300 - 1500
... crossed the straits of Gibraltar and made conquest of the Iberian Peninsula (Spain/Portugal) Ruled the peninsula for more than 700 years Cordoba – one of the wealthiest and most culturally advanced cities of the medieval world In 800’s and 900’s, Muslim raids in southern France, Rome Italy, and Cons ...
... crossed the straits of Gibraltar and made conquest of the Iberian Peninsula (Spain/Portugal) Ruled the peninsula for more than 700 years Cordoba – one of the wealthiest and most culturally advanced cities of the medieval world In 800’s and 900’s, Muslim raids in southern France, Rome Italy, and Cons ...
Note Taking Study Guide
... advanced cultures in Asia, overrun by invaders, and divided. The period from 500 to 1000 is sometimes called the Dark Ages. However, it was a time when Greco-Roman, Germanic, and Christian traditions slowly blended to create a new, medieval civilization called the Middle Ages. In the early Middle Ag ...
... advanced cultures in Asia, overrun by invaders, and divided. The period from 500 to 1000 is sometimes called the Dark Ages. However, it was a time when Greco-Roman, Germanic, and Christian traditions slowly blended to create a new, medieval civilization called the Middle Ages. In the early Middle Ag ...
Time Period
... women? Compare their status with the status of women in other parts of the world at that time. Discuss the images of mosques in Spain and Africa, considering the impact of geographical and cultural contexts on religion. Essay: Compare and Contrast Japanese and Western European feudalism; or Comp ...
... women? Compare their status with the status of women in other parts of the world at that time. Discuss the images of mosques in Spain and Africa, considering the impact of geographical and cultural contexts on religion. Essay: Compare and Contrast Japanese and Western European feudalism; or Comp ...
Note Taking Study Guide - Prentice Hall Bridge page
... advanced cultures in Asia, overrun by invaders, and divided. The period from 500 to 1000 is sometimes called the Dark Ages. However, it was a time when Greco-Roman, Germanic, and Christian traditions slowly blended to create a new, medieval civilization called the Middle Ages. In the early Middle Ag ...
... advanced cultures in Asia, overrun by invaders, and divided. The period from 500 to 1000 is sometimes called the Dark Ages. However, it was a time when Greco-Roman, Germanic, and Christian traditions slowly blended to create a new, medieval civilization called the Middle Ages. In the early Middle Ag ...
CP World History Organizer
... During the period from 1750-1914, the world saw a lot of major changes around the globe. As Europeans began to experience the wealth of the Age of Exploration and Absolutism, their role in non-European areas increased greatly. This changing role of Europeans would begin to have ripple effects in Asi ...
... During the period from 1750-1914, the world saw a lot of major changes around the globe. As Europeans began to experience the wealth of the Age of Exploration and Absolutism, their role in non-European areas increased greatly. This changing role of Europeans would begin to have ripple effects in Asi ...
Chapter 9 - Homework Market
... Islam by the sword must really be abandoned (that is, for the earliest era of the Arab diaspora), since a critical study of sources has shown that the victorious Arabs never presented the people they conquered with the choice between death and the acceptance of their faith…The alternative between Is ...
... Islam by the sword must really be abandoned (that is, for the earliest era of the Arab diaspora), since a critical study of sources has shown that the victorious Arabs never presented the people they conquered with the choice between death and the acceptance of their faith…The alternative between Is ...
Unit 3 Study Guide
... 3. How did government structures deal with, use, and adapt religion to control their populations? How did empires continue to prove their legitimacy to their subjects, especially newly-conquered peoples? Compare how different peoples organized their government structures. ...
... 3. How did government structures deal with, use, and adapt religion to control their populations? How did empires continue to prove their legitimacy to their subjects, especially newly-conquered peoples? Compare how different peoples organized their government structures. ...
Document
... World Studies is a combination of the study of world history and current world issues. The study of world history centers on investigating the events of the past and their effect on events today: i.e., ancient India, ancient China, rise of Islam, Europe since the Renaissance, Africa since Prehistory ...
... World Studies is a combination of the study of world history and current world issues. The study of world history centers on investigating the events of the past and their effect on events today: i.e., ancient India, ancient China, rise of Islam, Europe since the Renaissance, Africa since Prehistory ...
ap world history syllabus - Gull Lake Community Schools
... cultures and 70% of the course is devoted to the history of non western cultures. The following AP World History themes are addressed throughout the course to identify broad patterns and processes that explain change and continuity over time and to ask cross-period questions for the purpose of makin ...
... cultures and 70% of the course is devoted to the history of non western cultures. The following AP World History themes are addressed throughout the course to identify broad patterns and processes that explain change and continuity over time and to ask cross-period questions for the purpose of makin ...
As Word (text only) - Discover Islamic Art
... Prophet Muhammad sends a letter to Cyrus, the Byzantine Patriarch of Alexandria and ruler of Egypt, inviting him to accept Islam. Cyrus sends gifts to the Prophet in answer, together with two sisters from Upper Egypt. The Prophet married one of them, called Maria the Copt. She bore him his only son, ...
... Prophet Muhammad sends a letter to Cyrus, the Byzantine Patriarch of Alexandria and ruler of Egypt, inviting him to accept Islam. Cyrus sends gifts to the Prophet in answer, together with two sisters from Upper Egypt. The Prophet married one of them, called Maria the Copt. She bore him his only son, ...
Unit 4- Byzantine Emp
... 1 The early eastern European Slavic civilization at Kiev adopted the Eastern Orthodox religion, the Cyrillic alphabet, and certain styles of art and architecture as a result of (1) wars with Japan (2) conquests by Mongol invaders (3) visits to western European countries (4) trade with the Byzantine ...
... 1 The early eastern European Slavic civilization at Kiev adopted the Eastern Orthodox religion, the Cyrillic alphabet, and certain styles of art and architecture as a result of (1) wars with Japan (2) conquests by Mongol invaders (3) visits to western European countries (4) trade with the Byzantine ...
Ancient Times To The Present
... of China. The Yellow and Yangtze rivers provided water. The Yellow River often flooded causing disaster for the people. Crops could not be planted, and starvation followed. Mass migrations of Chinese took place because of this condition. Northern China was settled before southern China, but the peop ...
... of China. The Yellow and Yangtze rivers provided water. The Yellow River often flooded causing disaster for the people. Crops could not be planted, and starvation followed. Mass migrations of Chinese took place because of this condition. Northern China was settled before southern China, but the peop ...
Inheritors and Builders: From the Fall of Rome to Charlemagne
... 5) Although many Roman traditions were retained by the emerging kingdoms of Western Europe, there is strong archaeological evidence to show a partial collapse in the economic and productive base of western Europe. Thus pollution samples from icecores in Greenland show that level of lead, copper and ...
... 5) Although many Roman traditions were retained by the emerging kingdoms of Western Europe, there is strong archaeological evidence to show a partial collapse in the economic and productive base of western Europe. Thus pollution samples from icecores in Greenland show that level of lead, copper and ...
AP WORLD HISTORY Summer Work Requirements Metea Valley
... Part 3) In one well developed paragraph (7-10 sentences), explain which one of the following themes is most visible in the empire that you chose to research. Make sure you explain in detail and defend your answer. (These 5 overarching themes will be used throughout the AP World History course, it is ...
... Part 3) In one well developed paragraph (7-10 sentences), explain which one of the following themes is most visible in the empire that you chose to research. Make sure you explain in detail and defend your answer. (These 5 overarching themes will be used throughout the AP World History course, it is ...
Purpose Why is there a final exam? The final is meant to help you
... On the following pages is a list of each region of the world we studied this year and the objectives, or things you should know about, each region. You are encouraged to create a study tool that will help you prepare for the exam; that could be a huge stack of flashcards, a two-column chart, complet ...
... On the following pages is a list of each region of the world we studied this year and the objectives, or things you should know about, each region. You are encouraged to create a study tool that will help you prepare for the exam; that could be a huge stack of flashcards, a two-column chart, complet ...
Social Studies: World History and Civilization Pacing Guide 2015
... WH.2.9 Examine the significant achievements of the Greeks and Romans and their impact on the modern world. WH.3.1 Analyze the impact of trade networks such as the Silk Road and Indian Ocean trade network. WH.3.13 Explain and understand the achievements of the Tang and Song Dynasties. (Potential DBQ- ...
... WH.2.9 Examine the significant achievements of the Greeks and Romans and their impact on the modern world. WH.3.1 Analyze the impact of trade networks such as the Silk Road and Indian Ocean trade network. WH.3.13 Explain and understand the achievements of the Tang and Song Dynasties. (Potential DBQ- ...
World History Connections to Today
... • How did Germanic kingdoms gain power in the early Middle Ages? • How did Charlemagne briefly reunite much of Western Europe? ...
... • How did Germanic kingdoms gain power in the early Middle Ages? • How did Charlemagne briefly reunite much of Western Europe? ...
PowerPoint-2013 and Beyond/Mongols-History.pps
... ◦ Alexander Nevskii (lived around 1220-1263) argued for cooperation with Mongols rather than resistance. ...
... ◦ Alexander Nevskii (lived around 1220-1263) argued for cooperation with Mongols rather than resistance. ...
The Vikings
... cities were and people moved to the countryside The Roman Empire was carved into several and kingdoms whose borders often changed due to war Which empire unified Europe spreading of classical ideas, language and religion to distant European territories? What caused trade and learning to collapse ...
... cities were and people moved to the countryside The Roman Empire was carved into several and kingdoms whose borders often changed due to war Which empire unified Europe spreading of classical ideas, language and religion to distant European territories? What caused trade and learning to collapse ...
Student Handout #1 - The Carolingian Empire and Charlemagne
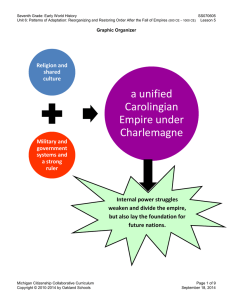
... when more than one son wanted to rule. As a result the kingdom got divided and weakened. This is what happened when Charlemagne’s son, Louis the Pious, died, and the empire was split between his sons. They fought each other in a civil war until they signed a treaty in 843, the Treaty of Verdun, and ...
... when more than one son wanted to rule. As a result the kingdom got divided and weakened. This is what happened when Charlemagne’s son, Louis the Pious, died, and the empire was split between his sons. They fought each other in a civil war until they signed a treaty in 843, the Treaty of Verdun, and ...
History of the Medieval World
... MEDIEVAL EUROPE The Middle Ages is a period in European history which, along with its adjective ‘Medieval’, was first referred to by Italian scholars and academics of the late 15th century. They were basically stating that the society in which they now lived was significantly more civilized and adva ...
... MEDIEVAL EUROPE The Middle Ages is a period in European history which, along with its adjective ‘Medieval’, was first referred to by Italian scholars and academics of the late 15th century. They were basically stating that the society in which they now lived was significantly more civilized and adva ...
Elizabeth Jeffreys, John Haldon and Robin Cormack (eds.)
... state, as well as the policies of the emperors differed significantly in these two periods. Some traits, nevertheless, characterize the entire period, from 1261 to 1453. The Byzantine Empire never recovered all of the territories it had held before 1204, not even in Greece and the Balkans. It was a ...
... state, as well as the policies of the emperors differed significantly in these two periods. Some traits, nevertheless, characterize the entire period, from 1261 to 1453. The Byzantine Empire never recovered all of the territories it had held before 1204, not even in Greece and the Balkans. It was a ...
The Mongol Empire
... This is the main page. At every bold faced title you need to return here to move to the next section. The Mongols’ Mark on Global History 1. Describe the stereotype the Mongols have gained from most Westerners. Why do you think this is? ...
... This is the main page. At every bold faced title you need to return here to move to the next section. The Mongols’ Mark on Global History 1. Describe the stereotype the Mongols have gained from most Westerners. Why do you think this is? ...
History 140 (C-ID Number: HIST 150) World History to 1500 (C
... D. Around the Pacific Rim: Eastern Eurasia and the Americas (4 hours) 1. The formation of Ancient China 2. The Zhou Dynasty 3. Ancient Southeast and Northeast Asia 4. Hunter and gatherer societies in North America 5. Olmec society 6. The Maya people 7. Early Andean states ...
... D. Around the Pacific Rim: Eastern Eurasia and the Americas (4 hours) 1. The formation of Ancient China 2. The Zhou Dynasty 3. Ancient Southeast and Northeast Asia 4. Hunter and gatherer societies in North America 5. Olmec society 6. The Maya people 7. Early Andean states ...
Post-classical history

Post-classical history (also called the Postclassical Era) is the period of time that immediately followed ancient history. Depending on the continent, the era generally falls between the years AD 200-600 and AD 1200–1500. The major classical civilizations the era follows are Han China (ending in 220), the Western Roman Empire (in 476), the Gupta Empire (in the 550s), and the Sasanian Empire (in 651). The post-classical era itself was followed by the early modern era, and forms the middle period in a three-period division of world history: ancient, post-classical, and modern. The era is thought to be characterized by invasions from Central Asia, the development of the great world religions (Christianity, Islam, and Buddhism), and of networks of trade and military contact between civilizations.The name of this era of history derives from classical antiquity (or the Greco-Roman era) of Europe. In European history, ""post-classical"" is synonymous with the medieval time or Middle Ages, the period of history from around the 5th century to the 15th century. In Europe, the fall of the Western Roman Empire saw the depopulation, deurbanization, and limited learning of the ""Dark Ages"" (except in Eastern Mediterranean Europe, where the Eastern Roman Empire flourished until 1204), but gradually revived somewhat under the institutions of feudalism and a powerful Catholic Church. Art and architecture were characterized by Christian themes. Several attempts by the Crusades to recapture the Holy Land for Christianity were unsuccessful.In Asia, the depredations of the Dark Ages were avoided, at least in the west, where the Spread of Islam created a new empire and civilization with trade between the Asian, African, and European continents, and advances in science. East Asia experienced the full establishment of power of Imperial China (after the interregnum chaos of the Six Dynasties), which established several prosperous dynasties influencing Korea, Vietnam, and Japan. Religions such as Buddhism and Neo-Confucianism spread. Gunpowder was originally developed in China during the post-classical era. The invention of gunpowder led to the invention of fireworks, then to its use in warfare. Also, the invention spread around the world. The Mongol Empire greatly affected much of Europe and Asia, the latter of which was conquered in many areas. The Mongols were able to create safe trade and stability between the two regions, but inadvertently encouraged the spread of the Black Plague.The timelines of the major civilizations of the Americas—Maya (AD 250 to 900), the Aztec (14th to 16th centuries), and the Inca (1438 to 1533)—do not correspond closely to the Classical Age of the Old World.Outstanding cultural achievement in the post-classical era include books like the Code of Justinian,The Story of the Western Wing, and The Tale of Genji; the mathematics of Fibonacci, Oresme, and Al-Khwārizmī; the philosophy of Avicenna, Thomas Aquinas, Petrarch, Zhu Xi, and Kabir; the painting of Giotto, Behzād, and Dong Yuan; the astronomy of Nasir al-Din al-Tusi and Su Song; the poetry of Rumi, Dante, Chaucer, and the Li Bai; the travels of Marco Polo and Ibn Battuta; the historiography of Leonardo Bruni and Ibn Khaldun; and the architecture of places like Chartres, the Mezquita, Angkor Wat, and Machu Picchu.