1 - Study Hungary
... 20 protons, 19 neutrons, 19 electrons 19 protons, 20 neutrons, 18 electrons 39 protons, 19 neutrons, 38 electrons 20 protons, 19 neutrons, 20 electrons 40 protons, 20 neutrons, 19 electrons ...
... 20 protons, 19 neutrons, 19 electrons 19 protons, 20 neutrons, 18 electrons 39 protons, 19 neutrons, 38 electrons 20 protons, 19 neutrons, 20 electrons 40 protons, 20 neutrons, 19 electrons ...
Chemistry
... mass, ionization energies, electronegativies…). 10 – 2 Know that the physical and chemical properties of a compound are determined by its molecular structure (e.g. constituent atoms, crystal or molecular geometry, type of bonding, etc) and the intermolecular forces between these molecules. 10 – 3 Un ...
... mass, ionization energies, electronegativies…). 10 – 2 Know that the physical and chemical properties of a compound are determined by its molecular structure (e.g. constituent atoms, crystal or molecular geometry, type of bonding, etc) and the intermolecular forces between these molecules. 10 – 3 Un ...
File - Ms McRae`s Science
... The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons. The number of protons is equal to the number of neutrons. The nucleus is made up of neutrons, protons and electrons. The nucleus is made up of neutrons and electrons. The nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons. Protons revolve around the ...
... The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons. The number of protons is equal to the number of neutrons. The nucleus is made up of neutrons, protons and electrons. The nucleus is made up of neutrons and electrons. The nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons. Protons revolve around the ...
preface The given educational edition on professional English
... nuclear force binds quarks together within protons, neutrons, and other subatomic particles; and, rather as the electromagnetic force is ultimately responsible for holding bulk matter together, so the strong force keeps protons and neutrons together within atomic nuclei. The fourth force is the weak ...
... nuclear force binds quarks together within protons, neutrons, and other subatomic particles; and, rather as the electromagnetic force is ultimately responsible for holding bulk matter together, so the strong force keeps protons and neutrons together within atomic nuclei. The fourth force is the weak ...
Integrated Science COS-Grade 9 2011 2012
... Science Course of Study Course Description Physical Science introduces students to key concepts and theories that provide a foundation for further study in other sciences and advanced science disciplines. Physical Science comprises the systematic study of the physical world as it relates to fundamen ...
... Science Course of Study Course Description Physical Science introduces students to key concepts and theories that provide a foundation for further study in other sciences and advanced science disciplines. Physical Science comprises the systematic study of the physical world as it relates to fundamen ...
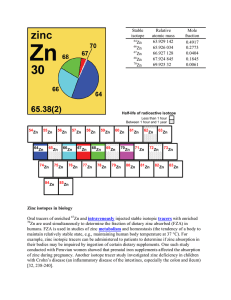
Zinc isotopes in biology Oral tracers of enriched Zn and
... isotope of the chemical element in the same system [706]. [return] isotopic composition – number and abundance of the isotopes of a chemical element that are naturally occurring [706]. [return] isotopic fractionation (stable-isotope fractionation) – preferential enrichment of one isotope of an eleme ...
... isotope of the chemical element in the same system [706]. [return] isotopic composition – number and abundance of the isotopes of a chemical element that are naturally occurring [706]. [return] isotopic fractionation (stable-isotope fractionation) – preferential enrichment of one isotope of an eleme ...
Column A
... J) Draw the electron dot diagram (Lewis Dot Structure) and then tell if it would give up or take on electrons to get a full shell. Also tell what charge it would have (positive or negative and how much ex: +2) ...
... J) Draw the electron dot diagram (Lewis Dot Structure) and then tell if it would give up or take on electrons to get a full shell. Also tell what charge it would have (positive or negative and how much ex: +2) ...
Nuclear Decay - Physics Rocks!
... maintaining a delicate balance between the number of protons and the number of neutrons in a nucleus. The higher the atomic number, the larger the neutron:proton ratio must be in order to remain stable Difference of +/- 1 neutron can result in an unstable nucleus ...
... maintaining a delicate balance between the number of protons and the number of neutrons in a nucleus. The higher the atomic number, the larger the neutron:proton ratio must be in order to remain stable Difference of +/- 1 neutron can result in an unstable nucleus ...
Nuclear Decay - Issaquah Connect
... maintaining a delicate balance between the number of protons and the number of neutrons in a nucleus. The higher the atomic number, the larger the neutron:proton ratio must be in order to remain stable Difference of +/- 1 neutron can result in an unstable nucleus ...
... maintaining a delicate balance between the number of protons and the number of neutrons in a nucleus. The higher the atomic number, the larger the neutron:proton ratio must be in order to remain stable Difference of +/- 1 neutron can result in an unstable nucleus ...
Question, hints, and answers. Look at hints if you need help. Look at
... Molecules in a sample of NH3(l) are held closely together by intermolecular forces *hint In the NH3 molecule, there is a covalent bond between N and H. But the N "wants" the electrons more than the H does, so it pulls them closer to itself. You end up with a little more than half the negative charge ...
... Molecules in a sample of NH3(l) are held closely together by intermolecular forces *hint In the NH3 molecule, there is a covalent bond between N and H. But the N "wants" the electrons more than the H does, so it pulls them closer to itself. You end up with a little more than half the negative charge ...
E = mc 2 - Gordon State College
... • consists of two protons and two neutrons (a helium nucleus) • loses energy quickly during interaction • can be stopped easily by a few pieces of paper due to its large mass and double positive charge • does not normally penetrate lightweight material (paper, clothing) • causes significant damage t ...
... • consists of two protons and two neutrons (a helium nucleus) • loses energy quickly during interaction • can be stopped easily by a few pieces of paper due to its large mass and double positive charge • does not normally penetrate lightweight material (paper, clothing) • causes significant damage t ...
Glossary
... Nuclear change in which the nuclei of certain isotopes with large mass numbers (such as uranium-235 and plutonium-239) are split apart into lighter nuclei when struck by a neutron. This process releases more neutrons and a large amount of energy. Compare nuclear fusion. ...
... Nuclear change in which the nuclei of certain isotopes with large mass numbers (such as uranium-235 and plutonium-239) are split apart into lighter nuclei when struck by a neutron. This process releases more neutrons and a large amount of energy. Compare nuclear fusion. ...
Chapter 25.1 Nuclear Radiation
... b. thermal vibrations. c. a chemical reaction. d. giving off heat. ...
... b. thermal vibrations. c. a chemical reaction. d. giving off heat. ...
I. Setting the Stage: Star Formation and Hydrogen Burning in Single
... in Physics in 1934 for the discovery of positrons. Positrons were first created in a laboratory by applying a very strong electric field, the energy source, to an empty chamber, a vacuum. When the electric field reached a critical value, out popped electrons and positrons. You can see the connection ...
... in Physics in 1934 for the discovery of positrons. Positrons were first created in a laboratory by applying a very strong electric field, the energy source, to an empty chamber, a vacuum. When the electric field reached a critical value, out popped electrons and positrons. You can see the connection ...
Nuclear Physics Fundamental and Application Prof. H. C. Verma
... path. You know all that geometry can be done, here I am interested in finding this minimum separation here, minimum separation. So, if you write the whole equation, I do not need that, but still the equation would be, if I take this as origin and then R theta this as flexibility axis as R. So, R wil ...
... path. You know all that geometry can be done, here I am interested in finding this minimum separation here, minimum separation. So, if you write the whole equation, I do not need that, but still the equation would be, if I take this as origin and then R theta this as flexibility axis as R. So, R wil ...
Interim Exam - Review H-Chem 2015
... 69. Which change in the temperature of a 1-gram sample of water would cause the greatest increase in the average kinetic energy of its molecules? 1. 1°C to 10°C 3. 50°C to 60°C 5. 500°C to 501°C ...
... 69. Which change in the temperature of a 1-gram sample of water would cause the greatest increase in the average kinetic energy of its molecules? 1. 1°C to 10°C 3. 50°C to 60°C 5. 500°C to 501°C ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... • What are the most commonly occurring elements in the food labels? • What items seemed to have the most amount of elements in them? • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on th ...
... • What are the most commonly occurring elements in the food labels? • What items seemed to have the most amount of elements in them? • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on th ...