Unit 3: European Middle Ages Chapter 13
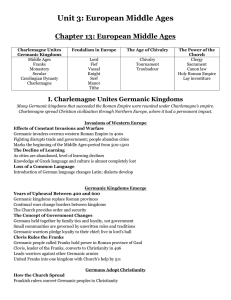
... ruled all of the lands where Roman Catholicism dominated, except modern-day England and Ireland. However, unlike the old Roman Empire in which Rome was the center of both political power and religious influence, Charlemagne’s kingdom was centered in Aachen, a northern European city. The unity forged ...
... ruled all of the lands where Roman Catholicism dominated, except modern-day England and Ireland. However, unlike the old Roman Empire in which Rome was the center of both political power and religious influence, Charlemagne’s kingdom was centered in Aachen, a northern European city. The unity forged ...
Pathfinder for Honors World History Building Empires
... Keyword search BRITISH EMPIRE British Empire | The National Archives www.nationalarchives.gov.uk › Education The British Empire http://www.victorianweb.org/history/empire/Empire.html THE MONGOL EMPIRE The Mongols in World History | Asia Topics in World History http://afe.easia.columbia.edu/mongols/c ...
... Keyword search BRITISH EMPIRE British Empire | The National Archives www.nationalarchives.gov.uk › Education The British Empire http://www.victorianweb.org/history/empire/Empire.html THE MONGOL EMPIRE The Mongols in World History | Asia Topics in World History http://afe.easia.columbia.edu/mongols/c ...
World History Connections to Today
... Byzantine world in the south. The city of Kiev was located at the heart of the vital trade network linking Vikings, Slavs, and Constantinople. Kiev would later become the center of the first Russian state. ...
... Byzantine world in the south. The city of Kiev was located at the heart of the vital trade network linking Vikings, Slavs, and Constantinople. Kiev would later become the center of the first Russian state. ...
World History Connections to Today
... Byzantine world in the south. The city of Kiev was located at the heart of the vital trade network linking Vikings, Slavs, and Constantinople. Kiev would later become the center of the first Russian state. ...
... Byzantine world in the south. The city of Kiev was located at the heart of the vital trade network linking Vikings, Slavs, and Constantinople. Kiev would later become the center of the first Russian state. ...
Medieval World - Calicut University
... 40.The Abbasid rule lasted till the 11th century when they were ousted from power by the ……………... a) Seljuk Turks b) Ottoman Turks c) Arabs d) Guptas 41. The Turks controlled the Arab empire thereafter till the 15th century when the ……………….became the rulers of the Arab territories. a) Ottoman Turks ...
... 40.The Abbasid rule lasted till the 11th century when they were ousted from power by the ……………... a) Seljuk Turks b) Ottoman Turks c) Arabs d) Guptas 41. The Turks controlled the Arab empire thereafter till the 15th century when the ……………….became the rulers of the Arab territories. a) Ottoman Turks ...
Social Science – World History and Geography: Ancient Civilizations
... 1. Students describe what is known through archaeological studies of the early physical and cultural development of humankind from the Paleolithic era to the agricultural revolution. 1.1 Describe the hunter-gatherer societies, including the development of tools and the use of fire. 1.2 Identify the ...
... 1. Students describe what is known through archaeological studies of the early physical and cultural development of humankind from the Paleolithic era to the agricultural revolution. 1.1 Describe the hunter-gatherer societies, including the development of tools and the use of fire. 1.2 Identify the ...
The Mongol Conquests in World History
... the book’s raison d’etre, the main sources for the study of Mongol history (including an intriguing reference to an expected English translation of the Yuanshi), and the danger of exaggerating the importance of the Mongols. The first part, “The Mongol Conquests as Catalyst” succinctly reviews the fo ...
... the book’s raison d’etre, the main sources for the study of Mongol history (including an intriguing reference to an expected English translation of the Yuanshi), and the danger of exaggerating the importance of the Mongols. The first part, “The Mongol Conquests as Catalyst” succinctly reviews the fo ...
6 SS Unit 6 - final
... Unit Summary: In this last unit students will study how people throughout the Ancient world communicated and interacted with each other. Students will begin their study with what life was like for people living in Europe during the Middle Ages and how their view of the world around them gradually gr ...
... Unit Summary: In this last unit students will study how people throughout the Ancient world communicated and interacted with each other. Students will begin their study with what life was like for people living in Europe during the Middle Ages and how their view of the world around them gradually gr ...
Middle Ages Student Handout - Troup County School System
... What events mark the beginning and end of the Middle Ages? AD 476 – Roman Emperor, Romulus Augustulus, overthrown by German forces AD 1453 – End of the Hundred Years’ War What influenced medieval culture? Medieval Culture: mixture of three (3) influences 1. The remnants of the Western Roman Empi ...
... What events mark the beginning and end of the Middle Ages? AD 476 – Roman Emperor, Romulus Augustulus, overthrown by German forces AD 1453 – End of the Hundred Years’ War What influenced medieval culture? Medieval Culture: mixture of three (3) influences 1. The remnants of the Western Roman Empi ...
On Commerce, Institutions, and Underdevelopment: A
... did not tolerate any centrifugal force; any encroachment by powerful landlords, local chiefs, or merchants was eliminated. These empires often relied on the services of a bureaucracy that was drawn from eunuchs, ex-slaves, and free soldiers not controlled by aristocracy.1 The Middle East is the regi ...
... did not tolerate any centrifugal force; any encroachment by powerful landlords, local chiefs, or merchants was eliminated. These empires often relied on the services of a bureaucracy that was drawn from eunuchs, ex-slaves, and free soldiers not controlled by aristocracy.1 The Middle East is the regi ...
The Feudal System - John Bowne High School
... emperor after another on the throne. Twenty-five emperors were murdered within one fifty-year period. Outside the empire, the sinking of land in northern Europe and pressure from Asian peoples to the east set off mass migrations across the borders of the Roman Empire. It took more than two hundred y ...
... emperor after another on the throne. Twenty-five emperors were murdered within one fifty-year period. Outside the empire, the sinking of land in northern Europe and pressure from Asian peoples to the east set off mass migrations across the borders of the Roman Empire. It took more than two hundred y ...
The Feudal System
... emperor after another on the throne. Twenty-five emperors were murdered within one fifty-year period. Outside the empire, the sinking of land in northern Europe and pressure from Asian peoples to the east set off mass migrations across the borders of the Roman Empire. It took more than two hundred y ...
... emperor after another on the throne. Twenty-five emperors were murdered within one fifty-year period. Outside the empire, the sinking of land in northern Europe and pressure from Asian peoples to the east set off mass migrations across the borders of the Roman Empire. It took more than two hundred y ...
Course Syllabus
... A survey of the political, economic, intellectual, cultural and religious development of the globe, from the Agricultural Revolution (c. 10,000 B.C.) to the sixteenth century A.D. Major topics will include, Ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt, the Hellenistic World, Ancient Indian Civilization, Imperial C ...
... A survey of the political, economic, intellectual, cultural and religious development of the globe, from the Agricultural Revolution (c. 10,000 B.C.) to the sixteenth century A.D. Major topics will include, Ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt, the Hellenistic World, Ancient Indian Civilization, Imperial C ...
Jane Burbank and Frederick Cooper. Empires in World History
... illustrates how differing governance structures ultimately led to similar outcomes in geographically distant regions. Burbank and Cooper elaborate in the introductory chapters about varying imperial themes and discuss how empires consolidated power, formulated strategies to govern their conquered ne ...
... illustrates how differing governance structures ultimately led to similar outcomes in geographically distant regions. Burbank and Cooper elaborate in the introductory chapters about varying imperial themes and discuss how empires consolidated power, formulated strategies to govern their conquered ne ...
Week 1 - AP world history
... Imperial Breakdown and Agrarian Disorder The Declining Position of Women in the Family and Society Nomadic Incursions and the Eclipse of Caliphal Power The Impact of the Christian Crusades An Age of Learning and Artistic Refinements The Full Flowering of Persian Literature Achievements ...
... Imperial Breakdown and Agrarian Disorder The Declining Position of Women in the Family and Society Nomadic Incursions and the Eclipse of Caliphal Power The Impact of the Christian Crusades An Age of Learning and Artistic Refinements The Full Flowering of Persian Literature Achievements ...
File - AP World History (WHAP)
... 2) Why did the power of the emperor decline from the 9th Century to the 12th Century? Describe the feudal system that developed as a result. 3) Compare the Japanese feudal system to the West European feudal system. 22) China’s Influence and Its Limits: Korea and Vietnam Pages 290-300 (Reading Assi ...
... 2) Why did the power of the emperor decline from the 9th Century to the 12th Century? Describe the feudal system that developed as a result. 3) Compare the Japanese feudal system to the West European feudal system. 22) China’s Influence and Its Limits: Korea and Vietnam Pages 290-300 (Reading Assi ...
Development of Feudalism in Europe
... against every creature living or dead, excepting my allegiance to Lord Enjourand of Coucy, Lord John of Arcis, and the count of Grandpre. It it should happen that the count of Grandpre shhould be at war wwith the Countess and count of Champagne in his own quarrel, I will aid the count of Grandpre in ...
... against every creature living or dead, excepting my allegiance to Lord Enjourand of Coucy, Lord John of Arcis, and the count of Grandpre. It it should happen that the count of Grandpre shhould be at war wwith the Countess and count of Champagne in his own quarrel, I will aid the count of Grandpre in ...
sample - Create Training
... considered negatively – if at all. Orthodox Christians (mainly Greeks, Slavs, and other Eastern European peoples, in Europe and throughout the world) generally know the names of Byzantine emperors and many saints, but others would hardly recognize a person or an event from Byzantine history, even th ...
... considered negatively – if at all. Orthodox Christians (mainly Greeks, Slavs, and other Eastern European peoples, in Europe and throughout the world) generally know the names of Byzantine emperors and many saints, but others would hardly recognize a person or an event from Byzantine history, even th ...
World History - Chicago Military Academy at Bronzeville
... Europe as the region slowly developed a new medieval culture? What political changes occurred during the rise of Europe and why are they important? What economic systems developed in Europe during the period 500-1300 and how are these economies different from the ancient economic systems? Why ...
... Europe as the region slowly developed a new medieval culture? What political changes occurred during the rise of Europe and why are they important? What economic systems developed in Europe during the period 500-1300 and how are these economies different from the ancient economic systems? Why ...
Chapter Two Review (review – noun
... However, after his death, the Carolingian Empire was weakened. Local nobles become more important as people turned to them for the protection that the empire could no longer provide. The system that developed from this, was feudalism. ...
... However, after his death, the Carolingian Empire was weakened. Local nobles become more important as people turned to them for the protection that the empire could no longer provide. The system that developed from this, was feudalism. ...
Did Islam Destroy Classical Civilizations?
... opportunity. There is however another factor: Pirenne, along with almost all historians of his age, assumed that Byzantium, which had not been overrun by the Barbarians, never experienced a Dark Age or a Medieval period. This view was prompted, in part at least, by Byzantine propaganda, which always ...
... opportunity. There is however another factor: Pirenne, along with almost all historians of his age, assumed that Byzantium, which had not been overrun by the Barbarians, never experienced a Dark Age or a Medieval period. This view was prompted, in part at least, by Byzantine propaganda, which always ...
The Middle Ages The Middle Ages
... -Ongoing battles against Muslims in Spain (began in 8th century) Late Middle Ages: 1250 – 1450 -Resurgence of learning and inventions lead to Renaissance -Increased Catholic Church power leads to Reformation -Regional Kingdoms gain power leading to increased trade routes and Exploration ...
... -Ongoing battles against Muslims in Spain (began in 8th century) Late Middle Ages: 1250 – 1450 -Resurgence of learning and inventions lead to Renaissance -Increased Catholic Church power leads to Reformation -Regional Kingdoms gain power leading to increased trade routes and Exploration ...
Post-classical history

Post-classical history (also called the Postclassical Era) is the period of time that immediately followed ancient history. Depending on the continent, the era generally falls between the years AD 200-600 and AD 1200–1500. The major classical civilizations the era follows are Han China (ending in 220), the Western Roman Empire (in 476), the Gupta Empire (in the 550s), and the Sasanian Empire (in 651). The post-classical era itself was followed by the early modern era, and forms the middle period in a three-period division of world history: ancient, post-classical, and modern. The era is thought to be characterized by invasions from Central Asia, the development of the great world religions (Christianity, Islam, and Buddhism), and of networks of trade and military contact between civilizations.The name of this era of history derives from classical antiquity (or the Greco-Roman era) of Europe. In European history, ""post-classical"" is synonymous with the medieval time or Middle Ages, the period of history from around the 5th century to the 15th century. In Europe, the fall of the Western Roman Empire saw the depopulation, deurbanization, and limited learning of the ""Dark Ages"" (except in Eastern Mediterranean Europe, where the Eastern Roman Empire flourished until 1204), but gradually revived somewhat under the institutions of feudalism and a powerful Catholic Church. Art and architecture were characterized by Christian themes. Several attempts by the Crusades to recapture the Holy Land for Christianity were unsuccessful.In Asia, the depredations of the Dark Ages were avoided, at least in the west, where the Spread of Islam created a new empire and civilization with trade between the Asian, African, and European continents, and advances in science. East Asia experienced the full establishment of power of Imperial China (after the interregnum chaos of the Six Dynasties), which established several prosperous dynasties influencing Korea, Vietnam, and Japan. Religions such as Buddhism and Neo-Confucianism spread. Gunpowder was originally developed in China during the post-classical era. The invention of gunpowder led to the invention of fireworks, then to its use in warfare. Also, the invention spread around the world. The Mongol Empire greatly affected much of Europe and Asia, the latter of which was conquered in many areas. The Mongols were able to create safe trade and stability between the two regions, but inadvertently encouraged the spread of the Black Plague.The timelines of the major civilizations of the Americas—Maya (AD 250 to 900), the Aztec (14th to 16th centuries), and the Inca (1438 to 1533)—do not correspond closely to the Classical Age of the Old World.Outstanding cultural achievement in the post-classical era include books like the Code of Justinian,The Story of the Western Wing, and The Tale of Genji; the mathematics of Fibonacci, Oresme, and Al-Khwārizmī; the philosophy of Avicenna, Thomas Aquinas, Petrarch, Zhu Xi, and Kabir; the painting of Giotto, Behzād, and Dong Yuan; the astronomy of Nasir al-Din al-Tusi and Su Song; the poetry of Rumi, Dante, Chaucer, and the Li Bai; the travels of Marco Polo and Ibn Battuta; the historiography of Leonardo Bruni and Ibn Khaldun; and the architecture of places like Chartres, the Mezquita, Angkor Wat, and Machu Picchu.