Cold War Origins: 1945-1962
... Post War Economic Security • The Bretton-Woods Conference • Summer 1944: 44 allied nations meet in NH • Set up the IMF (International Monetary fund), the World Bank, and the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) • Set up a foreign currency exchange standard ...
... Post War Economic Security • The Bretton-Woods Conference • Summer 1944: 44 allied nations meet in NH • Set up the IMF (International Monetary fund), the World Bank, and the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) • Set up a foreign currency exchange standard ...
OGT Multiple Choice
... • The United States and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) emerged as the two strongest powers in international affairs. Ideologically opposed, they challenged one another in a series of confrontations known as the Cold War. The costs of this prolonged contest weakened the USSR so that i ...
... • The United States and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) emerged as the two strongest powers in international affairs. Ideologically opposed, they challenged one another in a series of confrontations known as the Cold War. The costs of this prolonged contest weakened the USSR so that i ...
World War II unit test
... response. Use complete sentences. Circle the question you are answering. 7 points. 1. Discuss how TWO of the following battles WERE or COULD HAVE BEEN turning points in the war: Dunkirk, Midway, Stalingrad, and The Battle of the Bulge. 2. Describe the impact WWII had on American life on the home fro ...
... response. Use complete sentences. Circle the question you are answering. 7 points. 1. Discuss how TWO of the following battles WERE or COULD HAVE BEEN turning points in the war: Dunkirk, Midway, Stalingrad, and The Battle of the Bulge. 2. Describe the impact WWII had on American life on the home fro ...
World War II Begins B. What was Hitler`s motivation for German
... The pact stated that he was simply trying to . On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded declared war against Germany. ...
... The pact stated that he was simply trying to . On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded declared war against Germany. ...
The course of war: 1939-1944
... democracies would abandon Poland. Instead, under strong pressure from their own publics, Chamberlain and Daladier redeemed their promises. On September 3, Britain and France declared war on Germany. Few expected Poland to prevail, but the war nonetheless went worse for the Poles than nearly any obse ...
... democracies would abandon Poland. Instead, under strong pressure from their own publics, Chamberlain and Daladier redeemed their promises. On September 3, Britain and France declared war on Germany. Few expected Poland to prevail, but the war nonetheless went worse for the Poles than nearly any obse ...
Franklin D Roosevelt and the Shadow of War - apush
... persecute and exterminate about six million Jews, and occupy Austria—all because the European powers were appeasing him. ...
... persecute and exterminate about six million Jews, and occupy Austria—all because the European powers were appeasing him. ...
File
... Caribbean sinking more than 3,500 merchant ships and killing tens of thousands of Allied seaman • By 1943, radar, long-range bombers, convoys, and depth ...
... Caribbean sinking more than 3,500 merchant ships and killing tens of thousands of Allied seaman • By 1943, radar, long-range bombers, convoys, and depth ...
World War 2 Study Guide Answers
... a. The name given to the night that Jewish shops, businesses and synagogues were destroyed – Night of Broken Glass. ...
... a. The name given to the night that Jewish shops, businesses and synagogues were destroyed – Night of Broken Glass. ...
Benito Mussolini
... Non-Aggression Pact In 1939, Germany and the Soviet Union signed a 10 year NonAggression Pact. This allowed Russia to avoid involvement in a major war and gave them a free hand over eastern Poland and the Baltic States. The pact protected Germany from a two-front war and promised supplies and food f ...
... Non-Aggression Pact In 1939, Germany and the Soviet Union signed a 10 year NonAggression Pact. This allowed Russia to avoid involvement in a major war and gave them a free hand over eastern Poland and the Baltic States. The pact protected Germany from a two-front war and promised supplies and food f ...
Mussolini
... certain territory from Austria-Hungary. Italians were particularly interested in this territory because a lot of ethnic Italians lived in these territories. After the war, Italy received some of the promised territory, but some of it became a part of the newly created state Yugoslavia. Italian natio ...
... certain territory from Austria-Hungary. Italians were particularly interested in this territory because a lot of ethnic Italians lived in these territories. After the war, Italy received some of the promised territory, but some of it became a part of the newly created state Yugoslavia. Italian natio ...
CPUSH (Unit , # )
... airfields and cities. During the Battle of Britain, Prime Minister Winston Churchill inspired the British to fight back and “never surrender.” In 1940, France had fallen and Britain was under siege. On September 27, Germany, Italy, and Japan signed the Tripartite Pact. The three nations became known ...
... airfields and cities. During the Battle of Britain, Prime Minister Winston Churchill inspired the British to fight back and “never surrender.” In 1940, France had fallen and Britain was under siege. On September 27, Germany, Italy, and Japan signed the Tripartite Pact. The three nations became known ...
Cornell Notes Template - AP United States History
... As economies plummeted and unemployment rose, many people turned to powerful leaders and governments who promised success through military buildup and the conquest of territory. CAUSES OF JAPANESE EXPANSIONISM: ...
... As economies plummeted and unemployment rose, many people turned to powerful leaders and governments who promised success through military buildup and the conquest of territory. CAUSES OF JAPANESE EXPANSIONISM: ...
Chapter 13 The Rise of Dictators and World War II
... the British Prime future Prime Minister, Minister who came up said: “Britain and with the agreement, France had to choose said that he had between war and achieved “peace in shame. They chose our time” shame. They will get war, too.” ...
... the British Prime future Prime Minister, Minister who came up said: “Britain and with the agreement, France had to choose said that he had between war and achieved “peace in shame. They chose our time” shame. They will get war, too.” ...
ii. world war ii
... time and allowed for his slow military build up. Hitler’s goals were pursued not by any calculated agenda, but pragmatically in response to the inactions of the West. Opportunities to confront and possibly stop a much weaker Germany were squandered. II. WORLD WAR II The war was truly global, highly ...
... time and allowed for his slow military build up. Hitler’s goals were pursued not by any calculated agenda, but pragmatically in response to the inactions of the West. Opportunities to confront and possibly stop a much weaker Germany were squandered. II. WORLD WAR II The war was truly global, highly ...
48. World War II in Europe
... European war spilled over into North Africa. Italians tried to invade Egypt and failed, so the German Afrikakorps under General Erwin Rommel came and finished the job by April of 1941. Rommel was a brilliant tank commander who had written a book on tactics that he first put into action in Belgium on ...
... European war spilled over into North Africa. Italians tried to invade Egypt and failed, so the German Afrikakorps under General Erwin Rommel came and finished the job by April of 1941. Rommel was a brilliant tank commander who had written a book on tactics that he first put into action in Belgium on ...
Battle of the Bulge - Advance Placement US History
... – Hitler promised to rebuild Germany and this appealed to the people. – He denounced the Treaty of Versailles (Saying Germany would no longer follow it) – 1932 German elections, Nazi party becomes the most powerful party in Germany. – 1933 Hitler becomes chancellor of Germany. • (Head of Government… ...
... – Hitler promised to rebuild Germany and this appealed to the people. – He denounced the Treaty of Versailles (Saying Germany would no longer follow it) – 1932 German elections, Nazi party becomes the most powerful party in Germany. – 1933 Hitler becomes chancellor of Germany. • (Head of Government… ...
chapter 27 the european crisis: world war ii
... agreement. Why did they disagree so much? Did Chamberlain’s actions at Munich directly lead to World War II? Why or why not? In 1938, who was the “realist” and which was the “idealist” and why? (page 787) 3. “A German Soldier at Stalingrad”: What does this excerpt tell you about the attitude of Germ ...
... agreement. Why did they disagree so much? Did Chamberlain’s actions at Munich directly lead to World War II? Why or why not? In 1938, who was the “realist” and which was the “idealist” and why? (page 787) 3. “A German Soldier at Stalingrad”: What does this excerpt tell you about the attitude of Germ ...
World_War_II_1942_1945 (1)
... In February 1945, the Stalin agreed to send troops “Big Three” met at the to help the U.S. invade Japan Yalta Conference to They agreed to allow self-‐ determina,on (free elec,ons) in create a p ...
... In February 1945, the Stalin agreed to send troops “Big Three” met at the to help the U.S. invade Japan Yalta Conference to They agreed to allow self-‐ determina,on (free elec,ons) in create a p ...
WWII
... Begins rearming and rebuilding the army Banners in Germany read “Today Germany! Tomorrow the World!” Starts arming Germany using Soviet land 1936- Moves troops into the Rhineland 1937- Hitler makes the move to annex Austria also forbidden by the treaty. Next move was Czechoslovakia, Hitl ...
... Begins rearming and rebuilding the army Banners in Germany read “Today Germany! Tomorrow the World!” Starts arming Germany using Soviet land 1936- Moves troops into the Rhineland 1937- Hitler makes the move to annex Austria also forbidden by the treaty. Next move was Czechoslovakia, Hitl ...
Chapter 25: World War II
... Germany made an alliance with Italy, called the Axis. Hitler and Stalin sign a treaty Non-aggression pact: two countries agree not to attack each other Soviet Union signed a non-aggression pact. Stalin was afraid that his country was not ready to fight Germany Germany signed a non-aggression pact to ...
... Germany made an alliance with Italy, called the Axis. Hitler and Stalin sign a treaty Non-aggression pact: two countries agree not to attack each other Soviet Union signed a non-aggression pact. Stalin was afraid that his country was not ready to fight Germany Germany signed a non-aggression pact to ...
SOL 10 & 11 World War II
... • Single, political, and economic system ruled from Berlin by the Aryan race • Hitler wanted S.U. for food and raw materials and planned to starve the Soviets—they were inferior to the Slavs • (planned to eliminate inferior elements— ...
... • Single, political, and economic system ruled from Berlin by the Aryan race • Hitler wanted S.U. for food and raw materials and planned to starve the Soviets—they were inferior to the Slavs • (planned to eliminate inferior elements— ...
The Road to World War II
... - created a myth of his own greatness - dominated all aspects of Soviet life ...
... - created a myth of his own greatness - dominated all aspects of Soviet life ...
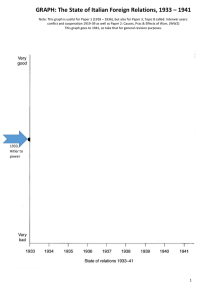
the-state-of-italian-foreign-relations-diagram_student
... The Spanish Civil War (1936-9) was a very important event during the tense1930s in Europe. Although it did not make World War II inevitable, it increased the likelihood of a general war a great deal. The war had a tremendous impact on Spain itself, leaving much of the state's economic and social inf ...
... The Spanish Civil War (1936-9) was a very important event during the tense1930s in Europe. Although it did not make World War II inevitable, it increased the likelihood of a general war a great deal. The war had a tremendous impact on Spain itself, leaving much of the state's economic and social inf ...
German–Soviet Axis talks

In October and November 1940, German–Soviet Axis talks occurred concerning the Soviet Union's potential entry as a fourth Axis Power in World War II. The negotiations included a two-day Berlin conference between Soviet Foreign Minister Vyacheslav Molotov, Adolf Hitler and German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ribbentrop, followed by both countries trading written proposed agreements. Germany never responded to a November 25, 1940, Soviet proposal, leaving the negotiations unresolved. Germany broke the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact in June 1941 by invading the Soviet Union.