* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download yogas
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Yoga Yajnavalkya wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Rajan Zed prayer protest wikipedia , lookup
Pratyabhijna wikipedia , lookup
Vishishtadvaita wikipedia , lookup
Hindu deities wikipedia , lookup
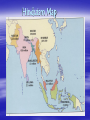
Desires, Moksha, Atman-Brahman, Personality Types, Yogas, Gods, Stages, Karma, Samsara, Maya Gandhi AUM The sound from which everything was created The buzz of the Cosmos All vowels included Big Questions Polytheism or Monotheism? Personal or Transpersonal? What is the purpose of life? What is the purpose of religion? How are religions paths? Big Ideas Big and Little Self-Emptying Paths - Different Strokes for Different Folks The Goal: Moksha, Atman-Brahman "It is only ignorance to regard the seeming separateness of objects in the external world as real. The only true reality is oneness with Brahman, and the only right and true purpose in human life is to realize this oneness. Man's essential duty is to transform his consciousness so that he can become one with Brahman" (Lamb, 27). Basics • World’s oldest, extremely diverse, constantly adapting • Goal – Atman (soul) Moksha (liberation) from cycle of Samsara (reincarnation), achieve unity with Brahman (universal spirit) by freeing self from earthly desires through discipline (yogas) • Lacks historical founder, organized priesthood, required creed of beliefs. Hinduism Map Where? India Ganges River (Benares, etc.) When? Pre-1500 B.C. Mother goddess cult in Indus Valley 1400-500 B.C. - Aryan people who wrote the Vedas - Ideas of hierarchies (higher and lower) - beliefs, castes, occupations, etc. emerged “People are different" No founder Four wants Four major stages of life Four major stations of life (castes) Four major paths to God (Yogas) All approaches to God equally valid Really Essential Questions When are you happy? When are you unhappy? What is your passion? When is your work your play? What does your symbol mean? What is an experience when words failed you? What is a symbol/image/picture you would use to depict your image of “God”? Who is a role model you admire enough to emulate and why? You can have what you want! What People Want: Path of Desire 1. Pleasure – not bad, right for a stage, seek intelligently, won’t last 2. Worldly success – a) wealth b) fame c) power - more satisfying –involves others You can have what you want! Why won’t worldly success last? Exclusive –hence competitive, precarious Drive is insatiable Centers meaning on self, not beyond self Finite and temporary – not eternal and transcendent – can’t take them with you The Question All Religion Begins With "Is this all?“ – Is there More? Turn from desire when desire turns from you Toys Psychological age v. chronological age What People Really Want: B. Path of Renunciation 3. To be needed, useful, helpful - Duty 4. Liberation (“Moksha”) – a) being (sit) b) awareness (chit) c) bliss (ananda) Goal Joy Human Limitations Obstacle suffering, unmet desire, boredom Knowledge ignorance Being space and time (“I wish you were here”, death, etc.) The Three Poisons 1. 2. 3. Desire/Grasping Aversion/Fear/Hatred Ignorance/Delusion Cause all suffering Reflect Personality types Fire Ice Caught between fear and desire Hindu Concept of the Self 1. Body (caterpillar) 2. Mind/Personality (conscious and subconscious) (butterfly) 3. Atman-Brahman (flying) Atman-Brahman The Beyond Within Detachment from finite self, or Attachment to whole of BEING Big Picture and Small Picture Whole One Energy Transcendent Spirit Idea/Word Tao unnamed Brahman – transpersonal, mono Parts Many Matter Immanent – Here/Now Flesh Incarnation/Flesh Tao named Gods – personal, poly Hinduism All is one – unity with Brahman Being is hierarchical World is multiple – Galaxies, accordion and Science Agrees – Physics – Big Bang – “pearl” of E, BOOM, “cooled” into matter – Physics/Chemistry - Atomic theory – Stuff/Matter Molecules Atoms Subatomic particles, quarks, no mass/diam, etc. Energy – Bio/Genetics – Sameness – Physics – String Theory? Strings of energy? Parallel Universes? Hinduism and Self is layered entity – Body – Conscious Mind – Subconscious Mind – Atman-Brahman Life is Developmental – stages of life, consciousness Samsara – Cycles of death and rebirth Karma – Moral cause and effect Science Agrees – Psychology – levels of consciousness Evolution, psychological theory Happens all the time in nature? – cycles of water, nutrients, etc. What goes around comes around? Parables, Symbols, Rituals, Myths Scriptures, etc. “awake us to realms of gold hidden at the depths of our being” Express inexpressible in everyday terms, pictures, etc. Upanishads - section of Vedas discussed relationship between Brahman and Atman Mahabharata and Ramayana - Long epic poems about a war, a quest Bhagavad Gita – part of Mahabharata – dialogue between warrior Arjuna and Krishna, lays out essential concepts. Hindu Scripture dialogue btw warrior Arjuna + charioteer Krishna - avatar of Vishnu Part of Mahabharata - about battle between Pandavas and 100 sons of Dhritarashtra In 18 Teachings, Krishna lays out much of Hindu philosophy of duty (dharma), moral choice and consequence (karma) and discipline (yoga), as well as the nature of the divine essence (Brahman), and it's relationship to the self (Atman). Bhagavad Gita Conceptions of God Personal – God with attributes – creator, loving, powerful, etc. Impersonal/Transpersonal – God without attributes – Godhead, Universal Essence, etc. Brahman, Tao, Nirvana? YHVH? Spirit? The Transcendent in the Immanent – Religion expresses the inexpressible in the everyday – Metaphors pointing to truth? Need concrete, use Supreme Hindu Concept Person of God Saguna Brahman - God w/ attributes - personal Thou Before Whom Nirguna Brahman - God All Words Recoil w/out attributes words fail "like trying transpersonal - how both? light = wave and particle to ladle the ocean "personal terms" - though with a net.“ not intervening Hindu Concept of God Brahman – unnamed, universal, transcendent essence permeating everything – Monotheistic? Hindu Gods – Polytheistic? Hindu Trinity Brahma – Creator Vishnu – Preserver – 10 Avatars (incarnations Krishna Rama Buddha Shiva – Destroyer – Destroys the barrier between illusion and reality – Shiva Nataraja Lord of the Dance Jot everything you see, and guess what it symbolizes More Gods How Many Gods? The whole aim of Eastern religion is to shift selfidentity from the light bulb to the light – Joseph Campbell Goal - Awareness “The only thing that is unqualifiedly good is extended vision, the enlargement of one’s understanding of the ultimate nature of things” (Smith, 8). For Hindus this vision is the awareness of the essential unity of all things as being one with Brahman Light Bulb or Light? Transformation of consciousness Yoga - The Paths to God India's obsession: “tap into supreme strength, fullness of wisdom, unquenchable joy within” Religion = path to higher states of being People are different – 5 yogas YOGA method of training/discipline designed to lead to integration or union Yoke – your own consciousness to transcendent. Get rid of Desire and Fear by shifting Consciousness Defined broadly – the discipline of “following your bliss” (Joseph Campbell) Different strokes for different folks Four Personality Traits and Paths: 1. reflective - knowledge - Jnana yoga 2. emotional - love - Bhakti yoga 3. active - work - Karma yoga 4. experimental – psychophysical experiments – Raja yoga Whereas focus in west is on strength, focus in east is on control Hatha Yoga Preparatory Jnana Yoga Reflective/Philosophical personality – Way to God through knowledge of Brahman Shortest and Steepest Path Staying “in the zone” Shift self-ID to eternal part Bhakti Yoga Religion (God, ritual) Emotions, Love Most popular Closest 2 Christianity Loving devotion to/ worship of chosen deity, family god Like devotion to saints? Myths, symbols, 1. Japam – Chanting God's name - "washing or weaving, planting or shopping, imperceptibly but indelibly these verbal droplets of aspiration soak down into the subconscious, loading it with the divine." 2. See God in various human relationships 3. Puja - Worship of chosen ideal Bhakti continued Karma Yoga Active Personality Way to God through work – find your passion, empty self of attachment/desire Work for God selflessly - in love (bhakti) or detachment (jnana) Starve the finite ego by detaching self from fruits of labor Of four yogas, main difference is between jnana and bhakti Habits to Cultivate First: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. non-injury truthfulness non-stealing self control cleanliness contentment self-discipline compelling desire to reach the goal. Raja Yoga Meditation For the scientific personality Through “psychophysical experiments 8 steps (control/tune out body, breathing, senses, etc. deepen mental concentration) a "determined refusal to allow the pitter patter of daily existence to distract from the unknown demands of some urgency within " - a "total strike" against the routine of existence. Eight Steps of Raja Yoga 1) 5 Don’t’s - cravings, injury, lying, stealing, sensuality, greed 2) 5 Do’s - cleanliness, contentment, self control, studiousness, contemplation of divine 1 and 2 - clear moral static - achieve calmness in conscience 3) Body - yogic postures work through the body to mind, rid distractions, - lotus position 4) Breathing, reduce air required – “light of lamp does not flicker in windless place” 5) Senses - Control and Tune Out- close doors of perception Up to now five intrusions - like damming of rivulets, but lake bottom streams and fantasies continue 6) Mind - Focus and Control still active/restless even now, allow thoughts that need release to exorcise themselves 7) Deepen Concentration – deepen to losing self-consciousness 8) Samadhi - state of mind of complete absorption in God, forms fall away, "The knower is united with what is known, been brought to the knowledge of total being, and for a spell, dissolved into it" The Chakras Kundalini – dragon journey Raja=Royal yoga Lotuses Psychotic drowns, yogi swims The Seven Chakras 7 – Crown 6 – Third Eye 5 – Larynx 4 – Heart 3 - Navel 2 - Genitals 1 – Base of Spine (root) 7 – The 1000 petal lotus – Distinctons disappear 6 – Soul beholds God 5 - Cleansing, Air, Aum 4 – Love (Divinity down, Human up) 3 – Power (most at 2 or 3) 2 - Pleasure 1 – Holding On - dragon Benefits? Hinduism agrees w/ psychoanalysis that if only we could tap into our subconscious we would experience a remarkable expansion of power and life 1. student - after rite of Stages initiation - 12 years old 2. householder - duty to family, vocation, community - first three wants 3. retirement - find meaning 4. Sannyasin - neither hates nor loves anything - identify with eternal self of Life 1. 2. 3. 4. Stations of Life - Castes Brahmins - seers - reflective philosophers, artists, religious leaders and teachers Kshatriyas - administrators Vaishyas - producers, artisans, farmers Shudras - followers, servants, unskilled laborers "perversion" with addition of 5th group - outcastes/untouchables Caste From Buddha to Gandhi, many reformers sought to remove untouchability from caste outlawed in India's constitution 5 perversions/deteriorations: 1. Untouchables 2. Breakup of 4 into over 3000 subcastes – 3. Proscriptions v. intermarriage, dining complicates society 4. Privileges - higher castes benefited at expense of lower 5. Caste became hereditary Samsara – Coming of age in the universe Reincarnation "When we outgrow a suit or find our house to cramped, we exchange these for roomier ones that offer our bodies freer play souls do the same." From Gita : "Worn out garments Are shed by the body. Worn out bodies Are shed by the dweller (soul)." “The function of your body is to put your jiva in the realm of temporary existence” – Joseph Campbell What Brings You Back? Two Things: Desire and Fear Karma Karma Moral law of cause and effect - present life is exact product of past wants and actions "As you sow, so shall you reap.“ “What goes around, comes around” Desire and Fear Two important psychological corollaries to Karma: 1. Complete personal responsibility 2. No accidents or chance events Karma Quote "It is as if each desire that aims at the ego's gratification adds a grain of concrete to the wall surrounding the individual self and insulates it from the infinite sea of being that surrounds it, while, conversely, each compassionate or disinterested act dislodges a grain from the confining dike" (66). Hindu Worldview Giant Accordion 1. Multiple - innumerable horizontal galaxies, vertical tiers, temporal cycles 2. Moral - law of Karma 3. Middle – never heaven or hell, but between 4. Maya = illusion/”tricky”, passes off “multiplicity, materiality and dualities as ultimate when they are provisional” 5. Training ground - people can develop 6. Lila - divine play in the cosmic dance Bird over the Himalayas Many Paths to the Same Summit "truth is one, the sages call it by many names" stained glass window Pun Fun