SC.4.P.11.1-11.2 - Energy Transfer and Transformation
... • SC.4.P.11.1 – Recognize that heat flows from a hot object to a cold object and that heat flow may cause materials to change temperature. • SC.4.P.11.2 – Identify common materials that conduct heat well or poorly. ...
... • SC.4.P.11.1 – Recognize that heat flows from a hot object to a cold object and that heat flow may cause materials to change temperature. • SC.4.P.11.2 – Identify common materials that conduct heat well or poorly. ...
Physical Science MidTerm Exam Study Guide
... 1. Name the chemical properties? 2. Density depends on what two things? 3. During physical changes, matter always retains its what? 4. The amount of space taken up by an object is known as the object's what? 5. Which group on the periodic table is the LEAST reactive? 6. Name 4 examples of physical c ...
... 1. Name the chemical properties? 2. Density depends on what two things? 3. During physical changes, matter always retains its what? 4. The amount of space taken up by an object is known as the object's what? 5. Which group on the periodic table is the LEAST reactive? 6. Name 4 examples of physical c ...
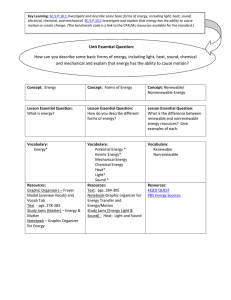
Energy Curriculum Map
... Key Learning: SC.5.P.10.1 Investigate and describe some basic forms of energy, including light, heat, sound, electrical, chemical, and mechanical SC.5.P.10.2 Investigate and explain that energy has the ability to cause motion or create change. (The benchmark code is a link to the CPALMs resources av ...
... Key Learning: SC.5.P.10.1 Investigate and describe some basic forms of energy, including light, heat, sound, electrical, chemical, and mechanical SC.5.P.10.2 Investigate and explain that energy has the ability to cause motion or create change. (The benchmark code is a link to the CPALMs resources av ...
Potential Energy
... Every change that occurs requires energy. Energy is the ability to do work. All moving objects have energy You can tell an object has energy when it: ...
... Every change that occurs requires energy. Energy is the ability to do work. All moving objects have energy You can tell an object has energy when it: ...
Superconcepts
... 1. Energy is the ability to move an object against a force, to raise the temperature of an object, or the potential to do either. 2. Unless they involve the use or production of gases, chemical reactions involve potential energy and heat, but not kinetic energy. 3. Energy is conserved, but is transf ...
... 1. Energy is the ability to move an object against a force, to raise the temperature of an object, or the potential to do either. 2. Unless they involve the use or production of gases, chemical reactions involve potential energy and heat, but not kinetic energy. 3. Energy is conserved, but is transf ...
Forms of Energy - Ms. Morgan's Science Spot
... The ability to do work or cause change Energy is measured in Joules (J) ...
... The ability to do work or cause change Energy is measured in Joules (J) ...
KE = 1 2 mv2
... • Energy takes many forms: mechanical, heat, light, and chemical are a few examples System – anything around which you can imagine a boundary Kinetic Energy – the energy an object has due to its mass and motion. • Equation for kinetic energy: ...
... • Energy takes many forms: mechanical, heat, light, and chemical are a few examples System – anything around which you can imagine a boundary Kinetic Energy – the energy an object has due to its mass and motion. • Equation for kinetic energy: ...
CURRICULUM MAPPING EXAMPLES Grade : 9 Physical Science
... (I, R, M) Gravity is a universal force that each mass exerts on every other mass. (SC-H-1.4.2) Students will examine how energy is transferred (e.g., collisions, light waves) and recognize that the total energy of the universe is constant; distinguish between types of energy (e.g., kinetic energy, p ...
... (I, R, M) Gravity is a universal force that each mass exerts on every other mass. (SC-H-1.4.2) Students will examine how energy is transferred (e.g., collisions, light waves) and recognize that the total energy of the universe is constant; distinguish between types of energy (e.g., kinetic energy, p ...
Curriculum Mapping Samples
... (I, R, M) Gravity is a universal force that each mass exerts on every other mass. (SC-H-1.4.2) Students will examine how energy is transferred (e.g., collisions, light waves) and recognize that the total energy of the universe is constant; distinguish between types of energy (e.g., kinetic energy, p ...
... (I, R, M) Gravity is a universal force that each mass exerts on every other mass. (SC-H-1.4.2) Students will examine how energy is transferred (e.g., collisions, light waves) and recognize that the total energy of the universe is constant; distinguish between types of energy (e.g., kinetic energy, p ...
potential energy.
... work is done on an object, energy is transferred to that object. Many forms of energy can be classified into two general types: kinetic energy and potential energy. ...
... work is done on an object, energy is transferred to that object. Many forms of energy can be classified into two general types: kinetic energy and potential energy. ...
Potential and Kinetic energy
... Example – 2. Energy is measured in _________________ B. Potential energy (PE) – 1. There are two types of potential energy a. _____________________________ – energy of position - Examples b. _____________________________ – stored energy - Examples 2. Energy that is waiting to be released C. __ ...
... Example – 2. Energy is measured in _________________ B. Potential energy (PE) – 1. There are two types of potential energy a. _____________________________ – energy of position - Examples b. _____________________________ – stored energy - Examples 2. Energy that is waiting to be released C. __ ...
How to Calculate Kinetic Energy
... velocity. To measure the smashing potential of this block, let’s determine the change in the block’s kinetic energy after the piston pushes it a distance d. The initial and final states of the process are pictured to the right. a) Draw a force diagram for the block. Use it to find an expression fo ...
... velocity. To measure the smashing potential of this block, let’s determine the change in the block’s kinetic energy after the piston pushes it a distance d. The initial and final states of the process are pictured to the right. a) Draw a force diagram for the block. Use it to find an expression fo ...
The modern atomic model has been developed using experimental
... 2. What do we call the little “packets” that our universe is made out of? (The small pieces that make everything else.) 3. The bigger a wavelength is, the ________ energy it has. We say that wavelength and energy are ___________ proportional. 4. The higher the frequency is, the _______ energy it has ...
... 2. What do we call the little “packets” that our universe is made out of? (The small pieces that make everything else.) 3. The bigger a wavelength is, the ________ energy it has. We say that wavelength and energy are ___________ proportional. 4. The higher the frequency is, the _______ energy it has ...
Properties of Matter
... Law of conservation of matter : matter is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction, ie., the total weight of substances before they react is the same as after they react. ...
... Law of conservation of matter : matter is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction, ie., the total weight of substances before they react is the same as after they react. ...
Forms of Energy Review
... converts electrical energy into light (electromagnetic) energy and heat (thermal) energy ...
... converts electrical energy into light (electromagnetic) energy and heat (thermal) energy ...
Mechanical Energy Conservation
... Energy is “conserved” if we can add up all of the different types of energy present in a closed system and see that the total sum remains constant. A “closed system” is one where no energy is added to or taken away from the system (in our case, a system with negligible friction) The types of ene ...
... Energy is “conserved” if we can add up all of the different types of energy present in a closed system and see that the total sum remains constant. A “closed system” is one where no energy is added to or taken away from the system (in our case, a system with negligible friction) The types of ene ...
Energy - RidenourMHS
... - Total amount of kinetic energy - The more particles move, the more kinetic energy, which means the more thermal energy ...
... - Total amount of kinetic energy - The more particles move, the more kinetic energy, which means the more thermal energy ...
ENERGY
... • Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it only changes form • Energy in = energy out • Heat, light and sound are common forms of energy transfer ...
... • Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it only changes form • Energy in = energy out • Heat, light and sound are common forms of energy transfer ...
Types and Forms of Energy
... everything from remotecontrolled cars to refrigerators. • Lightning and static electricity are also forms of electrical energy. ...
... everything from remotecontrolled cars to refrigerators. • Lightning and static electricity are also forms of electrical energy. ...
Forms of Energy Research Energy Form Description Examples and
... As you have studied potential and kinetic energy, you have realized that energy cannot be created or destroyed. Instead, energy transfers from one form to another. You are already familiar with mechanical energy, (the energy of motion), but what about when objects are not in motion? What are the oth ...
... As you have studied potential and kinetic energy, you have realized that energy cannot be created or destroyed. Instead, energy transfers from one form to another. You are already familiar with mechanical energy, (the energy of motion), but what about when objects are not in motion? What are the oth ...
Definitions: Thermal energy
... Our model of matter as composed of many small moving particles allows us to extend energy conservation to include resistive forces. The energy associated with the motion of a single object is coherent; all parts of the object move in the same way. The object has a net momentum associated with its ki ...
... Our model of matter as composed of many small moving particles allows us to extend energy conservation to include resistive forces. The energy associated with the motion of a single object is coherent; all parts of the object move in the same way. The object has a net momentum associated with its ki ...
Energy Terms and Concepts
... Energy can be converted from one form to another. For example stored chemical energy in a battery can be converted to light in a ...
... Energy can be converted from one form to another. For example stored chemical energy in a battery can be converted to light in a ...
Energy - TeacherWeb
... • Energy is the ability to do work, measured in joules (J) • Work is the amount of energy transferred by a force over a distance, also measured in joules (J) ...
... • Energy is the ability to do work, measured in joules (J) • Work is the amount of energy transferred by a force over a distance, also measured in joules (J) ...
Zero-energy building

A zero-energy building, also known as a zero net energy (ZNE) building, net-zero energy building (NZEB), or net zero building, is a building with zero net energy consumption, meaning the total amount of energy used by the building on an annual basis is roughly equal to the amount of renewable energy created on the site. These buildings consequently do not increase the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. They do at times consume non-renewable energy and produce greenhouse gases, but at other times reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas production elsewhere by the same amount.Most zero net energy buildings get half or more of their energy from the grid, and return the same amount at other times. Buildings that produce a surplus of energy over the year may be called ""energy-plus buildings"" and buildings that consume slightly more energy than they produce are called ""near-zero energy buildings"" or ""ultra-low energy houses"".Traditional buildings consume 40% of the total fossil fuel energy in the US and European Union and are significant contributors of greenhouse gases. The zero net energy consumption principle is viewed as a means to reduce carbon emissions and reduce dependence on fossil fuels and although zero-energy buildings remain uncommon even in developed countries, they are gaining importance and popularity.Most zero-energy buildings use the electrical grid for energy storage but some are independent of grid. Energy is usually harvested on-site through a combination of energy producing technologies like solar and wind, while reducing the overall use of energy with highly efficient HVAC and lighting technologies. The zero-energy goal is becoming more practical as the costs of alternative energy technologies decrease and the costs of traditional fossil fuels increase.The development of modern zero-energy buildings became possible not only through the progress made in new energy and construction technologies and techniques, but it has also been significantly improved by academic research, which collects precise energy performance data on traditional and experimental buildings and provides performance parameters for advanced computer models to predict the efficacy of engineering designs. Zero Energy Building is considered as a part of smart grid. Some advantages of these buildings are as follow: Integration of renewable energy resources Integration of plug-in electric vehicles Implementation of zero-energy conceptsThe net zero concept is applicable to a wide range of resources due to the many options for producing and conserving resources in buildings (e.g. energy, water, waste). Energy is the first resource to be targeted because it is highly managed, expected to continually become more efficient, and the ability to distribute and allocate it will improve disaster resiliency.