enzymatic resolution of a racemic mixture by acylation in
... also supercritical fluids (sc-fluids) and ionic liquids. Ionic liquids offer a new approach for catalyst recycling/reutilization when combined with a sc-fluid [1], [2]: e.g. the enzyme remains in the ionic liquid and reaction products can be extracted with sc-CO2. Biocatalysis is a convenient method ...
... also supercritical fluids (sc-fluids) and ionic liquids. Ionic liquids offer a new approach for catalyst recycling/reutilization when combined with a sc-fluid [1], [2]: e.g. the enzyme remains in the ionic liquid and reaction products can be extracted with sc-CO2. Biocatalysis is a convenient method ...
Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions
... - must consider regioselectivity when using substituted benzenes directing effects: o/p or m (see handout) ...
... - must consider regioselectivity when using substituted benzenes directing effects: o/p or m (see handout) ...
Exam 2
... worth studying. Also problems assigned for the text may also be helpful. Chap 9 &10-- Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1 reactions. -Know the definitions of Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1. -Be able to depict the reaction coordinate diagrams of each reaction -Be able to draw the mechanism, products and the stereochemical resu ...
... worth studying. Also problems assigned for the text may also be helpful. Chap 9 &10-- Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1 reactions. -Know the definitions of Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1. -Be able to depict the reaction coordinate diagrams of each reaction -Be able to draw the mechanism, products and the stereochemical resu ...
Addition reactions
... bond the H (the E+) adds to the C with the most hydrogens & the X (the Nu:) adds to the most substituted carbon. - Vladimir V. Markovnikov, Russian, 1870 Substrate is an alkene & acts as the Nu: ...
... bond the H (the E+) adds to the C with the most hydrogens & the X (the Nu:) adds to the most substituted carbon. - Vladimir V. Markovnikov, Russian, 1870 Substrate is an alkene & acts as the Nu: ...
Addition Reactions
... acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is regioselective; hydrogen adds preferentially to the sp2 carbon with less # of hydrogens. ...
... acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is regioselective; hydrogen adds preferentially to the sp2 carbon with less # of hydrogens. ...
Ethers, Sulfides, Epoxides
... What can happen? Reactants are the aldehyde and concentrated hydroxide. Hydroxide ion can act both as Base, but remember we have no acidic hydrogens (no a hydrogens). Nucleophile, attacking carbonyl group. ...
... What can happen? Reactants are the aldehyde and concentrated hydroxide. Hydroxide ion can act both as Base, but remember we have no acidic hydrogens (no a hydrogens). Nucleophile, attacking carbonyl group. ...
AlCl3 heat HCl
... 10. (3 points) For each of the following pairs of SN2 reactions, indicate which reaction occurs faster. Explain. ...
... 10. (3 points) For each of the following pairs of SN2 reactions, indicate which reaction occurs faster. Explain. ...
The Grignard Reagent
... change in color when the reaction has started. – Use your time wisely. While one partner monitors reaction 1 the other should prepare the ester for reaction 2. – Most of the Mg will dissolve during the reaction. Any remaining Mg will dissolve in the work-up (week 2). – At the end of this week’s proc ...
... change in color when the reaction has started. – Use your time wisely. While one partner monitors reaction 1 the other should prepare the ester for reaction 2. – Most of the Mg will dissolve during the reaction. Any remaining Mg will dissolve in the work-up (week 2). – At the end of this week’s proc ...
CHEMISTRY 1000
... Cleavage of ethers is done via substitution reactions as well. Consider the following reaction: ...
... Cleavage of ethers is done via substitution reactions as well. Consider the following reaction: ...
Chapter Nine: Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides
... o Mechanism/ no rearrangement/ inversion of configuration d. Formation of Alkyl tosylates by reaction with sulfonyl chlorides 9.13 o Mechanism/ retention of configuration o Subsequent reaction of alkyl tosylates with nucleophiles/bases: 9.12C: Can’t use acid and any nucleophile! e. Formation of ket ...
... o Mechanism/ no rearrangement/ inversion of configuration d. Formation of Alkyl tosylates by reaction with sulfonyl chlorides 9.13 o Mechanism/ retention of configuration o Subsequent reaction of alkyl tosylates with nucleophiles/bases: 9.12C: Can’t use acid and any nucleophile! e. Formation of ket ...
4.6, 4.7 test - A
... Name the type of substitution reaction which follows the formation of the reactive species above and outline a mechanism for this substitution. Type of substitution ........................................................................................... Mechanism ...
... Name the type of substitution reaction which follows the formation of the reactive species above and outline a mechanism for this substitution. Type of substitution ........................................................................................... Mechanism ...
Practice Exam 4 - BioChemWeb.net
... 1. (20 pts.) Circle the correct answer. a. Which compound has the lowest pKa for dissociation of an proton? O ...
... 1. (20 pts.) Circle the correct answer. a. Which compound has the lowest pKa for dissociation of an proton? O ...
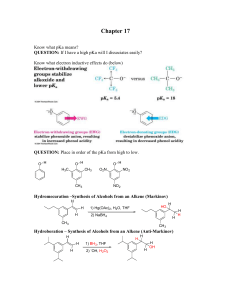
Chapter 17 - Ellis Benjamin
... Know what pKa means? QUESTION: If I have a high pKa will I dissociates easily? Know what electron inductive effects do (below) ...
... Know what pKa means? QUESTION: If I have a high pKa will I dissociates easily? Know what electron inductive effects do (below) ...
Chap Thirteen: Alcohols
... Predict the stereochemistry and optical activity of a product from an understanding of its mechanism of formation. Predict the acidity of alcohols relative to one another and relative to other functional groups Recognize structural features of a molecule that are key to its stability and react ...
... Predict the stereochemistry and optical activity of a product from an understanding of its mechanism of formation. Predict the acidity of alcohols relative to one another and relative to other functional groups Recognize structural features of a molecule that are key to its stability and react ...
Outline_CH13_Klein
... Predict the stereochemistry and optical activity of a product from an understanding of its mechanism of formation. Predict the acidity of alcohols relative to one another and relative to other functional groups Recognize structural features of a molecule that are key to its stability and react ...
... Predict the stereochemistry and optical activity of a product from an understanding of its mechanism of formation. Predict the acidity of alcohols relative to one another and relative to other functional groups Recognize structural features of a molecule that are key to its stability and react ...
handout alkenes from alcohols
... present as a catalyst which promotes the reaction but is not consumed in it. The hydroxyl group in R-OH is a poor-leaving group because it would have to leave as a hydroxide ion (HO-). Therefore, an acid is used to protonate the alcohol (step 1) and form R-OH2+ (see Figure 2). Thus, water (a much be ...
... present as a catalyst which promotes the reaction but is not consumed in it. The hydroxyl group in R-OH is a poor-leaving group because it would have to leave as a hydroxide ion (HO-). Therefore, an acid is used to protonate the alcohol (step 1) and form R-OH2+ (see Figure 2). Thus, water (a much be ...
handout alkenes from alcohols
... present as a catalyst which promotes the reaction but is not consumed in it. The hydroxyl group in R-OH is a poor-leaving group because it would have to leave as a hydroxide ion (HO-). Therefore, an acid is used to protonate the alcohol (step 1) and form R-OH2+ (see Figure 2). Thus, water (a much be ...
... present as a catalyst which promotes the reaction but is not consumed in it. The hydroxyl group in R-OH is a poor-leaving group because it would have to leave as a hydroxide ion (HO-). Therefore, an acid is used to protonate the alcohol (step 1) and form R-OH2+ (see Figure 2). Thus, water (a much be ...
Kazzie`s Guide to Orgo 2
... General Note: Some of these questions have been previously used in examples, etcetera, but they cover the things that I think are important to know from this semester. Try to work through them with as few resources as possible, and we will go through this at the final review. Chem 210 Stuff Identify ...
... General Note: Some of these questions have been previously used in examples, etcetera, but they cover the things that I think are important to know from this semester. Try to work through them with as few resources as possible, and we will go through this at the final review. Chem 210 Stuff Identify ...
PDF - International Journal of Medical Sciences
... the nuclear address (NLS) derived from SV40 T-antigen[32], which in turn is linked via a disulfide-bridge to a peptide facilitating the passage across cell membranes (CPP)[33]. This is our BioShuttle-conjugate resulting in a Cell Nucleus (NLS)-GdxSc3-xN@C80. For simplification in the text it is call ...
... the nuclear address (NLS) derived from SV40 T-antigen[32], which in turn is linked via a disulfide-bridge to a peptide facilitating the passage across cell membranes (CPP)[33]. This is our BioShuttle-conjugate resulting in a Cell Nucleus (NLS)-GdxSc3-xN@C80. For simplification in the text it is call ...
Exam 1 from 2008
... d) Although this is the structure that is usually drawn for amoxicillin (e.g., see Wikipedia), it is not accurate. Considering what you know about the acid-base properties of the functional groups in Amoxicillin, draw a more accurate representation. ...
... d) Although this is the structure that is usually drawn for amoxicillin (e.g., see Wikipedia), it is not accurate. Considering what you know about the acid-base properties of the functional groups in Amoxicillin, draw a more accurate representation. ...
Answers
... Draw a mechanism for the basic elimination of a beta-hydroxy carbonyl Draw a mechanism for the basic elimination of an alkyl halide Explain the basis of the thermodynamic favorability of basic eliminations Predict the product of elimination reactions ...
... Draw a mechanism for the basic elimination of a beta-hydroxy carbonyl Draw a mechanism for the basic elimination of an alkyl halide Explain the basis of the thermodynamic favorability of basic eliminations Predict the product of elimination reactions ...
Practice problems for week 8 PDF
... Chem 275 Practice Problem Set – Friday, October 15, 2010 – J. Magolan ...
... Chem 275 Practice Problem Set – Friday, October 15, 2010 – J. Magolan ...
Microsoft Word
... The reaction of an aldehyde with nitromethane in the presence of a chiral guanidine gave the expected nitroaldol product in 14-59% yield, albeit with low enantioselectivity (2-10% ee). Section B. The catalytic asymmetric Michael addition reaction. To the best of our knowledge, there is a sole study ...
... The reaction of an aldehyde with nitromethane in the presence of a chiral guanidine gave the expected nitroaldol product in 14-59% yield, albeit with low enantioselectivity (2-10% ee). Section B. The catalytic asymmetric Michael addition reaction. To the best of our knowledge, there is a sole study ...
Exam 3 - Chemistry
... For SN2, stabilization of the transition state speeds the reaction. By the Hammond postulate the transition state ‘resembles’ the starting alkyl halide. Both of these are secondary. But since ...
... For SN2, stabilization of the transition state speeds the reaction. By the Hammond postulate the transition state ‘resembles’ the starting alkyl halide. Both of these are secondary. But since ...
Diels–Alder reaction
.png?width=300)
The Diels–Alder reaction is an organic chemical reaction (specifically, a [4+2] cycloaddition) between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexene system. It was first described by Otto Paul Hermann Diels and Kurt Alder in 1928, for which work they were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1950. The Diels–Alder reaction is particularly useful in synthetic organic chemistry as a reliable method for forming 6-membered systems with good control over regio- and stereochemical properties. The underlying concept has also been applied to other π-systems, such as carbonyls and imines, to furnish the corresponding heterocycles, known as the hetero-Diels–Alder reaction. Diels–Alder reactions can be reversible under certain conditions; the reverse reaction is known as the retro-Diels–Alder reaction.