Science Outline NHPS: Chemistry
... change graphs. using ratios compounds. and ion charts. Describe the Calculate factors that Identify names masses and effect phase and formulas yields of changes. and uses for reactants and common products in a Describe the compounds reaction. physical and elements. properties of Understand the gases ...
... change graphs. using ratios compounds. and ion charts. Describe the Calculate factors that Identify names masses and effect phase and formulas yields of changes. and uses for reactants and common products in a Describe the compounds reaction. physical and elements. properties of Understand the gases ...
Sugárkémiai áttekintés Schiller Róbert
... Chemistry of the hydrated electron - The ideal of the reducing agent: no oxidised product left - the perfect nucleophyilic partner - very selective, in certain cases diffusion controlled rates - previously unknown products, e.g.Ag0, Cu0 A naive model (polaron in a dielectric ...
... Chemistry of the hydrated electron - The ideal of the reducing agent: no oxidised product left - the perfect nucleophyilic partner - very selective, in certain cases diffusion controlled rates - previously unknown products, e.g.Ag0, Cu0 A naive model (polaron in a dielectric ...
Ch. 2 - Ltcconline.net
... 5. Distinguish between atomic number and atomic weight or mass number of an atom. 6. Define an isotope and explain what makes some isotopes radioactive. Why are isotopes important in biology? 7. Explain how the electron configuration of an atom influences its behavior. 8. Distinguish among polar cov ...
... 5. Distinguish between atomic number and atomic weight or mass number of an atom. 6. Define an isotope and explain what makes some isotopes radioactive. Why are isotopes important in biology? 7. Explain how the electron configuration of an atom influences its behavior. 8. Distinguish among polar cov ...
Branches of Chemistry
... Nuclear chemists investigate changes that happen in atomic nuclei. Organic chemists study hydrocarbons – compounds of carbon and hydrogen – and other related compounds. Photochemists investigate the relationship between light and chemical reactions. Physical chemists use the principles of physics to ...
... Nuclear chemists investigate changes that happen in atomic nuclei. Organic chemists study hydrocarbons – compounds of carbon and hydrogen – and other related compounds. Photochemists investigate the relationship between light and chemical reactions. Physical chemists use the principles of physics to ...
S3 Chemistry - eduBuzz.org
... Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
... Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
California Chemistry Standards Test
... 1. temperature and heat flow-molecular motion 2. exothermic and endothermic reactions 3. heat release or absorbed during phase changes 4. solve heat problems Reaction Rates-(4) 1. rates of chemical reactions 2. rates depend on temperature, concentration, and pressure 3. role of catalyst Chemical Equ ...
... 1. temperature and heat flow-molecular motion 2. exothermic and endothermic reactions 3. heat release or absorbed during phase changes 4. solve heat problems Reaction Rates-(4) 1. rates of chemical reactions 2. rates depend on temperature, concentration, and pressure 3. role of catalyst Chemical Equ ...
Lesson 13: Nuclear Propulsion Basics
... microscopic distance, so their energy becomes converted into heat. • The balance of the energy comes from gamma rays emitted during or immediately following the fission process and from the kinetic energy of the neutrons. – Some of the latter are immediate (so-called prompt neutrons), but a small pr ...
... microscopic distance, so their energy becomes converted into heat. • The balance of the energy comes from gamma rays emitted during or immediately following the fission process and from the kinetic energy of the neutrons. – Some of the latter are immediate (so-called prompt neutrons), but a small pr ...
MASS-INDEPENDENT ISOTOPE FRACTIONATION OF CHROMIUM
... Introduction: Recently, the classic theory of stable isotope fractionation of the Bigeleisen-Mayer equation [1] has been expanded by the original author to include the mass-independent term named the nuclear field shift effect [2]. The improved theory successfully explained the observed non-linear i ...
... Introduction: Recently, the classic theory of stable isotope fractionation of the Bigeleisen-Mayer equation [1] has been expanded by the original author to include the mass-independent term named the nuclear field shift effect [2]. The improved theory successfully explained the observed non-linear i ...
Unit 3 - Princeton High School
... The half-life for this disintegration is approximately 30 years. This is the amount of time required for half the atoms in a sample to undergo decay. Assume that a 64-gram sample of Cs-137 is analyzed every 30 years for a 150 –year period. Calculate the grams of cesium and barium present each time t ...
... The half-life for this disintegration is approximately 30 years. This is the amount of time required for half the atoms in a sample to undergo decay. Assume that a 64-gram sample of Cs-137 is analyzed every 30 years for a 150 –year period. Calculate the grams of cesium and barium present each time t ...
PowerPoint Overview for Introduction
... and cell structures, regulating the body's pH, carrying charge, and driving chemical reactions. ...
... and cell structures, regulating the body's pH, carrying charge, and driving chemical reactions. ...
Chemistry: Nuclear Reactions Guided Inquiry + n → + + 3 n +
... have 4 hydrogen atoms and 2 oxygen atoms. Nuclear reactions are reactions that affect the nucleus of an atom. In nature, unstable nuclei undergo nuclear reactions to form more stable nuclei. Stable ...
... have 4 hydrogen atoms and 2 oxygen atoms. Nuclear reactions are reactions that affect the nucleus of an atom. In nature, unstable nuclei undergo nuclear reactions to form more stable nuclei. Stable ...
Chemistry Final Study Guide
... 44. The first group on the periodic table is called the __________ __________, and they are very reactive due to the fact that they tend to lose one __________. 45. Electrons in the outer energy level are called __________ __________. 46. The second group on the periodic table is called the ________ ...
... 44. The first group on the periodic table is called the __________ __________, and they are very reactive due to the fact that they tend to lose one __________. 45. Electrons in the outer energy level are called __________ __________. 46. The second group on the periodic table is called the ________ ...
Chapter 1: The Mole
... What does it mean? In a chemical reaction, matter is neither created nor destroyed. ...
... What does it mean? In a chemical reaction, matter is neither created nor destroyed. ...
Chem Unit 2 Review Guide ANSWERS
... 19.) What is an ion? By finding the elements’ location on the periodic table, how can you determine what kind of ion it will become? Ions are atoms with a charge due to electron loss/gain. We wrote what charges will be formed for most groups. 20.) How are anions and cations different? Anions are ne ...
... 19.) What is an ion? By finding the elements’ location on the periodic table, how can you determine what kind of ion it will become? Ions are atoms with a charge due to electron loss/gain. We wrote what charges will be formed for most groups. 20.) How are anions and cations different? Anions are ne ...
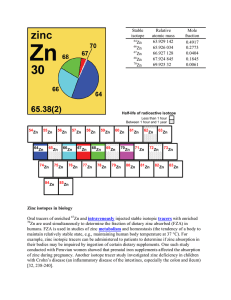
Zinc isotopes in biology Oral tracers of enriched Zn and
... the atomic nucleus. A pure chemical substance composed of atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus [703]. gamma rays (gamma radiation) – a stream of high-energy electromagnetic radiation given off by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay. The energies of gamma rays are hi ...
... the atomic nucleus. A pure chemical substance composed of atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus [703]. gamma rays (gamma radiation) – a stream of high-energy electromagnetic radiation given off by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay. The energies of gamma rays are hi ...
Welcome to Chemistry
... A numerate subject such as CHEMISTRY is useful for… • Accountancy/Business • Architecture • Law ...
... A numerate subject such as CHEMISTRY is useful for… • Accountancy/Business • Architecture • Law ...