Nineteenth Century Hindu Reform Movements
... Saw mice eating prasad and rejected "idol"/ "image" veneration. Became mendicant/quest for truth. Old guru predicted he would restore Vedic Hinduism/influenced by Rammohum Roy/denounce images/superstition of Puranas/Epics to be replaced by the Vedas/Upanishads formless, omnipotent, transcendant God ...
... Saw mice eating prasad and rejected "idol"/ "image" veneration. Became mendicant/quest for truth. Old guru predicted he would restore Vedic Hinduism/influenced by Rammohum Roy/denounce images/superstition of Puranas/Epics to be replaced by the Vedas/Upanishads formless, omnipotent, transcendant God ...
4 Main Varna
... Dravidians- original people of Indus/ Ganges River valleys, forced to move by Aryans Aryans-nomadic, warlike, fair-skinned, came from Central Asia and conquered India, many aspects of their culture can be found in Hinduism Contributions- sacred writings, belief in the soul and reincarnation, caste ...
... Dravidians- original people of Indus/ Ganges River valleys, forced to move by Aryans Aryans-nomadic, warlike, fair-skinned, came from Central Asia and conquered India, many aspects of their culture can be found in Hinduism Contributions- sacred writings, belief in the soul and reincarnation, caste ...
Introduction to Hinduism
... Festivals and Holy Days no set day of the week is holy-each days has its possibilities Religious festivals may be solar or lunar-lunar is preferred In order to keep festivals consistent, an additional lunar month is added to the calendar about every three years. Some numbered days of the month ...
... Festivals and Holy Days no set day of the week is holy-each days has its possibilities Religious festivals may be solar or lunar-lunar is preferred In order to keep festivals consistent, an additional lunar month is added to the calendar about every three years. Some numbered days of the month ...
Hinduism - University of Windsor
... Hindus believe in a universal eternal soul called Brahman, who created and is present in everything. However, they worship other deities such as Ram, Shiva, Lakshmi and Hanuman, recognizing different attributes of Brahman in them. Hindus believe that existence is a cycle of birth, death, and rebirth ...
... Hindus believe in a universal eternal soul called Brahman, who created and is present in everything. However, they worship other deities such as Ram, Shiva, Lakshmi and Hanuman, recognizing different attributes of Brahman in them. Hindus believe that existence is a cycle of birth, death, and rebirth ...
hinduism: “the oneness of it all”
... The belief that all is in God, but not all is God. God transcends the universe, but all the universe is God. Ritual worship of an idol or image, often including offerings of food or flowers, songs, bathing the image, etc. Can carried out in a temple or shrine, or performed at home The belief that wh ...
... The belief that all is in God, but not all is God. God transcends the universe, but all the universe is God. Ritual worship of an idol or image, often including offerings of food or flowers, songs, bathing the image, etc. Can carried out in a temple or shrine, or performed at home The belief that wh ...
Intro to Hinduism
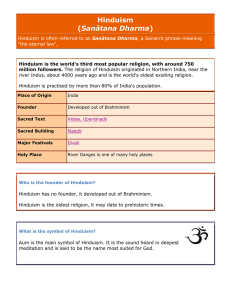
... Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian subcontinent. The tradition is known to its followers as Sanatana Dharma (“the eternal law”). This indigenous tradition has evolved in many forms over centuries, resulting in a wide range of expressions and interpretations. ...
... Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian subcontinent. The tradition is known to its followers as Sanatana Dharma (“the eternal law”). This indigenous tradition has evolved in many forms over centuries, resulting in a wide range of expressions and interpretations. ...
File
... • Hinduism is a collection of religious beliefs that developed slowly over a long period of time in India around 1700-1100 ...
... • Hinduism is a collection of religious beliefs that developed slowly over a long period of time in India around 1700-1100 ...
hinduism
... • Hinduism is a collection of religious beliefs that developed slowly over a long period of time in India around 1700-1100 ...
... • Hinduism is a collection of religious beliefs that developed slowly over a long period of time in India around 1700-1100 ...
Hindu Scriptures
... While the vedas and agamas are shared as part of every Hindu's primary scripture, shruti, each sect and lineage defines its own unique set of smriti. The sacred literature, punya shastra, from which smriti is drawn consists of writings, both ancient and modern, in many languages. Especially central ...
... While the vedas and agamas are shared as part of every Hindu's primary scripture, shruti, each sect and lineage defines its own unique set of smriti. The sacred literature, punya shastra, from which smriti is drawn consists of writings, both ancient and modern, in many languages. Especially central ...
hinduism (sanatana dharma)
... Worship means establishing a direct and personal communion with God. The ultimate purpose of ritualistic worship is the realisation of the Supreme Reality. There is immense degree of diversity in rituals of worship in Hinduism. It can be done at home or at temples and it can be personal or public. T ...
... Worship means establishing a direct and personal communion with God. The ultimate purpose of ritualistic worship is the realisation of the Supreme Reality. There is immense degree of diversity in rituals of worship in Hinduism. It can be done at home or at temples and it can be personal or public. T ...
The Upanishads - Michael Sudduth
... • Theism (belief in a single Supreme personal being) emerges in many of the later Upanishads (8th-‐6th centuries BCE). ...
... • Theism (belief in a single Supreme personal being) emerges in many of the later Upanishads (8th-‐6th centuries BCE). ...
TCI Ch. 15
... Dharma usually means “right conduct or behavior”. But remember that what is right conduct for a king may well be quite different from what is right conduct for a farmer. ...
... Dharma usually means “right conduct or behavior”. But remember that what is right conduct for a king may well be quite different from what is right conduct for a farmer. ...
Hinduism - Boise State University
... Another basic belief that affects Hindu ethics and conduct, and one of the most vital, is the teaching of Karma. This is the principle that every action has its consequences, positive or negative; it determines each existence of the reincarnated soul. On what does this belief hinge? The immortal sou ...
... Another basic belief that affects Hindu ethics and conduct, and one of the most vital, is the teaching of Karma. This is the principle that every action has its consequences, positive or negative; it determines each existence of the reincarnated soul. On what does this belief hinge? The immortal sou ...
slides - www3.telus.net
... The One/Brahman/God/Goddess Permeates all things, including the atman (soul) Knowledge of the One as means to moksha (liberation) ...
... The One/Brahman/God/Goddess Permeates all things, including the atman (soul) Knowledge of the One as means to moksha (liberation) ...
Hinduism - Miami Killian Senior High School
... • Early Indo-Aryan religion was recorded in their sacred writings called the Vedas. • This religious literature had been passed down orally by memorization for many centuries, until the Aryans developed Sanskrit writing. • The period from c.1500 - 1000 B.C.E. is called the Vedic Age. • Vedic practic ...
... • Early Indo-Aryan religion was recorded in their sacred writings called the Vedas. • This religious literature had been passed down orally by memorization for many centuries, until the Aryans developed Sanskrit writing. • The period from c.1500 - 1000 B.C.E. is called the Vedic Age. • Vedic practic ...
Aim: What does it mean to be Hindu?
... B) Hinduism did NOT have a single founder. Even today it is not an organized religion, but rather a federation of many different beliefs and philosophies. ...
... B) Hinduism did NOT have a single founder. Even today it is not an organized religion, but rather a federation of many different beliefs and philosophies. ...
In yoga - pptfun
... Mystical experience related the unity of all things fleetingly experienced in the ‘fourth’ state. ...
... Mystical experience related the unity of all things fleetingly experienced in the ‘fourth’ state. ...
1 Hinduism and the Caste System
... Vishnu is the preserver of human life. He is a generous God and known to be kind and merciful. Vishnu is the only God who is reborn whenever there is a crisis on earth. If righteousness is disturbed, Vishnu will descend to the earth as an avatar to fight the forces of evil. There have been ten avata ...
... Vishnu is the preserver of human life. He is a generous God and known to be kind and merciful. Vishnu is the only God who is reborn whenever there is a crisis on earth. If righteousness is disturbed, Vishnu will descend to the earth as an avatar to fight the forces of evil. There have been ten avata ...
Hinduism
... are three Buddhist central beliefs. They are known as the three jewels because they are so precious Belief in Buddha Dharma- The teaching of Buddha The Sangha- the Buddhist community made up of ordinary people as well as monks and nuns. The purpose is to help others and by doing so to cease to ...
... are three Buddhist central beliefs. They are known as the three jewels because they are so precious Belief in Buddha Dharma- The teaching of Buddha The Sangha- the Buddhist community made up of ordinary people as well as monks and nuns. The purpose is to help others and by doing so to cease to ...
File
... Avatars (10 of Vishnu; best known, Rama and Krishna; Jesus, Buddha, and Mohammad are avatars) Gurus (spiritual teachers: see below for gurus in America) C. View of Jesus For some Hindus, Jesus was an avatar or incarnation of Vishnu. He is seen by some as a great guru, spiritual teacher D. Sources of ...
... Avatars (10 of Vishnu; best known, Rama and Krishna; Jesus, Buddha, and Mohammad are avatars) Gurus (spiritual teachers: see below for gurus in America) C. View of Jesus For some Hindus, Jesus was an avatar or incarnation of Vishnu. He is seen by some as a great guru, spiritual teacher D. Sources of ...
Intro to Hinduism
... popularity in the West. Its different worldview and its tolerance for diversity in belief made it an attractive alternative to traditional Western religion. Although there are relatively few western converts to Hinduism, Hindu thought has influenced the West indirectly by way of religious movements ...
... popularity in the West. Its different worldview and its tolerance for diversity in belief made it an attractive alternative to traditional Western religion. Although there are relatively few western converts to Hinduism, Hindu thought has influenced the West indirectly by way of religious movements ...
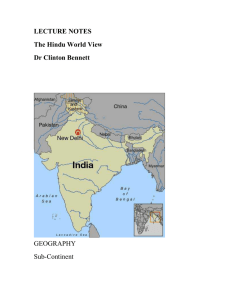
LECTURE NOTES
... YAJURVEDA (sacrificial formulas) SAMVEDA (chants) ATHARVEDA (incantations) feature Gods, demons (their frolics); creation stories, human origins. each Veda has a Brahmana (priests' manuals). Gods require sacrifices (grain, milk, flesh - worshippers eat; these are also 'gods'). Later, when belief in ...
... YAJURVEDA (sacrificial formulas) SAMVEDA (chants) ATHARVEDA (incantations) feature Gods, demons (their frolics); creation stories, human origins. each Veda has a Brahmana (priests' manuals). Gods require sacrifices (grain, milk, flesh - worshippers eat; these are also 'gods'). Later, when belief in ...
Hinduism Fact/Text
... The Hindu Holy Scriptures are mainly comprised of the following works written in the Sanskrit language: 1. The Vedas Rg-Veda (Rigveda), Yajur-Veda, Sama-Veda, Atharva-Veda 2. The Upanisads - These consider the nature of the individual soul (Atman) and the universal soul (Brahman.) One of the Upanish ...
... The Hindu Holy Scriptures are mainly comprised of the following works written in the Sanskrit language: 1. The Vedas Rg-Veda (Rigveda), Yajur-Veda, Sama-Veda, Atharva-Veda 2. The Upanisads - These consider the nature of the individual soul (Atman) and the universal soul (Brahman.) One of the Upanish ...
Om
Om (or Auṃ [ə̃ũ], Sanskrit: ॐ) is a sacred sound and a spiritual icon in Dharmic religions. It is also a mantra in Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism.Om is part of the iconography found in ancient and medieval era manuscripts, temples, monasteries and spiritual retreats in Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism. The symbol has a spiritual meaning in most Indian religions, but the meaning and connotations of Om vary between the diverse schools within and across the various traditions.In Hinduism, Om is one of the most important spiritual symbols (pratima). It refers to Atman (soul, self within) and Brahman (ultimate reality, entirety of the universe, truth, divine, supreme spirit, cosmic principles, knowledge). The syllable is often found at the beginning and the end of chapters in the Vedas, the Upanishads, and other Hindu texts. It is a sacred spiritual incantation made before and during the recitation of spiritual texts, during puja and private prayers, in ceremonies of rites of passages (sanskara) such as weddings, and sometimes during meditative and spiritual activities such as Yoga.The syllable is also referred to as omkara (ओंकार, oṃkāra), aumkara (औंकार, auṃkāra), and pranava (प्रणव, praṇava).