The structure of Matter
... O Compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. O Two of the simplest hydrocarbons are methane and ethane. O Many hydrocarbons are used as fuels. ...
... O Compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. O Two of the simplest hydrocarbons are methane and ethane. O Many hydrocarbons are used as fuels. ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... E. Aliphatic compounds are organic compounds that do not contain benzene rings. 12-8. Hydrocarbon Groups A. Hydrocarbon derivatives are compounds obtained by substituting other atoms or atom groups for one or more of the H atoms in hydrocarbon molecules. ...
... E. Aliphatic compounds are organic compounds that do not contain benzene rings. 12-8. Hydrocarbon Groups A. Hydrocarbon derivatives are compounds obtained by substituting other atoms or atom groups for one or more of the H atoms in hydrocarbon molecules. ...
File
... fluoride. The carbon tetrachloride was produced by reacting methane with chlorine. Draw structural formula equations to represent these two reactions. ...
... fluoride. The carbon tetrachloride was produced by reacting methane with chlorine. Draw structural formula equations to represent these two reactions. ...
Review Sheet: Unit 6 Name__________________ CHEMISTRY: A
... Fill in the blanks with the most appropriate term: Common names of substances like “milk of magnesia” or “lime” usually give no ...
... Fill in the blanks with the most appropriate term: Common names of substances like “milk of magnesia” or “lime” usually give no ...
Learning Standards vocab chemical basis and molecules of life 09
... Explain the meaning of a chemical formula for an ionic array (e.g., NaCl). Give examples to illustrate that molecules are groups of two or more atoms bonded together (e.g., a molecule of water is formed when one oxygen atom shares electrons with two hydrogen atoms). Explain the meaning of a ch ...
... Explain the meaning of a chemical formula for an ionic array (e.g., NaCl). Give examples to illustrate that molecules are groups of two or more atoms bonded together (e.g., a molecule of water is formed when one oxygen atom shares electrons with two hydrogen atoms). Explain the meaning of a ch ...
Chemistry-Chapter 2 Lecture Notes Page
... - Log scale (tenfold increase between numbers) - 0 to 14, 7.0 is Neutral ...
... - Log scale (tenfold increase between numbers) - 0 to 14, 7.0 is Neutral ...
Reactions
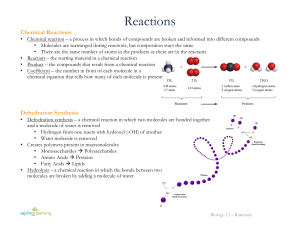
... • Chemical reaction – a process in which bonds of compounds are broken and reformed into different compounds • Molecules are rearranged during reactions, but composition stays the same • There are the same number of atoms in the products as there are in the reactants • Reactant – the starting materi ...
... • Chemical reaction – a process in which bonds of compounds are broken and reformed into different compounds • Molecules are rearranged during reactions, but composition stays the same • There are the same number of atoms in the products as there are in the reactants • Reactant – the starting materi ...
Unit_Chemistry_1a_Oil
... compounds. A mixture consists of two or more elements or compounds not chemically combined together. The chemical properties of each substance in the mixture are unchanged. It is possible to separate the substances in a mixture by physical methods including distillation. ...
... compounds. A mixture consists of two or more elements or compounds not chemically combined together. The chemical properties of each substance in the mixture are unchanged. It is possible to separate the substances in a mixture by physical methods including distillation. ...
Chapter 12
... •Inorganic compounds: cpds which are NOT hydrocarbons (~1.5 million) •Organic compounds: cpds which contain hydrogen & carbon (thus, hydrocarbons & derivatives) (~ 7 million) •“Organic Chemistry” started, as a branch of chemistry, when F. Wohler disproved the idea of “vital force.” Carbon Atoms Carb ...
... •Inorganic compounds: cpds which are NOT hydrocarbons (~1.5 million) •Organic compounds: cpds which contain hydrogen & carbon (thus, hydrocarbons & derivatives) (~ 7 million) •“Organic Chemistry” started, as a branch of chemistry, when F. Wohler disproved the idea of “vital force.” Carbon Atoms Carb ...
chapter 12_LO - Faculty Websites
... Why are there so many more organic compounds than inorganic compounds? You should be able to recognize and describe the different properties of organic compounds. Which elements are typically found in organic compounds? What is the difference between a hydrocarbon and a hydrocarbon derivative? How m ...
... Why are there so many more organic compounds than inorganic compounds? You should be able to recognize and describe the different properties of organic compounds. Which elements are typically found in organic compounds? What is the difference between a hydrocarbon and a hydrocarbon derivative? How m ...
FYBSc Revised Syllabus
... 1.2 Hybridization: sp3, sp2, sp hybridization of carbon and nitrogen; sp3 and sp2 hybridizations of oxygen in Organic compounds. 1.3 Overlap of atomic orbitals; Overlaps of atomic orbitals to form α and π bonds, shapes of organic molecules. 1.4 Electronic effects in organic molecules: Polarization o ...
... 1.2 Hybridization: sp3, sp2, sp hybridization of carbon and nitrogen; sp3 and sp2 hybridizations of oxygen in Organic compounds. 1.3 Overlap of atomic orbitals; Overlaps of atomic orbitals to form α and π bonds, shapes of organic molecules. 1.4 Electronic effects in organic molecules: Polarization o ...
Lecture syllabus - Linfield College
... - teach foundational principles that underlie the chemical and physical behavior of compounds constructed mainly of carbon atoms - foster scientific critical thinking skills - provide experience in common laboratory techniques and “chemical common sense” in the laboratory - provide practice in writi ...
... - teach foundational principles that underlie the chemical and physical behavior of compounds constructed mainly of carbon atoms - foster scientific critical thinking skills - provide experience in common laboratory techniques and “chemical common sense” in the laboratory - provide practice in writi ...
Chemistry 123: Physical and Organic Chemistry
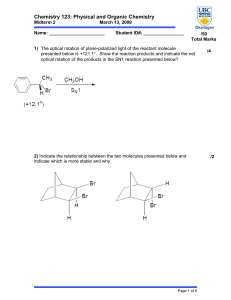
... 14) Which of the following would have the greater ΔS? (A) C(s) (B) C(g) (C) CO(g) (D) CO2(g) 15) If a reaction has a half-life of one day and it is initiated on Monday, how much remains on Friday? (A) ~20% (B) ~5% (C) ~3% (D) ~12% 16) For the reaction, N2(g) + 3 H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g) , the rate would be; ...
... 14) Which of the following would have the greater ΔS? (A) C(s) (B) C(g) (C) CO(g) (D) CO2(g) 15) If a reaction has a half-life of one day and it is initiated on Monday, how much remains on Friday? (A) ~20% (B) ~5% (C) ~3% (D) ~12% 16) For the reaction, N2(g) + 3 H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g) , the rate would be; ...
Chemistry and the Environment - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... 6. What class of compounds used as coolants and insulators was banned because of environmental hazards? PCB’s 7. What is the name of the 1980 law to clean up waste sites? Super Fund 8. When chemical wastes are burned what materials are released into the environment? Carbon dioxide and water vapor if ...
... 6. What class of compounds used as coolants and insulators was banned because of environmental hazards? PCB’s 7. What is the name of the 1980 law to clean up waste sites? Super Fund 8. When chemical wastes are burned what materials are released into the environment? Carbon dioxide and water vapor if ...
Episode 25 0 Chemistry and the Environment
... 6. What class of compounds used as coolants and insulators was banned because of environmental hazards? PCB’s 7. What is the name of the 1980 law to clean up waste sites? Super Fund 8. When chemical wastes are burned what materials are released into the environment? Carbon dioxide and water vapor if ...
... 6. What class of compounds used as coolants and insulators was banned because of environmental hazards? PCB’s 7. What is the name of the 1980 law to clean up waste sites? Super Fund 8. When chemical wastes are burned what materials are released into the environment? Carbon dioxide and water vapor if ...
Headline Text 28 Point Color Text 2
... Chemical informatics and medicinal chemistry databases How molecular motors work Computer modeling in support of chemical and drug design • Polymer delivery systems • Catalysts • Small molecule drugs ...
... Chemical informatics and medicinal chemistry databases How molecular motors work Computer modeling in support of chemical and drug design • Polymer delivery systems • Catalysts • Small molecule drugs ...
第一章 绪论
... of existing drugs, their biological properties, and their quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR). Pharmaceutical chemistry is focused on quality aspects of medicines and aims to assure fitness for the purpose of medicinal products. Medicinal chemistry is a highly interdisciplinary scie ...
... of existing drugs, their biological properties, and their quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR). Pharmaceutical chemistry is focused on quality aspects of medicines and aims to assure fitness for the purpose of medicinal products. Medicinal chemistry is a highly interdisciplinary scie ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Curriculum
... What are valence bond theory and hybridization? How are Lewis structures drawn and interpreted? How do organic compounds differ ...
... What are valence bond theory and hybridization? How are Lewis structures drawn and interpreted? How do organic compounds differ ...
compound - Coal City Unit #1
... 1st letter is always capitalized, second letter is always sm. case • most symbols come from their names • some symbols come from Latin or Greek names • some elem. named in honor of person or place they were discovered • ea. elem. has its own unique set of chem. and physical props. ...
... 1st letter is always capitalized, second letter is always sm. case • most symbols come from their names • some symbols come from Latin or Greek names • some elem. named in honor of person or place they were discovered • ea. elem. has its own unique set of chem. and physical props. ...
Gizmos: Types of Reactions
... is a substance consisting of one kind of atom, such as aluminum (Al) or oxygen gas (O2). A compound is a substance made of more than one kind of atom, such as water (H2O) or table salt (NaCl). Question: How are chemical reactions classified? 1. Match: Most chemical reactions can be classified as one ...
... is a substance consisting of one kind of atom, such as aluminum (Al) or oxygen gas (O2). A compound is a substance made of more than one kind of atom, such as water (H2O) or table salt (NaCl). Question: How are chemical reactions classified? 1. Match: Most chemical reactions can be classified as one ...
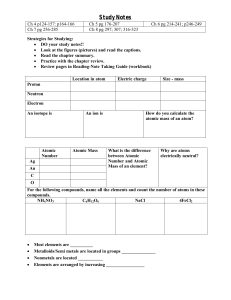
•What makes up an atom? Draw an atom
... the mass, but NOT the element • EX. C12 vs C14 • Carbon 14 is heavier since it has two more neutrons ...
... the mass, but NOT the element • EX. C12 vs C14 • Carbon 14 is heavier since it has two more neutrons ...
View PDF
... such as hygroscopicity, the activity of cloud condensation, the reactivity, the optical properties, etc. Aerosol particles consist of complex mixture of inorganic salts with hydrophilic and/or hygrophobic organic components which may evolved during their transportation into the atmosphere when they ...
... such as hygroscopicity, the activity of cloud condensation, the reactivity, the optical properties, etc. Aerosol particles consist of complex mixture of inorganic salts with hydrophilic and/or hygrophobic organic components which may evolved during their transportation into the atmosphere when they ...
Organic chemistry

Organic chemistry is a chemistry subdiscipline involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure includes many physical and chemical methods to determine the chemical composition and the chemical constitution of organic compounds and materials. Study of properties includes both physical properties and chemical properties, and uses similar methods as well as methods to evaluate chemical reactivity, with the aim to understand the behavior of the organic matter in its pure form (when possible), but also in solutions, mixtures, and fabricated forms. The study of organic reactions includes probing their scope through use in preparation of target compounds (e.g., natural products, drugs, polymers, etc.) by chemical synthesis, as well as the focused study of the reactivities of individual organic molecules, both in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study.The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry include hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen), as well as myriad compositions based always on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (these, included in many organic chemicals in biology) and the radiostable elements of the halogens.In the modern era, the range extends further into the periodic table, with main group elements, including:Group 1 and 2 organometallic compounds, i.e., involving alkali (e.g., lithium, sodium, and potassium) or alkaline earth metals (e.g., magnesium)Metalloids (e.g., boron and silicon) or other metals (e.g., aluminium and tin)In addition, much modern research focuses on organic chemistry involving further organometallics, including the lanthanides, but especially the transition metals; (e.g., zinc, copper, palladium, nickel, cobalt, titanium and chromium)Finally, organic compounds form the basis of all earthly life and constitute a significant part of human endeavors in chemistry. The bonding patterns open to carbon, with its valence of four—formal single, double, and triple bonds, as well as various structures with delocalized electrons—make the array of organic compounds structurally diverse, and their range of applications enormous. They either form the basis of, or are important constituents of, many commercial products including pharmaceuticals; petrochemicals and products made from them (including lubricants, solvents, etc.); plastics; fuels and explosives; etc. As indicated, the study of organic chemistry overlaps with organometallic chemistry and biochemistry, but also with medicinal chemistry, polymer chemistry, as well as many aspects of materials science.