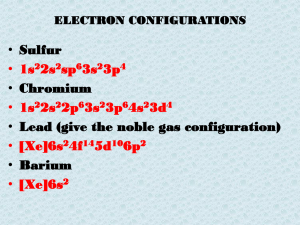
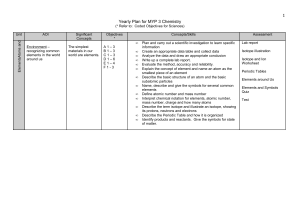
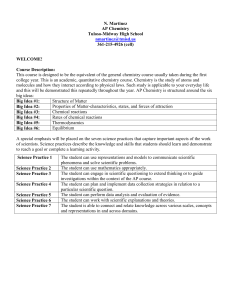
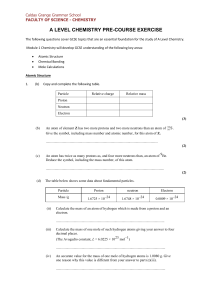
Chapter 1 Chemistry: The Study of Matter
... Heat- the energy that moves because of a temperature difference. Chemical energy- energy released or absorbed in a chemical change. Electrical energy - energy of moving ...
... Heat- the energy that moves because of a temperature difference. Chemical energy- energy released or absorbed in a chemical change. Electrical energy - energy of moving ...
Variation in Properties of Group II Compounds
... The oxides of group II elements react readily with water to form alkaline solutions. The reactivity of oxides towards water increases down the group. For example, BeO has a high degree of covalent characters, is inert and almost insoluble in water and acid; MgO is almost inert towards water but diss ...
... The oxides of group II elements react readily with water to form alkaline solutions. The reactivity of oxides towards water increases down the group. For example, BeO has a high degree of covalent characters, is inert and almost insoluble in water and acid; MgO is almost inert towards water but diss ...
atomic number - geraldinescience
... • Based on similarities in their chemical properties, elements on the periodic table are arranged in columns, which are called groups. • An atom’s chemical properties are largely determined by the number of the outermost electrons in an atom’s electron cloud. These electrons are called valence elect ...
... • Based on similarities in their chemical properties, elements on the periodic table are arranged in columns, which are called groups. • An atom’s chemical properties are largely determined by the number of the outermost electrons in an atom’s electron cloud. These electrons are called valence elect ...
effective nuclear charge
... ◦ in general, the increase in mass is greater than the increase in volume ...
... ◦ in general, the increase in mass is greater than the increase in volume ...
SOME BASIC CHEMICAL TERMS
... Most of the materials we encounter in our daily lives, such as air, milk, and steel, are mixtures. Mixtures contain two or more substances that can be physically separated from each other. Some mixtures, such as sand mixed with gravel, are heterogeneous, in other words, we would have no trouble dist ...
... Most of the materials we encounter in our daily lives, such as air, milk, and steel, are mixtures. Mixtures contain two or more substances that can be physically separated from each other. Some mixtures, such as sand mixed with gravel, are heterogeneous, in other words, we would have no trouble dist ...
AP Chemistry Syllabus 2013 Mawhiney
... 5. Predict reaction products for both electrolytic and voltaic cells. 6. Use a table of Standard Reduction Potentials to compute cell voltages. 7. Diagram voltaic cells using proper notation. 8. Establish the relationship between the free energy change, the cell potential, and the equilibrium consta ...
... 5. Predict reaction products for both electrolytic and voltaic cells. 6. Use a table of Standard Reduction Potentials to compute cell voltages. 7. Diagram voltaic cells using proper notation. 8. Establish the relationship between the free energy change, the cell potential, and the equilibrium consta ...
The format of this test is MULTIPLE CHOICE
... 4. How does the size of an ion compare to the size of the neutral atom from which it was created? Ions are bigger 5. How does an atom’s position on the periodic table provide information on that atom’s size (atomic radius)? The farther left in the period, the larger the atom, the further down a grou ...
... 4. How does the size of an ion compare to the size of the neutral atom from which it was created? Ions are bigger 5. How does an atom’s position on the periodic table provide information on that atom’s size (atomic radius)? The farther left in the period, the larger the atom, the further down a grou ...
Matter - Moodle
... The _______________ of an atom is usually ___________________ The number of protons _________________ the number of electrons Ex. C (carbon) atomic number of 6, so 6 protons and ____electrons ...
... The _______________ of an atom is usually ___________________ The number of protons _________________ the number of electrons Ex. C (carbon) atomic number of 6, so 6 protons and ____electrons ...
CHAPTER 1 Practice Exercises 1.1 12.3 g Cd 1.3 26.9814 u 1.5
... Conservation of mass derives from the postulate that atoms are not destroyed in chemical reactions. The Law of Definite Proportions derives from the notion that compounds are always composed of the same types and numbers of atoms of the various elements in the compound. ...
... Conservation of mass derives from the postulate that atoms are not destroyed in chemical reactions. The Law of Definite Proportions derives from the notion that compounds are always composed of the same types and numbers of atoms of the various elements in the compound. ...
Chemistry
... http://www.dailymotion.com/video/xlp2y1_billnye-chemical-reactions_tech#.URez2lrjk3I ...
... http://www.dailymotion.com/video/xlp2y1_billnye-chemical-reactions_tech#.URez2lrjk3I ...
A Study of Matter
... • Label properties as physical or chemical. • Label changes as physical or chemical. • State the Law of Conservation of Mass. ...
... • Label properties as physical or chemical. • Label changes as physical or chemical. • State the Law of Conservation of Mass. ...
Elements, basic principles, periodic table
... Ionization and Ionization Energy (aka ionization potential): Ionization energy measures how easy or hard it is to remove an electron from an element or ion. Energies of filled electronic orbitals give rise to common oxidation states for individual elements. Electronic structure determines ionic char ...
... Ionization and Ionization Energy (aka ionization potential): Ionization energy measures how easy or hard it is to remove an electron from an element or ion. Energies of filled electronic orbitals give rise to common oxidation states for individual elements. Electronic structure determines ionic char ...