Additional Energy Terms
... Name and describe different types of energy. • Potential: chemical, gravitational, elastic, nuclear, magnetic • Kinetic: motion, heat, electric, light, sound What can happen to energy? • Transfer or transformation. Always conserved. Heat energy: movement/vibration of molecules. Measured by temperatu ...
... Name and describe different types of energy. • Potential: chemical, gravitational, elastic, nuclear, magnetic • Kinetic: motion, heat, electric, light, sound What can happen to energy? • Transfer or transformation. Always conserved. Heat energy: movement/vibration of molecules. Measured by temperatu ...
Chapter 13
... both • Different forces can do the same amount of work – Figure 3 ( a box lifted vs a box pushed up a ramp ) ...
... both • Different forces can do the same amount of work – Figure 3 ( a box lifted vs a box pushed up a ramp ) ...
Energy Unit Class Notes
... Energy Unit Class Notes Energy – the ability to do work (joules) - kinetic and potential Types of Energy 1. Mechanical – the energy of movement or position (KE + PE) - sound is an example of mechanical energy 2. Thermal (heat) energy – total energy of the moving molecules within a substance Temperat ...
... Energy Unit Class Notes Energy – the ability to do work (joules) - kinetic and potential Types of Energy 1. Mechanical – the energy of movement or position (KE + PE) - sound is an example of mechanical energy 2. Thermal (heat) energy – total energy of the moving molecules within a substance Temperat ...
Energy - Reocities
... Energy Energy defined as the capacity to do work, may exist in potential, kinetic, thermal, electrical, chemical, nuclear, or other various forms. There are, moreover, heat and work-i.e. energy in the process of transfer from one body to another. After it has been transferred, energy is always desig ...
... Energy Energy defined as the capacity to do work, may exist in potential, kinetic, thermal, electrical, chemical, nuclear, or other various forms. There are, moreover, heat and work-i.e. energy in the process of transfer from one body to another. After it has been transferred, energy is always desig ...
File - Ms. Conger*6th Grade Science
... we talked about during this lesson (k_______ and p________) ...
... we talked about during this lesson (k_______ and p________) ...
Energy and Forces
... energy, and mechanical energy D3i Use examples of energy transformations from one form to another to explain that energy cannot be created or destroyed E2D Describe how matter and energy change from one form to another in living things and in the physical environment. …and take a stab at these new N ...
... energy, and mechanical energy D3i Use examples of energy transformations from one form to another to explain that energy cannot be created or destroyed E2D Describe how matter and energy change from one form to another in living things and in the physical environment. …and take a stab at these new N ...
Energy and energy resources
... Other types of energy Electrical- when the electrons in a wire ( or other substance) move back and forth. Sound- is the movement and vibrations of particles in the air, usually caused by movement. ( needs particles to work, there is no sound in space, so a space ship blowing up would actually b ...
... Other types of energy Electrical- when the electrons in a wire ( or other substance) move back and forth. Sound- is the movement and vibrations of particles in the air, usually caused by movement. ( needs particles to work, there is no sound in space, so a space ship blowing up would actually b ...
Energy Worksheet
... 1. Energy that is stored within an object is called ________ energy. 2. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands store_________ energy. 3. The vibration and movements of the atoms and molecules within substances is called heat or ________ energy. 4. The energy stored in the centre of atoms is c ...
... 1. Energy that is stored within an object is called ________ energy. 2. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands store_________ energy. 3. The vibration and movements of the atoms and molecules within substances is called heat or ________ energy. 4. The energy stored in the centre of atoms is c ...
How is Work and Power Related? Chapter 5 Work and Power
... energy, kinetic energy, potential energy, power and use the concept of conservation of energy ...
... energy, kinetic energy, potential energy, power and use the concept of conservation of energy ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy Notes
... Energy Conversion Examples • Kinetic to potential – skateboarding to the top of the ramp and doing a stall • Potential to kinetic – standing on a diving board then jumping off • Light energy to chemical – photosynthesis in plants • Chemical to kinetic – eating breakfast and using that energy to wal ...
... Energy Conversion Examples • Kinetic to potential – skateboarding to the top of the ramp and doing a stall • Potential to kinetic – standing on a diving board then jumping off • Light energy to chemical – photosynthesis in plants • Chemical to kinetic – eating breakfast and using that energy to wal ...
Energy - Office Mix
... Energy: Ability to do work Different Types of Energy The Ninja, a roller coaster at Six Flags over Georgia, has a height of 122 ft and a speed of 52 mi/h. The potential energy due to its height changes into kinetic energy of motion. ...
... Energy: Ability to do work Different Types of Energy The Ninja, a roller coaster at Six Flags over Georgia, has a height of 122 ft and a speed of 52 mi/h. The potential energy due to its height changes into kinetic energy of motion. ...
Classifying Matter and the Periodic Table
... .25 kg baseball at 50 m/s = ½ (.25kg) (50 m/s)2 = 312 J ...
... .25 kg baseball at 50 m/s = ½ (.25kg) (50 m/s)2 = 312 J ...
Energy and Power - Reeths
... • Example 1- A bike on top of a hill waiting to get the energy out by going down the hill. • Example 2- Sleeping before awakening to alarm ...
... • Example 1- A bike on top of a hill waiting to get the energy out by going down the hill. • Example 2- Sleeping before awakening to alarm ...
energy - staff.harrisonburg.k12.va
... 2. Potential energy - energy that is stored in an object Examples: holding a ball before you drop it, a book on the edge of a table, a roller coaster at the top *As potential energy decreases, kinetic energy increases. ...
... 2. Potential energy - energy that is stored in an object Examples: holding a ball before you drop it, a book on the edge of a table, a roller coaster at the top *As potential energy decreases, kinetic energy increases. ...
Energy Assesment 1
... Sources of Energy Q5 . Sources of energy are often divided into renewable and non-renewable. Briefly describe where mankind currently gets most of its energy and why this is unsustainable (in the long term) Q6. The following website provides some good information about energy. ...
... Sources of Energy Q5 . Sources of energy are often divided into renewable and non-renewable. Briefly describe where mankind currently gets most of its energy and why this is unsustainable (in the long term) Q6. The following website provides some good information about energy. ...
924 Lecture, Energy
... 1. Conservation of energy: Energy is neither created nor destroyed; it is transformed. you can't take out of a system more than you put in. you can't win 2. The entropy of the universe is continually increasing. perpetual motion and a heat engine with 100% efficiency are both impossible. you can't b ...
... 1. Conservation of energy: Energy is neither created nor destroyed; it is transformed. you can't take out of a system more than you put in. you can't win 2. The entropy of the universe is continually increasing. perpetual motion and a heat engine with 100% efficiency are both impossible. you can't b ...
Study Guide Energy
... 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? ____________ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? ____________ 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _________ ...
... 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? ____________ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? ____________ 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _________ ...
The BIG Idea— Energy is the ability to do work or make something
... headphone piece, which causes the air to vibrate. Energy Conversion [C]: The ipod has light energy. The electrical energy converts to light energy because it lights up the display screen on the ipod. ...
... headphone piece, which causes the air to vibrate. Energy Conversion [C]: The ipod has light energy. The electrical energy converts to light energy because it lights up the display screen on the ipod. ...
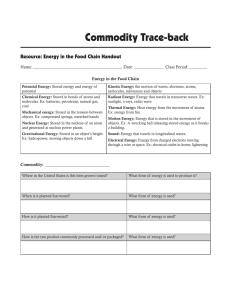
Energy in the Food Chain Handout
... objects. Ex: compressed springs, stretched bands Nuclear Energy: Stored in the nucleus of an atom and generated at nuclear power plants. Gravitational Energy: Stored in an object’s height. Ex: hydropower, moving objects down a hill ...
... objects. Ex: compressed springs, stretched bands Nuclear Energy: Stored in the nucleus of an atom and generated at nuclear power plants. Gravitational Energy: Stored in an object’s height. Ex: hydropower, moving objects down a hill ...
In every transformation, some energy is always transferred into
... What force affects potential energy due to position? What is meant by stored chemical energy? Give an example of potential energy due to position and potential energy due to chemical composition. How is the compression of an object considered potential energy? Students should be able to id ...
... What force affects potential energy due to position? What is meant by stored chemical energy? Give an example of potential energy due to position and potential energy due to chemical composition. How is the compression of an object considered potential energy? Students should be able to id ...
Transformations of Energy Notes
... There are two general categories of waves: Mechanical and Electromagnetic Mechanical waves must move through solids, liquids, or gases to transport their energy. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum (empty space). The matter that a wave travels through is called a medium. For example, t ...
... There are two general categories of waves: Mechanical and Electromagnetic Mechanical waves must move through solids, liquids, or gases to transport their energy. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum (empty space). The matter that a wave travels through is called a medium. For example, t ...
The Down-Low On Energy
... There are many ways to measure energy but one of the main constant units of measure is the: • BTU: British Thermal Unit • 1 BTU is the amount of energy it takes to heat 1 pound of water 1 degrees F. ...
... There are many ways to measure energy but one of the main constant units of measure is the: • BTU: British Thermal Unit • 1 BTU is the amount of energy it takes to heat 1 pound of water 1 degrees F. ...
Zero-energy building

A zero-energy building, also known as a zero net energy (ZNE) building, net-zero energy building (NZEB), or net zero building, is a building with zero net energy consumption, meaning the total amount of energy used by the building on an annual basis is roughly equal to the amount of renewable energy created on the site. These buildings consequently do not increase the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. They do at times consume non-renewable energy and produce greenhouse gases, but at other times reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas production elsewhere by the same amount.Most zero net energy buildings get half or more of their energy from the grid, and return the same amount at other times. Buildings that produce a surplus of energy over the year may be called ""energy-plus buildings"" and buildings that consume slightly more energy than they produce are called ""near-zero energy buildings"" or ""ultra-low energy houses"".Traditional buildings consume 40% of the total fossil fuel energy in the US and European Union and are significant contributors of greenhouse gases. The zero net energy consumption principle is viewed as a means to reduce carbon emissions and reduce dependence on fossil fuels and although zero-energy buildings remain uncommon even in developed countries, they are gaining importance and popularity.Most zero-energy buildings use the electrical grid for energy storage but some are independent of grid. Energy is usually harvested on-site through a combination of energy producing technologies like solar and wind, while reducing the overall use of energy with highly efficient HVAC and lighting technologies. The zero-energy goal is becoming more practical as the costs of alternative energy technologies decrease and the costs of traditional fossil fuels increase.The development of modern zero-energy buildings became possible not only through the progress made in new energy and construction technologies and techniques, but it has also been significantly improved by academic research, which collects precise energy performance data on traditional and experimental buildings and provides performance parameters for advanced computer models to predict the efficacy of engineering designs. Zero Energy Building is considered as a part of smart grid. Some advantages of these buildings are as follow: Integration of renewable energy resources Integration of plug-in electric vehicles Implementation of zero-energy conceptsThe net zero concept is applicable to a wide range of resources due to the many options for producing and conserving resources in buildings (e.g. energy, water, waste). Energy is the first resource to be targeted because it is highly managed, expected to continually become more efficient, and the ability to distribute and allocate it will improve disaster resiliency.