Energy review 2016 - Mayfield City Schools
... 1. The energy associated with the motion and position of an object. is known as ___________________________ It is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy. 2. _________________________ is a quantity that is related to the ability of an object to change or cause change. 3. _____________________ ...
... 1. The energy associated with the motion and position of an object. is known as ___________________________ It is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy. 2. _________________________ is a quantity that is related to the ability of an object to change or cause change. 3. _____________________ ...
Energy Review Name: Fill in: 1. The energy associated with the
... 1. The energy associated with the motion and position of an object. is known as ___________________________ It is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy. 2. _________________________ is a quantity that is related to the ability of an object to change or cause change. 3. _____________________ ...
... 1. The energy associated with the motion and position of an object. is known as ___________________________ It is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy. 2. _________________________ is a quantity that is related to the ability of an object to change or cause change. 3. _____________________ ...
Chapter 12: Work and Energy
... 7. Using the lever, explain why it is easier to open a door by pushing near the knob rather than by the hinges. 8. Choose a compound machine that you use every day and identify the simple machines it contains. ...
... 7. Using the lever, explain why it is easier to open a door by pushing near the knob rather than by the hinges. 8. Choose a compound machine that you use every day and identify the simple machines it contains. ...
Chapter 3 Test – Energy! Name: ______ At its basic level, energy is
... 12. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that ___________________ can neither be created nor destroyed. 13. For example, when using an electric fan, some energy is converted to _________________ energy to turn the fan blades. 14. Some energy is converted into unwanted __________________ energy. ...
... 12. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that ___________________ can neither be created nor destroyed. 13. For example, when using an electric fan, some energy is converted to _________________ energy to turn the fan blades. 14. Some energy is converted into unwanted __________________ energy. ...
Energy
... What does Conservation of Energy mean? • Energy can flow from one object to another. • Energy cannot be created or destroyed. • It is converted from one form to another. • Energy in an isolated system is conserved. • This is also known as the first law of thermodynamics ...
... What does Conservation of Energy mean? • Energy can flow from one object to another. • Energy cannot be created or destroyed. • It is converted from one form to another. • Energy in an isolated system is conserved. • This is also known as the first law of thermodynamics ...
Chapter 5.1 Energy Changes in Chemical and Nuclear Reactions
... • The bathtub of water has the lower temperature because the average water molecule is moving slower • The total quantity of thermal energy is higher in the bathtub because there are mover water molecules in total ...
... • The bathtub of water has the lower temperature because the average water molecule is moving slower • The total quantity of thermal energy is higher in the bathtub because there are mover water molecules in total ...
Section 3 What is energy? Energy “Ability to do work” Anything that
... • Gravity=9.8 m/s2 Mechanical energy ME= PE + KE Chemical PE Formation and breaking of bonds Match releases energy as light and heat Kinetic energy The energy of an object due to its motion Depends on mass and speed Equation KE(J)=1/2 x mass(kg)x speed2(m/s)2 KE=1/2mv2 Radiant en ...
... • Gravity=9.8 m/s2 Mechanical energy ME= PE + KE Chemical PE Formation and breaking of bonds Match releases energy as light and heat Kinetic energy The energy of an object due to its motion Depends on mass and speed Equation KE(J)=1/2 x mass(kg)x speed2(m/s)2 KE=1/2mv2 Radiant en ...
Geothermal energy
... Most energy that we use comes from the burning of fossil fuels Renewable resource- a resource that is present in great abundance and is continually produced. Solar power- collect energy from the Sun Wind power- Turbines powered by wind use generators to convert wind to energy we can use Geothermal e ...
... Most energy that we use comes from the burning of fossil fuels Renewable resource- a resource that is present in great abundance and is continually produced. Solar power- collect energy from the Sun Wind power- Turbines powered by wind use generators to convert wind to energy we can use Geothermal e ...
energy - WordPress.com
... The total amount of energy in any closed system is constant. Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be converted from one form to another. If a physical system gains an amount of energy, another physical system must experience a loss of energy of the same amount. ...
... The total amount of energy in any closed system is constant. Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be converted from one form to another. If a physical system gains an amount of energy, another physical system must experience a loss of energy of the same amount. ...
Heat Energy - Waconia High School
... Example: Water (H2O) Breaking water into H & O will cause a release of chemical energy. ...
... Example: Water (H2O) Breaking water into H & O will cause a release of chemical energy. ...
energy
... (During nuclear fission, a small particle called a neutron hits the uranium atom and splits it, releasing a great amount of energy as heat and radiation) ...
... (During nuclear fission, a small particle called a neutron hits the uranium atom and splits it, releasing a great amount of energy as heat and radiation) ...
A Winter Inquiry Land Answer Key - Science - Miami
... Electrical energy - delivered by tiny charged particles called electrons, typically moving through a wire. Lightning is an example of electrical energy in nature, so powerful that it is not confined to a wire. (Type: Kinetic Energy) Sources answers may vary depending on source of electricity/power ...
... Electrical energy - delivered by tiny charged particles called electrons, typically moving through a wire. Lightning is an example of electrical energy in nature, so powerful that it is not confined to a wire. (Type: Kinetic Energy) Sources answers may vary depending on source of electricity/power ...
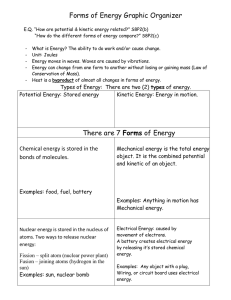
Forms of Energy
... What is Energy? The ability to do work and/or cause change. Unit: Joules Energy moves in waves. Waves are caused by vibrations. Energy can change from one form to another without losing or gaining mass (Law of Conservation of Mass). Heat is a byproduct of almost all changes in forms of energy. ...
... What is Energy? The ability to do work and/or cause change. Unit: Joules Energy moves in waves. Waves are caused by vibrations. Energy can change from one form to another without losing or gaining mass (Law of Conservation of Mass). Heat is a byproduct of almost all changes in forms of energy. ...
Pop Quiz pp. 151-155 What two forms of energy combine to make
... 1. What two forms of energy combine to make mechanical energy? 2. What kind of potential energy does a projectile have? 3. Lava was used as an example of this type of energy. 4. Food and fuels are examples of this type of energy. 5. What form of energy are microwaves? ...
... 1. What two forms of energy combine to make mechanical energy? 2. What kind of potential energy does a projectile have? 3. Lava was used as an example of this type of energy. 4. Food and fuels are examples of this type of energy. 5. What form of energy are microwaves? ...
Chapter 10 Energy PowerPoint
... Law of Conservation of Energy: Energy can neither be created or destroyed. When we use energy, we degrade its usefulness and the quality of that energy is lowered. Concentrated energy (like gasoline) used to do work becomes energy that is spread out throughout the universe. Energy concerns are b ...
... Law of Conservation of Energy: Energy can neither be created or destroyed. When we use energy, we degrade its usefulness and the quality of that energy is lowered. Concentrated energy (like gasoline) used to do work becomes energy that is spread out throughout the universe. Energy concerns are b ...
Resource Page Work, Power, and Energy
... SC.3.P.10.1 - Identify some basic forms of energy such as light, heat, sound, electrical, and mechanical. SC.3.P.10.2 - Recognize that energy has the ability to cause motion or create change. SC.3.P.10.3 - Demonstrate that light travels in a straight line until it strikes an object or travels from o ...
... SC.3.P.10.1 - Identify some basic forms of energy such as light, heat, sound, electrical, and mechanical. SC.3.P.10.2 - Recognize that energy has the ability to cause motion or create change. SC.3.P.10.3 - Demonstrate that light travels in a straight line until it strikes an object or travels from o ...
Energy Transformation Poster Rubric
... Create a poster of an energy transformation. Your transformation cannot be of one from class. being stored, transformed or transferred at all times. Any device that undergoes an energy conversion where stored energy (potential energy) is changed to active energy (kinetic energy) undergoes an energy ...
... Create a poster of an energy transformation. Your transformation cannot be of one from class. being stored, transformed or transferred at all times. Any device that undergoes an energy conversion where stored energy (potential energy) is changed to active energy (kinetic energy) undergoes an energy ...
short
... Energy Use per Person • The U.S. converts energy at the constant rate of about 10 kW per person • This is like having 100 “energy slaves” working full-time for every american child and adult person ...
... Energy Use per Person • The U.S. converts energy at the constant rate of about 10 kW per person • This is like having 100 “energy slaves” working full-time for every american child and adult person ...
CHAPTER 7: ENERGY RESOURCES
... 7. atomic: energy stored in the nucleus of an atom --Energy Conversions --changes in energy forms --most common energy conversions (convert: to change) 1. potential: energy at rest or stored energy 2. kinetic: energy put in motion --Law of Conservation: energy can be changed from one form to another ...
... 7. atomic: energy stored in the nucleus of an atom --Energy Conversions --changes in energy forms --most common energy conversions (convert: to change) 1. potential: energy at rest or stored energy 2. kinetic: energy put in motion --Law of Conservation: energy can be changed from one form to another ...
Chapter 5 Test
... 1) Objects that have been lifted against the force of _______________ have stored or potential energy. 2) A compressed spring also stores its __________ 3) Automobiles store _______________ energy in their gasoline tanks. C. Gravitational Potential Energy ...
... 1) Objects that have been lifted against the force of _______________ have stored or potential energy. 2) A compressed spring also stores its __________ 3) Automobiles store _______________ energy in their gasoline tanks. C. Gravitational Potential Energy ...
Extreme Energy - davis.k12.ut.us
... The Universe: Extreme Energy 1. Energy can be neither __________________ or ___________________, it can only be ___________________ from 1 type to another. 2. Where does the energy of the car crash come from? 3. What is potential energy? 4. What is Kinetic energy 5. When the bullet hits the target, ...
... The Universe: Extreme Energy 1. Energy can be neither __________________ or ___________________, it can only be ___________________ from 1 type to another. 2. Where does the energy of the car crash come from? 3. What is potential energy? 4. What is Kinetic energy 5. When the bullet hits the target, ...
Zero-energy building

A zero-energy building, also known as a zero net energy (ZNE) building, net-zero energy building (NZEB), or net zero building, is a building with zero net energy consumption, meaning the total amount of energy used by the building on an annual basis is roughly equal to the amount of renewable energy created on the site. These buildings consequently do not increase the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. They do at times consume non-renewable energy and produce greenhouse gases, but at other times reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas production elsewhere by the same amount.Most zero net energy buildings get half or more of their energy from the grid, and return the same amount at other times. Buildings that produce a surplus of energy over the year may be called ""energy-plus buildings"" and buildings that consume slightly more energy than they produce are called ""near-zero energy buildings"" or ""ultra-low energy houses"".Traditional buildings consume 40% of the total fossil fuel energy in the US and European Union and are significant contributors of greenhouse gases. The zero net energy consumption principle is viewed as a means to reduce carbon emissions and reduce dependence on fossil fuels and although zero-energy buildings remain uncommon even in developed countries, they are gaining importance and popularity.Most zero-energy buildings use the electrical grid for energy storage but some are independent of grid. Energy is usually harvested on-site through a combination of energy producing technologies like solar and wind, while reducing the overall use of energy with highly efficient HVAC and lighting technologies. The zero-energy goal is becoming more practical as the costs of alternative energy technologies decrease and the costs of traditional fossil fuels increase.The development of modern zero-energy buildings became possible not only through the progress made in new energy and construction technologies and techniques, but it has also been significantly improved by academic research, which collects precise energy performance data on traditional and experimental buildings and provides performance parameters for advanced computer models to predict the efficacy of engineering designs. Zero Energy Building is considered as a part of smart grid. Some advantages of these buildings are as follow: Integration of renewable energy resources Integration of plug-in electric vehicles Implementation of zero-energy conceptsThe net zero concept is applicable to a wide range of resources due to the many options for producing and conserving resources in buildings (e.g. energy, water, waste). Energy is the first resource to be targeted because it is highly managed, expected to continually become more efficient, and the ability to distribute and allocate it will improve disaster resiliency.