Pre-Knowledge: Chemistry and Physics Vocabulary Atomic Number
... isotope is predictable. That is, we cannot predict when a specific atom will decay, but after one half-life half of the atoms will have decayed into a daughter nuclide. ...
... isotope is predictable. That is, we cannot predict when a specific atom will decay, but after one half-life half of the atoms will have decayed into a daughter nuclide. ...
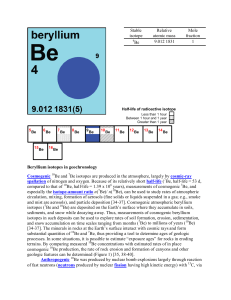
1 The Nucleus Total number of nucleons: mass number Number of
... Further fission Covers 200 isotopes, 35 elements Produces 2.4 neutron in average More neutrons are produced – may be explosive Size of the sample Too small: neutron escapes before striking a nucleus – subcritical Too large: neutrons are completely consumed – super critical In between: chain reacti ...
... Further fission Covers 200 isotopes, 35 elements Produces 2.4 neutron in average More neutrons are produced – may be explosive Size of the sample Too small: neutron escapes before striking a nucleus – subcritical Too large: neutrons are completely consumed – super critical In between: chain reacti ...
GLOSSARY OF SCIENTIFIC TERMS IN THE MYSTERY OF MATTER
... Any of the five nonmetallic elements with similar properties: fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine. A form of energy resulting from the movement of particles. ...
... Any of the five nonmetallic elements with similar properties: fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine. A form of energy resulting from the movement of particles. ...
nuclear chemistry - Wood County Schools
... Beta Decay: Medium-level radiation from the emission of beta particles (electrons). Positron Emission: Medium-level radiation from the emission of a positron, which is the same as an electron, only with a positive charge, converting a proton into a neutron. Electron Capture: When an atom takes in an ...
... Beta Decay: Medium-level radiation from the emission of beta particles (electrons). Positron Emission: Medium-level radiation from the emission of a positron, which is the same as an electron, only with a positive charge, converting a proton into a neutron. Electron Capture: When an atom takes in an ...
Chapter 1 Learning Objective Summary
... 6. Learn to balance common nuclear reactions, know the common radioactive particles involved, and understand fission and fusion Chemical reactions involve the gain, loss, or sharing of the outer electrons, whereas nuclear reactions involve changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that ...
... 6. Learn to balance common nuclear reactions, know the common radioactive particles involved, and understand fission and fusion Chemical reactions involve the gain, loss, or sharing of the outer electrons, whereas nuclear reactions involve changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... number of protons. Scientists knew that the nucleus consisted of protons and neutrons in _______ [1730 1830 1930] The number of ________ determines the identity of atoms. Isotopes have different numbers of ____________. Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many ne ...
... number of protons. Scientists knew that the nucleus consisted of protons and neutrons in _______ [1730 1830 1930] The number of ________ determines the identity of atoms. Isotopes have different numbers of ____________. Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many ne ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... number of protons. Scientists knew that the nucleus consisted of protons and neutrons in _______ [1730 1830 1930] The number of ________ determines the identity of atoms. Isotopes have different numbers of ____________. Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many ne ...
... number of protons. Scientists knew that the nucleus consisted of protons and neutrons in _______ [1730 1830 1930] The number of ________ determines the identity of atoms. Isotopes have different numbers of ____________. Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many ne ...
Inside the Atom connections to the lower secondary (KS3
... • a simple (Dalton) atomic model • differences between atoms, elements and compounds • chemical symbols and formulae for elements and compounds • conservation of mass changes of state and chemical reactions. Most of the nuclear physics related content in the KS3 curriculum is taught in the chemi ...
... • a simple (Dalton) atomic model • differences between atoms, elements and compounds • chemical symbols and formulae for elements and compounds • conservation of mass changes of state and chemical reactions. Most of the nuclear physics related content in the KS3 curriculum is taught in the chemi ...
Nuclear Fission sim
... Why do we care about half-lives? Knowing how long a radioisotope used in a medical test will remain active in the body lets doctors get information but minimize harm to a patient. We can plan how to best store hazardous nuclear waste from nuclear power plants. Scientists can estimate the ages of bon ...
... Why do we care about half-lives? Knowing how long a radioisotope used in a medical test will remain active in the body lets doctors get information but minimize harm to a patient. We can plan how to best store hazardous nuclear waste from nuclear power plants. Scientists can estimate the ages of bon ...
nuclear chemistry - La Salle High School
... 5. Gamma ray emission – in many cases, radioactive decay results in a daughter nucleus that is in an excited state; the excited state is unstable and goes to a lower-energy state by releasing energ y in the form of gamma rays. ...
... 5. Gamma ray emission – in many cases, radioactive decay results in a daughter nucleus that is in an excited state; the excited state is unstable and goes to a lower-energy state by releasing energ y in the form of gamma rays. ...
Nuclear Chemistry PowerPoint
... Nuclear Fission • Reactions in which an atom's nucleus splits into smaller parts, releasing a large amount of energy in the process. Most commonly this is done by "firing" a neutron at the nucleus of an atom. The energy of the neutron "bullet" causes the target element to split into two (or more) e ...
... Nuclear Fission • Reactions in which an atom's nucleus splits into smaller parts, releasing a large amount of energy in the process. Most commonly this is done by "firing" a neutron at the nucleus of an atom. The energy of the neutron "bullet" causes the target element to split into two (or more) e ...