chapter02_part1_lecture - bloodhounds Incorporated
... 2.2 Elements and Compounds • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
... 2.2 Elements and Compounds • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
1. What are micelles? Give two examples of micellar systems. Sol. A
... 1. What are micelles? Give two examples of micellar systems. Sol. A micelleis an aggregate of surfactant molecules dispersed in a liquid colloid. A typical micelle in aqueous solution forms an aggregate with the hydrophilic "head" regions in contact with surrounding solvent, sequestering the hydroph ...
... 1. What are micelles? Give two examples of micellar systems. Sol. A micelleis an aggregate of surfactant molecules dispersed in a liquid colloid. A typical micelle in aqueous solution forms an aggregate with the hydrophilic "head" regions in contact with surrounding solvent, sequestering the hydroph ...
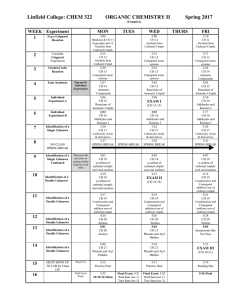
Course Syllabus General Chemistry 1412 Spring 2016
... a single problem - skip it for the time being and go on to another. Try working some of the sample practice exercises. They are worked out in the chapter and are very helpful. Get a good, scientific calculator that has scientific notation ("EE" or "EXP" key), log, ln, x2, , etc. Business calculator ...
... a single problem - skip it for the time being and go on to another. Try working some of the sample practice exercises. They are worked out in the chapter and are very helpful. Get a good, scientific calculator that has scientific notation ("EE" or "EXP" key), log, ln, x2, , etc. Business calculator ...
Lecture syllabus - Linfield College
... predictable. Exploring and learning these principles will allow the student to have a basic understanding of how and why various classes of carbon-containing compounds react, so that he or she will be scientifically literate with respect to environmental or economic issues. Chemistry is all around u ...
... predictable. Exploring and learning these principles will allow the student to have a basic understanding of how and why various classes of carbon-containing compounds react, so that he or she will be scientifically literate with respect to environmental or economic issues. Chemistry is all around u ...
1.1 to 1.4
... elements - in groups 1,2, and 13-18 g. transition elements in groups 3-12 - exhibit a wide range of properties ...
... elements - in groups 1,2, and 13-18 g. transition elements in groups 3-12 - exhibit a wide range of properties ...
Science, Systems, Matter, and Energy
... Feedback loop – when output of matter, energy, or information is fed back into the system as an input that changes the system. • Positive Feedback – causes change in the same direction • Negative Feedback – one change leads to a lessoning of that change. ...
... Feedback loop – when output of matter, energy, or information is fed back into the system as an input that changes the system. • Positive Feedback – causes change in the same direction • Negative Feedback – one change leads to a lessoning of that change. ...
File
... 5. The number of protons in an atom equals the number of electrons. The positive charges of the protons are cancelled by the negative charges of the electrons, so overall an atom has a neutral charge. 6. The mass of a proton is 1 amu. The mass of a neutron is 1 amu. The mass of an electron is almo ...
... 5. The number of protons in an atom equals the number of electrons. The positive charges of the protons are cancelled by the negative charges of the electrons, so overall an atom has a neutral charge. 6. The mass of a proton is 1 amu. The mass of a neutron is 1 amu. The mass of an electron is almo ...
What You Need To Know for the Chemistry Regents
... 5. The number of protons in an atom equals the number of electrons. The positive charges of the protons are cancelled by the negative charges of the electrons, so overall an atom has a neutral charge. 6. The mass of a proton is 1 amu. The mass of a neutron is 1 amu. The mass of an electron is almo ...
... 5. The number of protons in an atom equals the number of electrons. The positive charges of the protons are cancelled by the negative charges of the electrons, so overall an atom has a neutral charge. 6. The mass of a proton is 1 amu. The mass of a neutron is 1 amu. The mass of an electron is almo ...
What You Need To Know for the Chemistry Regents Exam
... symbols which represent atomic nuclei (with mass number and atomic number), subatomic particles (with mass and charge) and emitted particles. 7. Energy from nuclear reactions comes from the very small fraction of mass that is lost – the reaction converts matter into energy. Einstein’s E=mc2 descri ...
... symbols which represent atomic nuclei (with mass number and atomic number), subatomic particles (with mass and charge) and emitted particles. 7. Energy from nuclear reactions comes from the very small fraction of mass that is lost – the reaction converts matter into energy. Einstein’s E=mc2 descri ...
High School Curriculum Standards: Chemistry
... Chemistry is the study of matter—its properties and its changes. The idea that matter is made up of particles is over 2000 years old, but the idea of using properties of these particles to explain observable characteristics of matter has more recent origins. In ancient Greece, it was proposed that m ...
... Chemistry is the study of matter—its properties and its changes. The idea that matter is made up of particles is over 2000 years old, but the idea of using properties of these particles to explain observable characteristics of matter has more recent origins. In ancient Greece, it was proposed that m ...
primes - The Institute of Mathematical Sciences
... not tell you everything about its properties. Chemical compounds are to be found in the world around us, and chemists have to find out how the different atoms fit around each other. For example, water does not look like H-H-O but it is like H-O-H, a big fat oxygen atom with two little hydrogen atoms ...
... not tell you everything about its properties. Chemical compounds are to be found in the world around us, and chemists have to find out how the different atoms fit around each other. For example, water does not look like H-H-O but it is like H-O-H, a big fat oxygen atom with two little hydrogen atoms ...