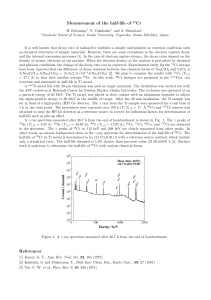
Cluster Fragmentation and Catalysis
... Because a large fraction of chemical reactions occur in solution, it is of fundamental interest to study solvent effects on the thermodynamic and dynamic properties of species. Hence, theoretical investigations of clusters are extremely useful to study basic processes such as the role of microsolvat ...
... Because a large fraction of chemical reactions occur in solution, it is of fundamental interest to study solvent effects on the thermodynamic and dynamic properties of species. Hence, theoretical investigations of clusters are extremely useful to study basic processes such as the role of microsolvat ...
The Atom
... 2. Gamma radiation is a pure energy form and the most dangerous of the three radiation types. 3. Gamma radiation penetrates the farthest; several centimeters of lead, or an even greater thickness of concrete. It will travel right through our bodies and thus has the potential to do much damage. 4. Ga ...
... 2. Gamma radiation is a pure energy form and the most dangerous of the three radiation types. 3. Gamma radiation penetrates the farthest; several centimeters of lead, or an even greater thickness of concrete. It will travel right through our bodies and thus has the potential to do much damage. 4. Ga ...
2 KClO 3
... number comes from. •Earlier we said "Let one atom of H have 1 atomic mass unit" •Now, we have a problem, because H has 3 isotopes: •So.....we cannot use "hydrogen" as it usually exists (mixed isotopes) for our mass standard. •We must purify it. •Easier to purify carbon, so carbon became the mass sta ...
... number comes from. •Earlier we said "Let one atom of H have 1 atomic mass unit" •Now, we have a problem, because H has 3 isotopes: •So.....we cannot use "hydrogen" as it usually exists (mixed isotopes) for our mass standard. •We must purify it. •Easier to purify carbon, so carbon became the mass sta ...
Test Review: Unit 1 - Ms. Hill`s Pre
... 27. Can you solve for energy required (+q) or lost (-q)? Can you solve for mass (m) and change in temperature (ΔT)? Remember Cp (specific heat is NEVER a negative value) 28. Nuclear Chemistry…ch 21 pg 681 a. Fusion: The combination of smaller molecule into larger ones. This happens on the sun. b. Fi ...
... 27. Can you solve for energy required (+q) or lost (-q)? Can you solve for mass (m) and change in temperature (ΔT)? Remember Cp (specific heat is NEVER a negative value) 28. Nuclear Chemistry…ch 21 pg 681 a. Fusion: The combination of smaller molecule into larger ones. This happens on the sun. b. Fi ...
Chapter 4.3: How Atoms Differ
... Number of ____________ identifies an _______ as part of a particular ___________. Referred to as ___________ ______________. ...
... Number of ____________ identifies an _______ as part of a particular ___________. Referred to as ___________ ______________. ...
So where did all the matter on Earth come from - Bennatti
... letters. The first letter is always capitalized. If it has two or three letters only the first letter is capitalized. For example the chemical symbol for the element magnesium is Mg. Note the letter g is lower case. This is important as Co is the element cobalt but CO is the compound carbon monoxide ...
... letters. The first letter is always capitalized. If it has two or three letters only the first letter is capitalized. For example the chemical symbol for the element magnesium is Mg. Note the letter g is lower case. This is important as Co is the element cobalt but CO is the compound carbon monoxide ...
Chemistry Vocab for Quiz 12/21 or 12/22 Atom – The smallest
... Physical change – A change that alters the form or appearance of a material but does not make the material into a different substance. Chemical change – A change in matter that produces a new substance. Solution – A well mixed mixture. Solubility – A measure of how well a solute can be dissolved at ...
... Physical change – A change that alters the form or appearance of a material but does not make the material into a different substance. Chemical change – A change in matter that produces a new substance. Solution – A well mixed mixture. Solubility – A measure of how well a solute can be dissolved at ...
CHEM IB Lecture notes as of 8-29-06
... interaction between people working together; specifically : such interaction when harmonious or effective My definition: Chemists explain what is visible by processes that are not visible to the human eye, but detectable by scientific means. So what? Is chemistry important ...
... interaction between people working together; specifically : such interaction when harmonious or effective My definition: Chemists explain what is visible by processes that are not visible to the human eye, but detectable by scientific means. So what? Is chemistry important ...
Chemistry is a material science
... Chemistry is a material science! How is chemistry defined? Chemistry is the _______ of ______ its ____________, the ______ matter undergoes, and the _______ associated with these changes. Matter is anything that has _______ and takes up _________. This fundamental definition of matter leads to a com ...
... Chemistry is a material science! How is chemistry defined? Chemistry is the _______ of ______ its ____________, the ______ matter undergoes, and the _______ associated with these changes. Matter is anything that has _______ and takes up _________. This fundamental definition of matter leads to a com ...
Regents Review Packet B2 Answer Key
... 13. Complete the nuclear equation below for the decay of K-40 by writing a notation for the missing nuclide. ...
... 13. Complete the nuclear equation below for the decay of K-40 by writing a notation for the missing nuclide. ...
Nuclear Astrophysics (1)
... a noninteracting gas can be represented by a 3D box in which it is contained (with ...
... a noninteracting gas can be represented by a 3D box in which it is contained (with ...
Chemistry Semester Test Study Guide Chapters
... What state of matter has a definite volume and takes the shape of its container? Which state of matter takes both the shape and volume of its container? In a chemical reaction, what are the reactants and what are the products? If the total mass of the reactants in a chemical reaction is 60 g, what i ...
... What state of matter has a definite volume and takes the shape of its container? Which state of matter takes both the shape and volume of its container? In a chemical reaction, what are the reactants and what are the products? If the total mass of the reactants in a chemical reaction is 60 g, what i ...