world war looms
... Here a Nazi unit is en route to Poland at the end of September, 1939. Handwritten on the side of the train car is, "We are going to Poland to thrash the Jews." Photo credit: Meczenstwo Walka, Zaglada Zydów Polsce 1939-1945. Poland. No. 26. ...
... Here a Nazi unit is en route to Poland at the end of September, 1939. Handwritten on the side of the train car is, "We are going to Poland to thrash the Jews." Photo credit: Meczenstwo Walka, Zaglada Zydów Polsce 1939-1945. Poland. No. 26. ...
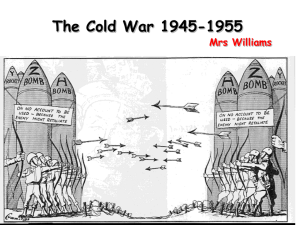
The Cold War 1943
... control the people to such an extent they would be afraid to even think of opposing him. Throughout his time in power he used his secret police, to crush opponents of his policies. By 1937 an estimated 18 million people had been transported to labour camps. Ten million died. The people of the Soviet ...
... control the people to such an extent they would be afraid to even think of opposing him. Throughout his time in power he used his secret police, to crush opponents of his policies. By 1937 an estimated 18 million people had been transported to labour camps. Ten million died. The people of the Soviet ...
WWII: Europe
... As we entered the camp, the living skeletons still able to walk crowded around us and, though we wanted to drive farther into the place, the milling, pressing crowd would not let us. It is not an exaggeration to say that almost every inmate was insane with hunger. Just the sight of an American broug ...
... As we entered the camp, the living skeletons still able to walk crowded around us and, though we wanted to drive farther into the place, the milling, pressing crowd would not let us. It is not an exaggeration to say that almost every inmate was insane with hunger. Just the sight of an American broug ...
Thesis Paper Summary Alyssa Penny Controversial Question
... -Since Hitler violated the Munich agreement, Britain feared that Hitler would take over Poland,so Chamberlin made a guarantee which stated, “In the event of any action which clearly threatened Polish independence… His Majesty’s government would feel themselves bound at once to lend the Polish Govern ...
... -Since Hitler violated the Munich agreement, Britain feared that Hitler would take over Poland,so Chamberlin made a guarantee which stated, “In the event of any action which clearly threatened Polish independence… His Majesty’s government would feel themselves bound at once to lend the Polish Govern ...
Great Patriotic War (USSR) - IB 20th c. World History Y2
... On August 23, enemies Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union surprised the world by signing the German-Soviet Nonaggression Pact, in which the two countries agreed to take no military action against each other for the next 10 years. “For sheer cynicism, the Nazi dictator had met his match in the Soviet d ...
... On August 23, enemies Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union surprised the world by signing the German-Soviet Nonaggression Pact, in which the two countries agreed to take no military action against each other for the next 10 years. “For sheer cynicism, the Nazi dictator had met his match in the Soviet d ...
World War II
... 4. The North African Front A. Erwin Rommel (“Desert Fox”)– secure N. Africa for AXIS Powers B. “Beat Hitler first” strategy – defeat AXIS Powers in Europe first ...
... 4. The North African Front A. Erwin Rommel (“Desert Fox”)– secure N. Africa for AXIS Powers B. “Beat Hitler first” strategy – defeat AXIS Powers in Europe first ...
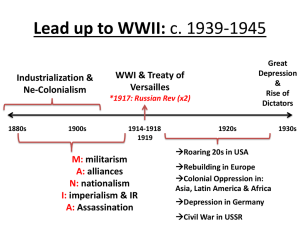
Causes - Glen Innes High School
... So it is in fact easy to answer: 'Why did the USA-USSR alliance begin to break down in 1945?' As soon as the common threats of Hitler and Japan were removed, it was inevitable that the allies would fall out. During the war, there had been growing tensions: ...
... So it is in fact easy to answer: 'Why did the USA-USSR alliance begin to break down in 1945?' As soon as the common threats of Hitler and Japan were removed, it was inevitable that the allies would fall out. During the war, there had been growing tensions: ...
Continued
... The Soviet Union Declares Neutrality • March 1939, German troops occupy rest of Czechoslovakia • Hitler charges Poles mistreat Germans in Poland • Many think he’s bluffing; invading Poland would bring two-front war • Stalin, Hitler sign nonaggression pact—will not attack each other • Sign second, se ...
... The Soviet Union Declares Neutrality • March 1939, German troops occupy rest of Czechoslovakia • Hitler charges Poles mistreat Germans in Poland • Many think he’s bluffing; invading Poland would bring two-front war • Stalin, Hitler sign nonaggression pact—will not attack each other • Sign second, se ...
Final Review World History WWI, Depression, WII, Cold War, China
... 11. What events led to the beginning of WWII? 12. What policy was Great Britain following that allowed Hitler to continue on his path? 13. Why did Germany want to attack the Soviet Union? 14. How did the Allies slow Hitler’s occupation of Europe? 15. What were the turning points for the Allies? 16. ...
... 11. What events led to the beginning of WWII? 12. What policy was Great Britain following that allowed Hitler to continue on his path? 13. Why did Germany want to attack the Soviet Union? 14. How did the Allies slow Hitler’s occupation of Europe? 15. What were the turning points for the Allies? 16. ...
WWII Study Guide
... WWII Study Guide People to Know – who they were and what they did: Joseph Stalin ...
... WWII Study Guide People to Know – who they were and what they did: Joseph Stalin ...
world war ii european theater notes 2013
... Neutral nations fell quickly ---> Denmark, Netherlands, Belgium, Norway ...
... Neutral nations fell quickly ---> Denmark, Netherlands, Belgium, Norway ...
world war ii european theater
... Neutral nations fell quickly ---> Denmark, Netherlands, Belgium, Norway ...
... Neutral nations fell quickly ---> Denmark, Netherlands, Belgium, Norway ...
European Theater
... Summer/Fall, 1940: Battle of Britain (German Luftwaffe vs. Royal Air Force RAF) ...
... Summer/Fall, 1940: Battle of Britain (German Luftwaffe vs. Royal Air Force RAF) ...
The American Pageant, Chapter 35: America in WWII
... Poland; Blitzkrieg- Britain, France, and the Axis. What? German tanks and planes began a full-scale invasion of Poland, causing Britain and France to declare war on Germany, and soon afterward Germany had the support of its Axis allies; By June 1940, the only ally that remained free of German troo ...
... Poland; Blitzkrieg- Britain, France, and the Axis. What? German tanks and planes began a full-scale invasion of Poland, causing Britain and France to declare war on Germany, and soon afterward Germany had the support of its Axis allies; By June 1940, the only ally that remained free of German troo ...
chapter 35 - cloudfront.net
... a. After a period of inaction over the winter of 1939–1940, called the “_____________ war,” Hitler invaded and conquered _______________ (through Scandinavia, Netherlands, and Belgium). The British successfully evacuated their troops from the French port of _______________. Prime Minister Winston __ ...
... a. After a period of inaction over the winter of 1939–1940, called the “_____________ war,” Hitler invaded and conquered _______________ (through Scandinavia, Netherlands, and Belgium). The British successfully evacuated their troops from the French port of _______________. Prime Minister Winston __ ...
WebQuest: Causes of World War II - Carla D`s E-Portfolio
... Appeasement means to make calm or to satisfy. b. What were the five most important reasons why Britain appeased Hitler? -Some people agreed with Hitler’s policies -British hoped strong German could stop the growing of Communist Russia -A lot of people felt that events occurring in Europe were non of ...
... Appeasement means to make calm or to satisfy. b. What were the five most important reasons why Britain appeased Hitler? -Some people agreed with Hitler’s policies -British hoped strong German could stop the growing of Communist Russia -A lot of people felt that events occurring in Europe were non of ...
WWII Part I PowerPoint
... a. British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain told his nation he had achieved “peace for our time” b. British politician Winston Churchill – reaction – “They had to choose between war and dishonor. They chose dishonor; they will have war.” ...
... a. British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain told his nation he had achieved “peace for our time” b. British politician Winston Churchill – reaction – “They had to choose between war and dishonor. They chose dishonor; they will have war.” ...
Section 5- World War II Ends - Waverly
... Americans, Soviets, British, and French would each occupy one of these sectors. Berlin was also divided into four sectors. Another agreement had to do with the fate of Poland and other Eastern European countries now occupied by the Soviets. Stalin agreed to hold elections in these countries after th ...
... Americans, Soviets, British, and French would each occupy one of these sectors. Berlin was also divided into four sectors. Another agreement had to do with the fate of Poland and other Eastern European countries now occupied by the Soviets. Stalin agreed to hold elections in these countries after th ...
The Battle of Stalingrad
... German capture of the city would effectively sever the transportation of resources and goods to the north. • Second, its capture would secure the right flank of the German armies as they advanced into the oil-rich Caucasus region – with the strategic goal of cutting off fuel to Stalin's war machine. ...
... German capture of the city would effectively sever the transportation of resources and goods to the north. • Second, its capture would secure the right flank of the German armies as they advanced into the oil-rich Caucasus region – with the strategic goal of cutting off fuel to Stalin's war machine. ...
Note Taking Study Guide
... Anschluss, or union with Austria. Next, Hitler set his sights on the Sudentenland. This was a part of Czechoslovakia where three million Germans lived. At the Munich Conference, which was held to discuss the situation, British and French leaders chose appeasement and allowed Hitler to annex the terr ...
... Anschluss, or union with Austria. Next, Hitler set his sights on the Sudentenland. This was a part of Czechoslovakia where three million Germans lived. At the Munich Conference, which was held to discuss the situation, British and French leaders chose appeasement and allowed Hitler to annex the terr ...
Note Taking Study Guide
... Anschluss, or union with Austria. Next, Hitler set his sights on the Sudentenland. This was a part of Czechoslovakia where three million Germans lived. At the Munich Conference, which was held to discuss the situation, British and French leaders chose appeasement and allowed Hitler to annex the terr ...
... Anschluss, or union with Austria. Next, Hitler set his sights on the Sudentenland. This was a part of Czechoslovakia where three million Germans lived. At the Munich Conference, which was held to discuss the situation, British and French leaders chose appeasement and allowed Hitler to annex the terr ...
Name: Date:
... Dwight D. Eisenhower United States general who supervised the invasion of Normandy and the defeat of Nazi Germany; 34th President of the United States ...
... Dwight D. Eisenhower United States general who supervised the invasion of Normandy and the defeat of Nazi Germany; 34th President of the United States ...
Ch - My CCSD
... 2) Describe the relationship between the military and the civilian government in Japan in the 1930s. 3) (a) What characteristics did fascism under Mussolini and Hitler have in common with communism under Stalin? (b) What are two important differences between fascism and communism? 4) Why didn’t Roos ...
... 2) Describe the relationship between the military and the civilian government in Japan in the 1930s. 3) (a) What characteristics did fascism under Mussolini and Hitler have in common with communism under Stalin? (b) What are two important differences between fascism and communism? 4) Why didn’t Roos ...
German–Soviet Axis talks

In October and November 1940, German–Soviet Axis talks occurred concerning the Soviet Union's potential entry as a fourth Axis Power in World War II. The negotiations included a two-day Berlin conference between Soviet Foreign Minister Vyacheslav Molotov, Adolf Hitler and German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ribbentrop, followed by both countries trading written proposed agreements. Germany never responded to a November 25, 1940, Soviet proposal, leaving the negotiations unresolved. Germany broke the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact in June 1941 by invading the Soviet Union.