Forms of Energy
... Energy is found in different forms including light, heat, chemical, and motion. There are many forms of energy, but they can all be put into two categories: potential and kinetic. ...
... Energy is found in different forms including light, heat, chemical, and motion. There are many forms of energy, but they can all be put into two categories: potential and kinetic. ...
Energy Vocabulary I
... thermal energy elastic energy insulation potential energy efficiency light gravitational potential energy conduction insulator electrical energy calories Law of Conservation of Energy energy transformation Fill in the blank with the correct term ...
... thermal energy elastic energy insulation potential energy efficiency light gravitational potential energy conduction insulator electrical energy calories Law of Conservation of Energy energy transformation Fill in the blank with the correct term ...
Energy & Its Conservation
... A large chunk of ice with a mass Of 15 kg falls from a roof 8 m Above the ground. Find the Kinetic Energy of the ice when It reaches the ground. What is The speed of the ice when it Reaches the ground? 1180 J ...
... A large chunk of ice with a mass Of 15 kg falls from a roof 8 m Above the ground. Find the Kinetic Energy of the ice when It reaches the ground. What is The speed of the ice when it Reaches the ground? 1180 J ...
Study Guide
... 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? ____________ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? ____________ 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _________ ...
... 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? ____________ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? ____________ 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _________ ...
Energy - ability of an object to do work
... Energy - ability of an object to do work Potential energy – ability of an object to have energy Kinetic energy – the actual movement of an object Mechanical – when potential and kinetic energy are put to an object Electric energy – form of moving energy that has a flow of electric charges Circuit- a ...
... Energy - ability of an object to do work Potential energy – ability of an object to have energy Kinetic energy – the actual movement of an object Mechanical – when potential and kinetic energy are put to an object Electric energy – form of moving energy that has a flow of electric charges Circuit- a ...
What Is Energy Power Point
... (with or without simple machines), the amount of work done is the same. • No matter how you transfer energy (with or without simple machines), the amount of energy transferred is the same. ...
... (with or without simple machines), the amount of work done is the same. • No matter how you transfer energy (with or without simple machines), the amount of energy transferred is the same. ...
Energy Conservation Notes Filled-in
... Chemical Energy 6. Energy of position or place, especially dealing with height differences. Gravitational Energy 7. Movement of charges through a conductor. Electrical Energy 8. Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom. Nuclear Energy 9. Electromagnetic energy such as gamma rays, x-rays, and visible ...
... Chemical Energy 6. Energy of position or place, especially dealing with height differences. Gravitational Energy 7. Movement of charges through a conductor. Electrical Energy 8. Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom. Nuclear Energy 9. Electromagnetic energy such as gamma rays, x-rays, and visible ...
No Slide Title
... • Increasingly, facilities are viewed as strategic resources, rather than as an expense • The facility manager is being elevated to the role of asset manager, supporting the organization's overall business goals ...
... • Increasingly, facilities are viewed as strategic resources, rather than as an expense • The facility manager is being elevated to the role of asset manager, supporting the organization's overall business goals ...
Mechanical Energy PP
... reach by the bottom of the hill if it was frictionless. b) Real hills, even icy ones have friction. When the child reaches the bottom, she is going 10.0m/s. Compute the work done by friction, and size of the friction force. ...
... reach by the bottom of the hill if it was frictionless. b) Real hills, even icy ones have friction. When the child reaches the bottom, she is going 10.0m/s. Compute the work done by friction, and size of the friction force. ...
Mechanical Energy - Miss Burnett`s 6th grade Classroom
... What Are Other Forms of Energy? 7 Forms of energy to know 1. Mechanical – motion of object 2. Sound - vibrations 3. Nuclear – fusion and fission 4. Thermal – temperature of object 5. Electrical – batteries or power lines 6. Electromagnetic – visible light, microwaves 7. Chemical – food, cells in yo ...
... What Are Other Forms of Energy? 7 Forms of energy to know 1. Mechanical – motion of object 2. Sound - vibrations 3. Nuclear – fusion and fission 4. Thermal – temperature of object 5. Electrical – batteries or power lines 6. Electromagnetic – visible light, microwaves 7. Chemical – food, cells in yo ...
Different forms of energy
... particles in a substance. All matter is made up of atoms ( particles) that move faster when they heat up. The faster the particles move, higher the temperature. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy Heat always moves from hotter objects to colder objects ...
... particles in a substance. All matter is made up of atoms ( particles) that move faster when they heat up. The faster the particles move, higher the temperature. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy Heat always moves from hotter objects to colder objects ...
Forms of Energy Conversions
... Forms of Energy Conversions: use the back of this page for drawing if you need more room. There are six forms of energy: thermal (heat), electrical (moving electrons), electromagnetic (light), nuclear (energy that binds the nuclei of atoms), chemical and mechanical (a kind of kinetic energy of movin ...
... Forms of Energy Conversions: use the back of this page for drawing if you need more room. There are six forms of energy: thermal (heat), electrical (moving electrons), electromagnetic (light), nuclear (energy that binds the nuclei of atoms), chemical and mechanical (a kind of kinetic energy of movin ...
Energy Test Study Guide
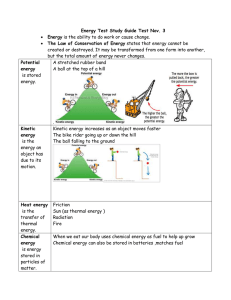
... Energy Test Study Guide Test Nov. 3 Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It may be transformed from one form into another, but the total amount of energy never changes. A stretched rubber band A ball at ...
... Energy Test Study Guide Test Nov. 3 Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It may be transformed from one form into another, but the total amount of energy never changes. A stretched rubber band A ball at ...
Energy Notes with Answers energy_notes_with_answers
... Energy Notes Energy: The work that energy allows us to do can be divided into 5 main tasks. 1.) Produce ...
... Energy Notes Energy: The work that energy allows us to do can be divided into 5 main tasks. 1.) Produce ...
1 - Kawameeh Middle School
... Heterozygous 28. A child has blue eyes, but both of the child’s parents have brown eyes. Create a Punnett Square below that explains how this is possible. (B represents brown eye allele, b represents blue eye allele) ...
... Heterozygous 28. A child has blue eyes, but both of the child’s parents have brown eyes. Create a Punnett Square below that explains how this is possible. (B represents brown eye allele, b represents blue eye allele) ...
Example
... in terms of minutes. So mathematics can enable us to get the number of bacteria without counting them under microscope. ...
... in terms of minutes. So mathematics can enable us to get the number of bacteria without counting them under microscope. ...
Energy_Basics
... Forms of Energy Can be found in many forms Can be converted from one form or another Conversion can be both man made and natural process All forms of energy fall under two categories: – Potential - gravitational, chemical, nuclear and stored mechanical; – Kinetic - sound, electrical, thermal, radia ...
... Forms of Energy Can be found in many forms Can be converted from one form or another Conversion can be both man made and natural process All forms of energy fall under two categories: – Potential - gravitational, chemical, nuclear and stored mechanical; – Kinetic - sound, electrical, thermal, radia ...
Slide 1
... 3) Electrical Energy- the energy of moving electrons. Electrons are negatively charged particles of an ...
... 3) Electrical Energy- the energy of moving electrons. Electrons are negatively charged particles of an ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy Problems
... 1) What is the gravitational constant on Earth? 2) What is the Potential Energy of a 10 N (pay attention to the unit, Newtons, here) book that is placed on a shelf that is 2.5 meters high? 3) Determine the amount of potential energy of a 5 N book that is moved to three different shelves on a bookcas ...
... 1) What is the gravitational constant on Earth? 2) What is the Potential Energy of a 10 N (pay attention to the unit, Newtons, here) book that is placed on a shelf that is 2.5 meters high? 3) Determine the amount of potential energy of a 5 N book that is moved to three different shelves on a bookcas ...
Energy Resources Notes
... Natural gas is used for heating and generating electricity. Methane is the main component of natural gas. Butane and propane also come from natural gas. ...
... Natural gas is used for heating and generating electricity. Methane is the main component of natural gas. Butane and propane also come from natural gas. ...
Energy Study Guide Key
... 6. List and briefly explain the renewable energy sources. a. Wind: uneven heating of the earth’s surface by the sun; used to make electricity and thought to be always available b. Hydroelectric power (water): created on rivers; uses renewable natural resources; generates electrical energy c. Solar: ...
... 6. List and briefly explain the renewable energy sources. a. Wind: uneven heating of the earth’s surface by the sun; used to make electricity and thought to be always available b. Hydroelectric power (water): created on rivers; uses renewable natural resources; generates electrical energy c. Solar: ...
Zero-energy building

A zero-energy building, also known as a zero net energy (ZNE) building, net-zero energy building (NZEB), or net zero building, is a building with zero net energy consumption, meaning the total amount of energy used by the building on an annual basis is roughly equal to the amount of renewable energy created on the site. These buildings consequently do not increase the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. They do at times consume non-renewable energy and produce greenhouse gases, but at other times reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas production elsewhere by the same amount.Most zero net energy buildings get half or more of their energy from the grid, and return the same amount at other times. Buildings that produce a surplus of energy over the year may be called ""energy-plus buildings"" and buildings that consume slightly more energy than they produce are called ""near-zero energy buildings"" or ""ultra-low energy houses"".Traditional buildings consume 40% of the total fossil fuel energy in the US and European Union and are significant contributors of greenhouse gases. The zero net energy consumption principle is viewed as a means to reduce carbon emissions and reduce dependence on fossil fuels and although zero-energy buildings remain uncommon even in developed countries, they are gaining importance and popularity.Most zero-energy buildings use the electrical grid for energy storage but some are independent of grid. Energy is usually harvested on-site through a combination of energy producing technologies like solar and wind, while reducing the overall use of energy with highly efficient HVAC and lighting technologies. The zero-energy goal is becoming more practical as the costs of alternative energy technologies decrease and the costs of traditional fossil fuels increase.The development of modern zero-energy buildings became possible not only through the progress made in new energy and construction technologies and techniques, but it has also been significantly improved by academic research, which collects precise energy performance data on traditional and experimental buildings and provides performance parameters for advanced computer models to predict the efficacy of engineering designs. Zero Energy Building is considered as a part of smart grid. Some advantages of these buildings are as follow: Integration of renewable energy resources Integration of plug-in electric vehicles Implementation of zero-energy conceptsThe net zero concept is applicable to a wide range of resources due to the many options for producing and conserving resources in buildings (e.g. energy, water, waste). Energy is the first resource to be targeted because it is highly managed, expected to continually become more efficient, and the ability to distribute and allocate it will improve disaster resiliency.