Introduction to Organic Synthesis 2011
... Me O functional groups into the molecule at Me the right places! Me O • That can often be a problem, as the ...
... Me O functional groups into the molecule at Me the right places! Me O • That can often be a problem, as the ...
Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides
... Don’t forget about using tosylates in substitution and elimination reactions as well. In many cases, they are better than their halide counterparts. Reaction of ethers and epoxides: ...
... Don’t forget about using tosylates in substitution and elimination reactions as well. In many cases, they are better than their halide counterparts. Reaction of ethers and epoxides: ...
14_chapter 8
... The preparation of aromatic aldehydes from benzylic halides, therefore, is an attractive route to aromatic aldehydes as it involves no special conditions such as very high temperature, pressure and proceeds smoothly without any special catalyst and several methods have been developed to carry out t ...
... The preparation of aromatic aldehydes from benzylic halides, therefore, is an attractive route to aromatic aldehydes as it involves no special conditions such as very high temperature, pressure and proceeds smoothly without any special catalyst and several methods have been developed to carry out t ...
PowerPoint **
... Draw mechanisms for the following reaction and explain why carbonyl acid can’t undergo similar reaction ...
... Draw mechanisms for the following reaction and explain why carbonyl acid can’t undergo similar reaction ...
The Aldol Condensation Preparation of 4
... The activation of the alpha hydrogen by a carbonyl group had been encountered empirically before van't Hoff's speculation. Use of the aldol condensation resulted from Wurtz's studies of aldehydes … The aldol condensation proved to be a general reaction of aldehydes with some ketones, provided hydrog ...
... The activation of the alpha hydrogen by a carbonyl group had been encountered empirically before van't Hoff's speculation. Use of the aldol condensation resulted from Wurtz's studies of aldehydes … The aldol condensation proved to be a general reaction of aldehydes with some ketones, provided hydrog ...
Option G Further Organic Chemistry
... The directing effects can be explained in terms of the charge distribution of the intermediates. The slightly increased reactivity due to the presence of –CH3 can be explained in terms of its electronreleasing nature. The greatly increased reactivity due to the presence of –OH can be explained in te ...
... The directing effects can be explained in terms of the charge distribution of the intermediates. The slightly increased reactivity due to the presence of –CH3 can be explained in terms of its electronreleasing nature. The greatly increased reactivity due to the presence of –OH can be explained in te ...
HONORS ORGANIC CHEM. HAHS MRS. RICHARDS 1 ORGANIC
... 29. We have seen two types of reaction mechanisms that do not occur through carbocation intermediates. What are they? (*We have seen several reactions that do not occur through carbocations; this question is specifically about reactions for which we have seen mechanisms.) 30. Draw the mechanism for ...
... 29. We have seen two types of reaction mechanisms that do not occur through carbocation intermediates. What are they? (*We have seen several reactions that do not occur through carbocations; this question is specifically about reactions for which we have seen mechanisms.) 30. Draw the mechanism for ...
Physical Organic Chemistry
... unsimilar alkyls on alkyl halides like 2-chloro-2-methylbutane, can form one alkene or more. Depending on the relativity rate of beta elimination The use of HO - or NH2 - will form more stable alkene which contain less number of Hydrogen and more number of alkyl groups bonded to double bond carb ...
... unsimilar alkyls on alkyl halides like 2-chloro-2-methylbutane, can form one alkene or more. Depending on the relativity rate of beta elimination The use of HO - or NH2 - will form more stable alkene which contain less number of Hydrogen and more number of alkyl groups bonded to double bond carb ...
CHM2210 Organic Chemistry 1
... 3. evaluating potential energy diagrams to determine the relative energy of reactants and products and to establish whether a reaction is endothermic, exothermic, endergonic or exergonic. 4. evaluating potential energy diagrams to determine the relative stability of conformers. 5. justifying the ...
... 3. evaluating potential energy diagrams to determine the relative energy of reactants and products and to establish whether a reaction is endothermic, exothermic, endergonic or exergonic. 4. evaluating potential energy diagrams to determine the relative stability of conformers. 5. justifying the ...
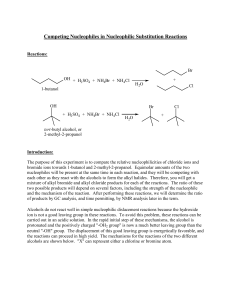
Competing Nucleophiles in Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
... speed up this cooling process by immersing the reaction flask in a beaker of cold water. Do not remove the condenser until the flask is cool. At this point you should see an organic layer on top of the reaction mixture (The solvent-nucleophile medium has a large density). Add 1.5 mL of diethyl ether ...
... speed up this cooling process by immersing the reaction flask in a beaker of cold water. Do not remove the condenser until the flask is cool. At this point you should see an organic layer on top of the reaction mixture (The solvent-nucleophile medium has a large density). Add 1.5 mL of diethyl ether ...
Chapter 15
... • Activators are electron donors, so their stabilizing effects would be greater with the carbocation directly bonded to them. • Thus, all activators are ortho/para directors • By contrast, deactivator are electron withdrawing groups, so they want to avoid being directly bonded to the carbocation • T ...
... • Activators are electron donors, so their stabilizing effects would be greater with the carbocation directly bonded to them. • Thus, all activators are ortho/para directors • By contrast, deactivator are electron withdrawing groups, so they want to avoid being directly bonded to the carbocation • T ...
Experiment 7 – Dehydration of Methylcyclohexanols
... product. The regiospecificity of the reaction is dependent on Zaitsev’s rule, where the major product tends to be the more substituted alkene. When two different products are possible, these products are constitutional isomers of each other or in this case can be referred to as regioisomers. The typ ...
... product. The regiospecificity of the reaction is dependent on Zaitsev’s rule, where the major product tends to be the more substituted alkene. When two different products are possible, these products are constitutional isomers of each other or in this case can be referred to as regioisomers. The typ ...
Modules 261 12th edition
... How to test for Chirality: Planes of symmetry Naming Enantiomers: The R, S –System How to Assign (R) and (S) Configurations Properties of Enantiomers: Optical Activity - specific rotation - Plane polarized light - The polarimeter Racemic forms - Racemic forms and Enantiomeric Excess The Synthesis of ...
... How to test for Chirality: Planes of symmetry Naming Enantiomers: The R, S –System How to Assign (R) and (S) Configurations Properties of Enantiomers: Optical Activity - specific rotation - Plane polarized light - The polarimeter Racemic forms - Racemic forms and Enantiomeric Excess The Synthesis of ...
Stereoselective Reduction of Ketones with Sodium Borohydride
... – The carbon atoms is nuclophilic – Widely used to make new carbon-carbon bonds – Used to attach carbonyl groups of aldehydes, ketones, and ...
... – The carbon atoms is nuclophilic – Widely used to make new carbon-carbon bonds – Used to attach carbonyl groups of aldehydes, ketones, and ...
NaBH4 Reduction of Vanillin
... Aside from a lack of selectivity, LAH reacts violently with water and other hydroxylic compounds, and reductions using this reagent must be carried out under non‐protic, anhydrous conditions. This not only limits the solvents with which LAH can be used, but it presents greater challenges in th ...
... Aside from a lack of selectivity, LAH reacts violently with water and other hydroxylic compounds, and reductions using this reagent must be carried out under non‐protic, anhydrous conditions. This not only limits the solvents with which LAH can be used, but it presents greater challenges in th ...
Edexcel GCE - The Student Room
... (c) Lithium can react with chlorine to produce lithium chloride. When a sample of lithium chloride is heated in a Bunsen flame, a red colour is seen. (i) Draw a ‘dot and cross’ diagram of lithium chloride showing all the electrons. Indicate the charges clearly on your diagram. ...
... (c) Lithium can react with chlorine to produce lithium chloride. When a sample of lithium chloride is heated in a Bunsen flame, a red colour is seen. (i) Draw a ‘dot and cross’ diagram of lithium chloride showing all the electrons. Indicate the charges clearly on your diagram. ...
Reductive etherification of substituted cyclohexanones with
... donors. With MeOH only acetal formation occurred. Acid sites appear to be essential, since with Na-MCM-22 as catalyst in the etherification of 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone only a 5% yield was obtained after 24 h. The reductive etherification is irreversible. Starting from the ether, water and acetone i ...
... donors. With MeOH only acetal formation occurred. Acid sites appear to be essential, since with Na-MCM-22 as catalyst in the etherification of 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone only a 5% yield was obtained after 24 h. The reductive etherification is irreversible. Starting from the ether, water and acetone i ...
synthesis in industry
... give very low yields of the desired 2-alkyl-3-chloronaphthoquinones. Dialkylation and reduction of the quinone are major complications. Mild alkylating agents such as tetraalkyltins do not react with the dichloro compound unassisted, but we found that the alkylation can be catalyzed. For example, th ...
... give very low yields of the desired 2-alkyl-3-chloronaphthoquinones. Dialkylation and reduction of the quinone are major complications. Mild alkylating agents such as tetraalkyltins do not react with the dichloro compound unassisted, but we found that the alkylation can be catalyzed. For example, th ...
Organic Chemistry I Laboratory
... as they are formed. Their removal will shift the equilibrium towards formation of the alkene and thus increase the overall yield. If the reaction mixture is heated to a temperature above the boiling points of the product alkenes but below that of the reacting alcohol, most of the unreacted alcohol w ...
... as they are formed. Their removal will shift the equilibrium towards formation of the alkene and thus increase the overall yield. If the reaction mixture is heated to a temperature above the boiling points of the product alkenes but below that of the reacting alcohol, most of the unreacted alcohol w ...
Synthesis of (−)-Epibatidine - David A. Evans
... syntheses have been reported, few full syntheses are enantioselective.4 In this Letter, we wish to report a highly stereoselective synthesis of (-)-epibatidine by a route that is readily amenable to analogue production. Our approach to 1 relies on a selective hetero Diels-Alder reaction between bis- ...
... syntheses have been reported, few full syntheses are enantioselective.4 In this Letter, we wish to report a highly stereoselective synthesis of (-)-epibatidine by a route that is readily amenable to analogue production. Our approach to 1 relies on a selective hetero Diels-Alder reaction between bis- ...
Nucleophilic Substitution
... All nucleophiles will be more reactive in aprotic than protic solvents Those species that were most strongly solvated in polar protic solvents will "gain" the most reactivity in polar aprotic (e.g. F-). Polar aprotic solvents are typically only used when a polar protic solvent gives poor results due ...
... All nucleophiles will be more reactive in aprotic than protic solvents Those species that were most strongly solvated in polar protic solvents will "gain" the most reactivity in polar aprotic (e.g. F-). Polar aprotic solvents are typically only used when a polar protic solvent gives poor results due ...
Exam III
... stereospecific reactions, be able to show the structures for the alkene reactants. -given the structures of the reactants and the products be able to state whether a reaction is syn- or anti-. ...
... stereospecific reactions, be able to show the structures for the alkene reactants. -given the structures of the reactants and the products be able to state whether a reaction is syn- or anti-. ...
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
... If the nucleophile that adds to the aldehyde or ketone is an O or an N, a nucleophilic addition–elimination reaction ...
... If the nucleophile that adds to the aldehyde or ketone is an O or an N, a nucleophilic addition–elimination reaction ...
Diels–Alder reaction
.png?width=300)
The Diels–Alder reaction is an organic chemical reaction (specifically, a [4+2] cycloaddition) between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexene system. It was first described by Otto Paul Hermann Diels and Kurt Alder in 1928, for which work they were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1950. The Diels–Alder reaction is particularly useful in synthetic organic chemistry as a reliable method for forming 6-membered systems with good control over regio- and stereochemical properties. The underlying concept has also been applied to other π-systems, such as carbonyls and imines, to furnish the corresponding heterocycles, known as the hetero-Diels–Alder reaction. Diels–Alder reactions can be reversible under certain conditions; the reverse reaction is known as the retro-Diels–Alder reaction.