The Origins of Hinduism
... destroyer of life and earth He is the most powerful and important of Hindu gods Not concerned with human matters or concerns He is married to Shakti who intervenes in human matters ...
... destroyer of life and earth He is the most powerful and important of Hindu gods Not concerned with human matters or concerns He is married to Shakti who intervenes in human matters ...
Answers
... They teach about one spiritual reality – Brahman, the one Being that is the essence of all things. The innermost self or Atman is the same as Brahman. ...
... They teach about one spiritual reality – Brahman, the one Being that is the essence of all things. The innermost self or Atman is the same as Brahman. ...
Sacred Symbols - Himalayan Academy
... ymbols adorn our world at every turn, in our spiritual, social and political experience. A ring or gold pendant silently strengthens and attests to wedded love. A sign with a truck silhouette on an angled line warns drivers of steep grades ahead. The red cross signifies aid in crises. Golden arches ...
... ymbols adorn our world at every turn, in our spiritual, social and political experience. A ring or gold pendant silently strengthens and attests to wedded love. A sign with a truck silhouette on an angled line warns drivers of steep grades ahead. The red cross signifies aid in crises. Golden arches ...
The Upanishads (Hindu Religious Texts) Ebook
... considered by Hindus to contain revealed truths (Sruti) concerning the nature of ultimate reality (brahman) and describing the character and form of human salvation (moksha). The Upanishads are found mostly in the concluding part of the Brahmanas and Aranyakas and have been passed down in oral tradi ...
... considered by Hindus to contain revealed truths (Sruti) concerning the nature of ultimate reality (brahman) and describing the character and form of human salvation (moksha). The Upanishads are found mostly in the concluding part of the Brahmanas and Aranyakas and have been passed down in oral tradi ...
Hinduism PPT - Mrs. Ennis: East High School History Classes
... 1. Karma (set of activities that determine fate) 2. Moksha (final union with Brahma – part of the universe) 3. Kama (pleasure) 4. Artha (wealth and power) Activity on earth is play, but still relevant Life on earth (Maya) is an illusion compared to Moksha ...
... 1. Karma (set of activities that determine fate) 2. Moksha (final union with Brahma – part of the universe) 3. Kama (pleasure) 4. Artha (wealth and power) Activity on earth is play, but still relevant Life on earth (Maya) is an illusion compared to Moksha ...
THE HINDU TRINITY
... root out sinners, and to establish Sacred Law, I am born from age to age.” (Bhagavad Gita IV, 6-8) Followers of Vishnu worship him as the preserver, greatest of the gods. His role is to maintain a balance between good and evil powers in the universe. In order to do this, Vishnu returns to earth in d ...
... root out sinners, and to establish Sacred Law, I am born from age to age.” (Bhagavad Gita IV, 6-8) Followers of Vishnu worship him as the preserver, greatest of the gods. His role is to maintain a balance between good and evil powers in the universe. In order to do this, Vishnu returns to earth in d ...
Chapter 5 Lesson 1: The Origins of Hindu India
... • Also gave hope to those in lower castes, because if they obeyed their caste dharma, they would improve their condition in the next life. ...
... • Also gave hope to those in lower castes, because if they obeyed their caste dharma, they would improve their condition in the next life. ...
Hinduism
... earth many times in different forms trying to become one with Brahman). The soul moves up or down a hierarchy depending on their behavior in life. A person moves closer to Brahman by obeying the law of karma. Karma is the sum of all your deeds, good and bad. Good deeds involve following your dharma, ...
... earth many times in different forms trying to become one with Brahman). The soul moves up or down a hierarchy depending on their behavior in life. A person moves closer to Brahman by obeying the law of karma. Karma is the sum of all your deeds, good and bad. Good deeds involve following your dharma, ...
Lesson 3: Hinduism
... There are four Vedas in Hinduism. The oldest is the Rig Veda. It contains more than 1,000 hymns that are dedicated to Aryan gods. Hindus recite verses from the Vedas. Today Hindus still sing hymns from the Rig Veda at ceremonies such as weddings and funerals. However, some of the beliefs and practic ...
... There are four Vedas in Hinduism. The oldest is the Rig Veda. It contains more than 1,000 hymns that are dedicated to Aryan gods. Hindus recite verses from the Vedas. Today Hindus still sing hymns from the Rig Veda at ceremonies such as weddings and funerals. However, some of the beliefs and practic ...
Hinduism and Buddhism - Parkway C-2
... create present and future experiences, thus making one responsible for one's own life. With good karma, a person can be reborn into a higher caste, or even to godhood. Bad karma can relegate one to a lower caste, or even to life as an animal in their next life. ...
... create present and future experiences, thus making one responsible for one's own life. With good karma, a person can be reborn into a higher caste, or even to godhood. Bad karma can relegate one to a lower caste, or even to life as an animal in their next life. ...
Hinduism is referred to as Sanātana Dharma, a Sanskrit phrase
... The ultimate goal of life, referred to as moksha or nirvana, is understood in several different ways: as the realization of one's union with God; as the realization of one's eternal relationship with God; realization of the unity of all existence; perfect unselfishness and knowledge of the Self; as ...
... The ultimate goal of life, referred to as moksha or nirvana, is understood in several different ways: as the realization of one's union with God; as the realization of one's eternal relationship with God; realization of the unity of all existence; perfect unselfishness and knowledge of the Self; as ...
Chapter 19 section 2 Origins of Hinduism Power Point Notes
... • People with good karma are born into a higher caste in their next lives. • Hinduism taught that each person had a duty to accept his/her place in the world without complaint. This is called obeying one’s dharma. • Through reincarnation, Hinduism offered rewards to ...
... • People with good karma are born into a higher caste in their next lives. • Hinduism taught that each person had a duty to accept his/her place in the world without complaint. This is called obeying one’s dharma. • Through reincarnation, Hinduism offered rewards to ...
Hindu Sacred Writings
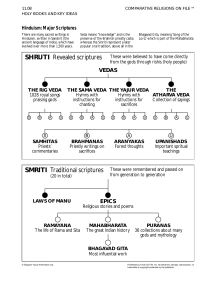
... Hinduism: Major Scriptures There are many sacred writings in Hinduism, written in Sanskrit (the ancient language of India), which have evolved over more than 1,500 years. ...
... Hinduism: Major Scriptures There are many sacred writings in Hinduism, written in Sanskrit (the ancient language of India), which have evolved over more than 1,500 years. ...
Hinduism - inglenookreligion
... between gods and humans. • Atman the human soul, often this term would be part of philosophical discussions. Closely related to Vayu, the god of wind or air, the atman is considered to be the “breath” of human life. • Hinduism is a dogmatic religion, meaning one is free to worship any set of doctrin ...
... between gods and humans. • Atman the human soul, often this term would be part of philosophical discussions. Closely related to Vayu, the god of wind or air, the atman is considered to be the “breath” of human life. • Hinduism is a dogmatic religion, meaning one is free to worship any set of doctrin ...
Nontheistic Religions www.AssignmentPoint.com Nontheistic
... Divine Being, one that emphasises an impersonal Absolute and a third that is pluralistic and non-absolute. The latter two traditions can be seen as nontheistic. ...
... Divine Being, one that emphasises an impersonal Absolute and a third that is pluralistic and non-absolute. The latter two traditions can be seen as nontheistic. ...
Hinduism Buddhism
... Moksha – freedom from the cycle of reincarnation, become one with the universe (Brahman) ...
... Moksha – freedom from the cycle of reincarnation, become one with the universe (Brahman) ...
Section 2 Reading
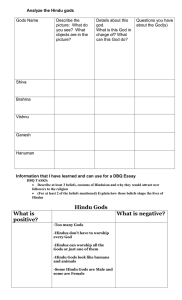
... _____ 2. Hinduism is based on four major principles: Injure no life, tell the truth, do not steal, and own no property. _________________________________________________________ _____ 3. Brahma the Creator, Siva the Destroyer, and Vishnu the Preserver are three gods of Hinduism, the largest religion ...
... _____ 2. Hinduism is based on four major principles: Injure no life, tell the truth, do not steal, and own no property. _________________________________________________________ _____ 3. Brahma the Creator, Siva the Destroyer, and Vishnu the Preserver are three gods of Hinduism, the largest religion ...
Document
... at the beginning of prayers, blessings, and meditation. The symbol is not worshipped but meditated on as a means ...
... at the beginning of prayers, blessings, and meditation. The symbol is not worshipped but meditated on as a means ...
Indian Belief Systems
... AUM - (also spelled Om) is a Hindu sacred sound that is considered the greatest of all mantras. The syllable Om is composed of the three sounds a-u-m (in Sanskrit, the vowels a and u combine to become o) and the symbol's threefold nature is central to its meaning. It represent several important tria ...
... AUM - (also spelled Om) is a Hindu sacred sound that is considered the greatest of all mantras. The syllable Om is composed of the three sounds a-u-m (in Sanskrit, the vowels a and u combine to become o) and the symbol's threefold nature is central to its meaning. It represent several important tria ...
Lesson 3a
... karma, a concept first recorded in the Upanishads. Karma (literally: action) is the sum of one's actions and the force that determines one's next reincarnation. The cycle of death and rebirth, governed by karma, is referred to as samsara. Hinduism teaches that the soul goes on repeatedly being passe ...
... karma, a concept first recorded in the Upanishads. Karma (literally: action) is the sum of one's actions and the force that determines one's next reincarnation. The cycle of death and rebirth, governed by karma, is referred to as samsara. Hinduism teaches that the soul goes on repeatedly being passe ...
Origins of Hinduism
... • The Vedas and other Vedic texts influenced religion in India for centuries. As time went forward, ideas from Persian culture and Central Asia blended in with Aryan religion to create the religion of Hinduism, the largest religion in India today. ...
... • The Vedas and other Vedic texts influenced religion in India for centuries. As time went forward, ideas from Persian culture and Central Asia blended in with Aryan religion to create the religion of Hinduism, the largest religion in India today. ...
Hinduism and Buddhism Develop
... Hinduism Evolves over Centuries • Hinduism is a collection of religious beliefs that developed over a long period of time – some aspects can be traced back to ancient times, but not one founder with one set of ideals. • Hindus share a common belief that religion is a way of liberating the soul from ...
... Hinduism Evolves over Centuries • Hinduism is a collection of religious beliefs that developed over a long period of time – some aspects can be traced back to ancient times, but not one founder with one set of ideals. • Hindus share a common belief that religion is a way of liberating the soul from ...
India and Hinduism
... 4. Dharma – duties specific to each caste; pride in fulfilling Dharma 5. Karma – all thoughts & actions result in future consequences (good or bad) 6. Moksha – spiritual goal for Hindus; release from cycle of rebirth; join world soul Reincarnation ...
... 4. Dharma – duties specific to each caste; pride in fulfilling Dharma 5. Karma – all thoughts & actions result in future consequences (good or bad) 6. Moksha – spiritual goal for Hindus; release from cycle of rebirth; join world soul Reincarnation ...
Hindu beliefs and practices
... comes to evaluating other faiths. Probably the most wellknown Hindu saying about religion is: "Truth is one; sages call it by different names." 7. However, there are some beliefs common to nearly all forms of Hinduism that can be identified, and these basic beliefs are generally regarded as bou ...
... comes to evaluating other faiths. Probably the most wellknown Hindu saying about religion is: "Truth is one; sages call it by different names." 7. However, there are some beliefs common to nearly all forms of Hinduism that can be identified, and these basic beliefs are generally regarded as bou ...
hindu-beliefs-and
... 1. About 80 percent of India's population regard themselves as Hindus and 30 million more Hindus live outside of India. There are a total of 900 million Hindus worldwide, making Hinduism the third largest religion (after Christianity and Islam). The term "Hinduism" includes numerous traditions, whic ...
... 1. About 80 percent of India's population regard themselves as Hindus and 30 million more Hindus live outside of India. There are a total of 900 million Hindus worldwide, making Hinduism the third largest religion (after Christianity and Islam). The term "Hinduism" includes numerous traditions, whic ...
Om
Om (or Auṃ [ə̃ũ], Sanskrit: ॐ) is a sacred sound and a spiritual icon in Dharmic religions. It is also a mantra in Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism.Om is part of the iconography found in ancient and medieval era manuscripts, temples, monasteries and spiritual retreats in Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism. The symbol has a spiritual meaning in most Indian religions, but the meaning and connotations of Om vary between the diverse schools within and across the various traditions.In Hinduism, Om is one of the most important spiritual symbols (pratima). It refers to Atman (soul, self within) and Brahman (ultimate reality, entirety of the universe, truth, divine, supreme spirit, cosmic principles, knowledge). The syllable is often found at the beginning and the end of chapters in the Vedas, the Upanishads, and other Hindu texts. It is a sacred spiritual incantation made before and during the recitation of spiritual texts, during puja and private prayers, in ceremonies of rites of passages (sanskara) such as weddings, and sometimes during meditative and spiritual activities such as Yoga.The syllable is also referred to as omkara (ओंकार, oṃkāra), aumkara (औंकार, auṃkāra), and pranava (प्रणव, praṇava).