religion as dharma. Hinduism worshiped many different gods; polytheism. Gurus – Brahmans who served as teachers for the princes of the imperial court. The divine aspects of brahma are within several different gods; Vishnu ...
Hh notes hinduism
... Another common belief among most Hindus and described in the Upanishads, written around 800-400 BCE, is the idea that while Hindus worship many gods they are all part of one universal spirit “Brahman” (this leads some Hindus to see Hinduism as monotheistic or polymorphic monotheism). In fact all ind ...
... Another common belief among most Hindus and described in the Upanishads, written around 800-400 BCE, is the idea that while Hindus worship many gods they are all part of one universal spirit “Brahman” (this leads some Hindus to see Hinduism as monotheistic or polymorphic monotheism). In fact all ind ...
Ancient India
... • Its most sacred scriptures are the Vedas, which means "knowledge" in Sanskrit, the ritual language of Hinduism. The Vedas began as an oral tradition, and modern scholars have speculated that they date back as far as 6500 B.C.E. • Historians believe that the Vedas were written down around 1000 B.C. ...
... • Its most sacred scriptures are the Vedas, which means "knowledge" in Sanskrit, the ritual language of Hinduism. The Vedas began as an oral tradition, and modern scholars have speculated that they date back as far as 6500 B.C.E. • Historians believe that the Vedas were written down around 1000 B.C. ...
37 Hinduism Complete PowerPoint
... • Most Hindus believe in a supreme spiritual force, Brahman, the “universal soul”. • Brahman is one, but has many incarnations. – Many Hindus believe that all the Hindu gods are different aspects (forms) of Brahman. • “God is one – but wise men know it by many names.” ...
... • Most Hindus believe in a supreme spiritual force, Brahman, the “universal soul”. • Brahman is one, but has many incarnations. – Many Hindus believe that all the Hindu gods are different aspects (forms) of Brahman. • “God is one – but wise men know it by many names.” ...
Hinduism
... Because Aryans were nomadic no temples were built in the early days Animals, dairy products (poured onto the god), fire, juice of soma plant, ...
... Because Aryans were nomadic no temples were built in the early days Animals, dairy products (poured onto the god), fire, juice of soma plant, ...
Section 15.2 - cloudfront.net
... which comes from India’s prehistoric periods, through the oral tradition from fathers to sons. 4. The Vedas, Sanskrit for ________________ , are a large collection of ancient and sacred _________________ , _______________ , and __________________. 5. The Vedas describe four main social classes that ...
... which comes from India’s prehistoric periods, through the oral tradition from fathers to sons. 4. The Vedas, Sanskrit for ________________ , are a large collection of ancient and sacred _________________ , _______________ , and __________________. 5. The Vedas describe four main social classes that ...
World-Religions-only
... that developed slowly over time and is the only religion that cannot be traced back to one founder with a single set of ideas. It’s the major religion of India They worship many gods, all of which represent different forms of Brahman- the most divine spirit ...
... that developed slowly over time and is the only religion that cannot be traced back to one founder with a single set of ideas. It’s the major religion of India They worship many gods, all of which represent different forms of Brahman- the most divine spirit ...
Om
Om (or Auṃ [ə̃ũ], Sanskrit: ॐ) is a sacred sound and a spiritual icon in Dharmic religions. It is also a mantra in Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism.Om is part of the iconography found in ancient and medieval era manuscripts, temples, monasteries and spiritual retreats in Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism. The symbol has a spiritual meaning in most Indian religions, but the meaning and connotations of Om vary between the diverse schools within and across the various traditions.In Hinduism, Om is one of the most important spiritual symbols (pratima). It refers to Atman (soul, self within) and Brahman (ultimate reality, entirety of the universe, truth, divine, supreme spirit, cosmic principles, knowledge). The syllable is often found at the beginning and the end of chapters in the Vedas, the Upanishads, and other Hindu texts. It is a sacred spiritual incantation made before and during the recitation of spiritual texts, during puja and private prayers, in ceremonies of rites of passages (sanskara) such as weddings, and sometimes during meditative and spiritual activities such as Yoga.The syllable is also referred to as omkara (ओंकार, oṃkāra), aumkara (औंकार, auṃkāra), and pranava (प्रणव, praṇava).