Synopsis
... diastereomeric sulfilimines behave in a stereoconvergent fashion and afford products with the same configuration at carbon. An efficient route to αhydroxy-β-amino acid derivatives AHDA and AHPBA was developed using a common advanced intermediate. The methodology provides aminoalcohol derivatives wit ...
... diastereomeric sulfilimines behave in a stereoconvergent fashion and afford products with the same configuration at carbon. An efficient route to αhydroxy-β-amino acid derivatives AHDA and AHPBA was developed using a common advanced intermediate. The methodology provides aminoalcohol derivatives wit ...
n - TU Chemnitz
... a) S. Kirchmeyer, A. Mertens, G. A. Olah, Synthesis 1983, 500–502; b) A. Hassner, R. Fibiger, A. S. Amarasekara, J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 22–27. a) P. Herczegh, M. Zsély, I. Kovács, G. Batta, F. J. Sztaricskai, Tetrahedron Lett. 1990, 31, 1195–1198. b) C. Gauthier, Y. Ramondenc, G. Plé, ...
... a) S. Kirchmeyer, A. Mertens, G. A. Olah, Synthesis 1983, 500–502; b) A. Hassner, R. Fibiger, A. S. Amarasekara, J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 22–27. a) P. Herczegh, M. Zsély, I. Kovács, G. Batta, F. J. Sztaricskai, Tetrahedron Lett. 1990, 31, 1195–1198. b) C. Gauthier, Y. Ramondenc, G. Plé, ...
Demonstrate skill in organic chemistry techniques.
... Predict the products of substitution and elimination reactions and explain what factors favor each type of reaction. Predict which mechanisms and products are most likely for a given set of reaction conditions. ...
... Predict the products of substitution and elimination reactions and explain what factors favor each type of reaction. Predict which mechanisms and products are most likely for a given set of reaction conditions. ...
Demonstrate skill in organic chemistry techniques.
... Predict the products of substitution and elimination reactions and explain what factors favor each type of reaction. Predict which mechanisms and products are most likely for a given set of reaction conditions. ...
... Predict the products of substitution and elimination reactions and explain what factors favor each type of reaction. Predict which mechanisms and products are most likely for a given set of reaction conditions. ...
Microwave-Enhanced Sulphated Zirconia and SZ/MCM
... When the aminolysis reaction takes place mainly through microwave assistance, the yields are typically lower than 5 %, although entries 11, 13, 15, 17 and 19 gave yields of 11, 12, 11, 36 and 9 %, respectively. Entries 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 14 and 18 did not afford any reaction products. The appl ...
... When the aminolysis reaction takes place mainly through microwave assistance, the yields are typically lower than 5 %, although entries 11, 13, 15, 17 and 19 gave yields of 11, 12, 11, 36 and 9 %, respectively. Entries 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 14 and 18 did not afford any reaction products. The appl ...
... is advantageous over the chemical ones, as they ensure the stereo-selective obtaining of the product. Although it has been shown that their chemical synthesis was well-developed, the method still employs toxic and expensive compounds to yield α and β-configuration products via several steps. Hence, ...
reactions of the conjugated dienes butadiene and isoprene alone
... Five types of modified clay catalysts were used in this study. Ni 2+-, Co 2+-, and Cr3+-montmorillonites were employed because they are known to be acidic catalysts; the Cr3+-exchanged samples are somewhat more acidic than the N F +- and Co2+-exchanged materials (see, e.g., Adams et al., 1982b; Mort ...
... Five types of modified clay catalysts were used in this study. Ni 2+-, Co 2+-, and Cr3+-montmorillonites were employed because they are known to be acidic catalysts; the Cr3+-exchanged samples are somewhat more acidic than the N F +- and Co2+-exchanged materials (see, e.g., Adams et al., 1982b; Mort ...
answer
... compound (Y), whose structure is shown on the right. Explain the formation of this product. ...
... compound (Y), whose structure is shown on the right. Explain the formation of this product. ...
Παρουσίαση του PowerPoint
... colorings and flavorings, perfumes, detergents and disinfectants. Research chemists synthesize natural products whose structure is uncertain, compounds for mechanistic investigations, possible intermediate in chemical and biological processes, thousands of potential drugs used in medical practice, a ...
... colorings and flavorings, perfumes, detergents and disinfectants. Research chemists synthesize natural products whose structure is uncertain, compounds for mechanistic investigations, possible intermediate in chemical and biological processes, thousands of potential drugs used in medical practice, a ...
Παρουσίαση του PowerPoint
... Before and during these syntheses, groups of chemists sitting around blackboards or piles of paper plan the work they are about to undertake. Possible routes are drawn out, criticized, modified again when the behavior of the compounds in the flask turns out to be different from what was expected, un ...
... Before and during these syntheses, groups of chemists sitting around blackboards or piles of paper plan the work they are about to undertake. Possible routes are drawn out, criticized, modified again when the behavior of the compounds in the flask turns out to be different from what was expected, un ...
Ch 23 Carbonyl Condensations
... - The first part is an alpha substitution, where the deprotonated C is the Nu and a + carbon (generally a carbonyl) on another molecule is the E+. - If the other molecule’s carbonyl has no LG, the reaction proceeds as Nu addition. - If the carbonyl does have an LG, the reaction proceeds as Nu sub ...
... - The first part is an alpha substitution, where the deprotonated C is the Nu and a + carbon (generally a carbonyl) on another molecule is the E+. - If the other molecule’s carbonyl has no LG, the reaction proceeds as Nu addition. - If the carbonyl does have an LG, the reaction proceeds as Nu sub ...
Organic Compounds Containing C, H and O
... Ans. i. a. Nitro (-NO2) group is an electron withdrawing whereas methoxy (-OCH3) group is electron releasing in nature. o-nitrophenol produces H+ ions easily but methoxyphenol does not. This is because o-nitrophenoxide ion is stabilised due to resonance. This is not true with o-methoxyphenoxide ion. ...
... Ans. i. a. Nitro (-NO2) group is an electron withdrawing whereas methoxy (-OCH3) group is electron releasing in nature. o-nitrophenol produces H+ ions easily but methoxyphenol does not. This is because o-nitrophenoxide ion is stabilised due to resonance. This is not true with o-methoxyphenoxide ion. ...
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 21 – Phenoles and Aryl
... – Formally this results in removal of a pair of electrons and two protons from hydroquinone - This reaction is reversible ...
... – Formally this results in removal of a pair of electrons and two protons from hydroquinone - This reaction is reversible ...
SCI2199 - Introduction to Organic Chemistry II
... SCI2199 - Introduction to Organic Chemistry II - Fall 2016 Homework 2 _______________________________________________________________________ 1. Which of the following could not be used to synthesize 2-bromopentane efficiently? A) 1-Pentene + HBr → B) 2-Pentene + HBr → C) 2-Pentanol + HBr → D) 2-Pen ...
... SCI2199 - Introduction to Organic Chemistry II - Fall 2016 Homework 2 _______________________________________________________________________ 1. Which of the following could not be used to synthesize 2-bromopentane efficiently? A) 1-Pentene + HBr → B) 2-Pentene + HBr → C) 2-Pentanol + HBr → D) 2-Pen ...
aldehydes and ketones
... • Ketones have greater steric crowding in their transition states, so they have less stable transition states. ...
... • Ketones have greater steric crowding in their transition states, so they have less stable transition states. ...
... as reaction media by water minimizes the environmental impact, besides lowering the cost and decreasing operational danger. In addition to the economic and human aspects, water presents many physico–chemical properties that can be useful in the reactions, such as high polarity, ion solvating capacit ...
CN>Chapter 22CT>Carbonyl Alpha
... Carbonyl compounds can act as weak acids (pKa of acetone = 19.3; pKa of ethane = 60) The conjugate base of a ketone or aldehyde is an enolate ion - the negative charge is delocalized onto oxygen ...
... Carbonyl compounds can act as weak acids (pKa of acetone = 19.3; pKa of ethane = 60) The conjugate base of a ketone or aldehyde is an enolate ion - the negative charge is delocalized onto oxygen ...
Exam 2
... Chern 24 2 (w 2016) exam #2B 1. (10 pts) Circle what is true about Substitution and elimination reactions. ...
... Chern 24 2 (w 2016) exam #2B 1. (10 pts) Circle what is true about Substitution and elimination reactions. ...
PTT102 Aldehydes and Ketones
... 1. Claisen Condensation Condensation of Two Ester Molecules. The product of a Claisen condensation is a βketo ester. In a Claisen condensation, one molecule of carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and t ...
... 1. Claisen Condensation Condensation of Two Ester Molecules. The product of a Claisen condensation is a βketo ester. In a Claisen condensation, one molecule of carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and t ...
PTT102 Aldehydes and Ketones
... 1. Claisen Condensation Condensation of Two Ester Molecules. The product of a Claisen condensation is a βketo ester. In a Claisen condensation, one molecule of carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and t ...
... 1. Claisen Condensation Condensation of Two Ester Molecules. The product of a Claisen condensation is a βketo ester. In a Claisen condensation, one molecule of carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and t ...
chapter 8 lecture
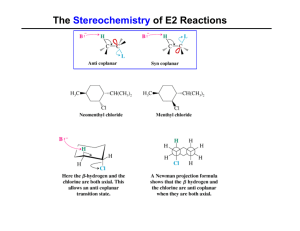
... formed. The slow step is unimolecular, involving only the alkyl halide. • The E1 and E2 mechanisms both involve the same number of bonds broken and formed. The only difference is timing. In an E1, the leaving group comes off before the proton is removed, and the reaction occurs in two steps. In an ...
... formed. The slow step is unimolecular, involving only the alkyl halide. • The E1 and E2 mechanisms both involve the same number of bonds broken and formed. The only difference is timing. In an E1, the leaving group comes off before the proton is removed, and the reaction occurs in two steps. In an ...
A2 LEVEL CHEMISTRY 4.1.1 ARENES TEST Answer all questions
... In this question, one mark is available for the quality of use and organisation of scientific terms. Describe how benzene could be converted into nitrobenzene. State the reagents and conditions, give a balanced equation for each stage and show the structure of the product. ...
... In this question, one mark is available for the quality of use and organisation of scientific terms. Describe how benzene could be converted into nitrobenzene. State the reagents and conditions, give a balanced equation for each stage and show the structure of the product. ...
Topics 10 and 20 Outline
... • SN1 represents a nucleophilic unimolecular substitution reaction and SN2 represents a nucleophilic bimolecular substitution reaction. SN1 involves a carbocation intermediate. SN2 involves a concerted reaction with a transition state. • For tertiary halogenoalkanes the predominant mechanism is SN1 ...
... • SN1 represents a nucleophilic unimolecular substitution reaction and SN2 represents a nucleophilic bimolecular substitution reaction. SN1 involves a carbocation intermediate. SN2 involves a concerted reaction with a transition state. • For tertiary halogenoalkanes the predominant mechanism is SN1 ...
Diels–Alder reaction
.png?width=300)
The Diels–Alder reaction is an organic chemical reaction (specifically, a [4+2] cycloaddition) between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexene system. It was first described by Otto Paul Hermann Diels and Kurt Alder in 1928, for which work they were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1950. The Diels–Alder reaction is particularly useful in synthetic organic chemistry as a reliable method for forming 6-membered systems with good control over regio- and stereochemical properties. The underlying concept has also been applied to other π-systems, such as carbonyls and imines, to furnish the corresponding heterocycles, known as the hetero-Diels–Alder reaction. Diels–Alder reactions can be reversible under certain conditions; the reverse reaction is known as the retro-Diels–Alder reaction.