Coordination Chemistry of Life Processes: Bioinorganic Chemistry
... plays a crucial role in controlling the reactivity of the metal site. In some cases the protein can force metal ions into unusual geometries; the protein environment may be the determining factor controlling the activity of the increasing number of functionally distinct metalloproteins that have ess ...
... plays a crucial role in controlling the reactivity of the metal site. In some cases the protein can force metal ions into unusual geometries; the protein environment may be the determining factor controlling the activity of the increasing number of functionally distinct metalloproteins that have ess ...
Chemistry Standards Checklist
... b. Consider possible effects of measurement errors on calculations. ...
... b. Consider possible effects of measurement errors on calculations. ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... a. High heat capacity (absorbs/releases heat without fluctuations in temperature) b. High heat vaporization (much heat is lost during evaporation…which is beneficial when we sweat) c. Universal solvent (required for most chemical reactions to occur) e.g. blood, CSF, urine, mucus d. Important reactan ...
... a. High heat capacity (absorbs/releases heat without fluctuations in temperature) b. High heat vaporization (much heat is lost during evaporation…which is beneficial when we sweat) c. Universal solvent (required for most chemical reactions to occur) e.g. blood, CSF, urine, mucus d. Important reactan ...
Review Questions
... 5. Find the percent composition of Oxygen in Na2S2O3 __________________________ ...
... 5. Find the percent composition of Oxygen in Na2S2O3 __________________________ ...
Slide 1 - Effingham County Schools
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
The Atom Power point - Effingham County Schools
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
form revision a
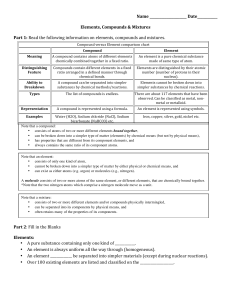
... There are two types of compound. Covalent compounds form when non-metal atoms form covalent bonds by sharing their outer electrons. Covalent compounds exist as molecules. Ionic compounds form when metal atoms join to non-metal atoms by transferring electron(s) from the metal to the non-metal. The re ...
... There are two types of compound. Covalent compounds form when non-metal atoms form covalent bonds by sharing their outer electrons. Covalent compounds exist as molecules. Ionic compounds form when metal atoms join to non-metal atoms by transferring electron(s) from the metal to the non-metal. The re ...
Nutritional Pattern Among Orgnaisms
... microbes for synthesis of cellular materials • Protein synthesis nitrogen and sulfur • DNA or RNA synthesis nitrogen, Many bacteria derive nitrogen by decomposing protein phosphorus • ATP synthesis nitrogen and phosphorus • Some bacteria ammonium ions in organic material • nitrogen from nitrates • N ...
... microbes for synthesis of cellular materials • Protein synthesis nitrogen and sulfur • DNA or RNA synthesis nitrogen, Many bacteria derive nitrogen by decomposing protein phosphorus • ATP synthesis nitrogen and phosphorus • Some bacteria ammonium ions in organic material • nitrogen from nitrates • N ...
atomic theory of matter
... PROPORTIONS • Some elements can form more than one compound when they react together (C & O: CO and CO2; N & O: N2O, NO, NO2, etc.). Dalton’s law predicted that the mass proportions should be proportional. Experiment confirmed this leading to this law. • Law of multiple proportions: when two element ...
... PROPORTIONS • Some elements can form more than one compound when they react together (C & O: CO and CO2; N & O: N2O, NO, NO2, etc.). Dalton’s law predicted that the mass proportions should be proportional. Experiment confirmed this leading to this law. • Law of multiple proportions: when two element ...
syllabus for entrance examination - NTU.edu
... A group of reactive metals which are essentially similar to each other with only gradual changes as their atomic numbers increase. (a) ...
... A group of reactive metals which are essentially similar to each other with only gradual changes as their atomic numbers increase. (a) ...
Chapter Two:
... that combine with 1 gram of the first element can always be reduced to small whole numbers. ...
... that combine with 1 gram of the first element can always be reduced to small whole numbers. ...
Elements Combine to Form Compounds
... one kind of element in which the atoms of the elements are joined together. Compounds form through chemical bonds: these are links between two or more atoms that hold the atoms together Two types of Compounds (chemical bonds) Ionic Compounds Molecular (covalent) Compounds ...
... one kind of element in which the atoms of the elements are joined together. Compounds form through chemical bonds: these are links between two or more atoms that hold the atoms together Two types of Compounds (chemical bonds) Ionic Compounds Molecular (covalent) Compounds ...
Naming Compounds
... determine the elements involved in the chemical formula (compound)…. Metals and Non- Metals determine the type of compound (Ionic or Molecular) follow the rules outline for Ionic or Molecular ...
... determine the elements involved in the chemical formula (compound)…. Metals and Non- Metals determine the type of compound (Ionic or Molecular) follow the rules outline for Ionic or Molecular ...
Microbiology: A Systems Approach
... Molecules important to life consist of inorganic and organic substances. Inorganic – either C or H maybe present (e,g, CO2, H2) Organic- C and H (hydrocarbons) are present (e.g. CH3) ...
... Molecules important to life consist of inorganic and organic substances. Inorganic – either C or H maybe present (e,g, CO2, H2) Organic- C and H (hydrocarbons) are present (e.g. CH3) ...
Chemistry Content Standards
... e. Compare and contrast types of chemical bonds (i.e. ionic, covalent). f. Relate light emission and the movement of electrons to element identification. SC4. Students will use the organization of the Periodic Table to predict properties of elements. a. Use the Periodic Table to predict periodic tre ...
... e. Compare and contrast types of chemical bonds (i.e. ionic, covalent). f. Relate light emission and the movement of electrons to element identification. SC4. Students will use the organization of the Periodic Table to predict properties of elements. a. Use the Periodic Table to predict periodic tre ...
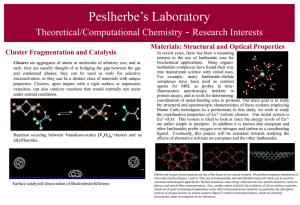
Cluster Fragmentation and Catalysis
... useful to study basic processes such as the role of microsolvation in chemical reactions. For example, the study of simple ion-cluster properties can show the role played by the microscopic interactions between species. As well, when exploring properties of ion pairs in clusters, it is possible to i ...
... useful to study basic processes such as the role of microsolvation in chemical reactions. For example, the study of simple ion-cluster properties can show the role played by the microscopic interactions between species. As well, when exploring properties of ion pairs in clusters, it is possible to i ...
Section 2-4 “Chemical Reactions and Enzymes”
... Products – Elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction ...
... Products – Elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction ...
30.09.2013 1 Chapter 2 Atoms and Molecules Warning!! Chapter
... • Ionic compounds are electrically neutral and are named in order of “cation anion”, as in sodium chloride. • The cation retains its full name. • Monoatomic cation charge can often be found by position in the periodic table. • Cations with more than one charge (e.g., transition metals) are named usi ...
... • Ionic compounds are electrically neutral and are named in order of “cation anion”, as in sodium chloride. • The cation retains its full name. • Monoatomic cation charge can often be found by position in the periodic table. • Cations with more than one charge (e.g., transition metals) are named usi ...
Stoichiometry
... Law of Conservation of Mass Regular reactions: atoms and masses balance Redox reactions: atoms, masses, and charges balance Here there will be change in the oxidation state of ions during the reaction. One element will be oxidized; that means that it will lose electrons and become more posi ...
... Law of Conservation of Mass Regular reactions: atoms and masses balance Redox reactions: atoms, masses, and charges balance Here there will be change in the oxidation state of ions during the reaction. One element will be oxidized; that means that it will lose electrons and become more posi ...
Compound vs Element chart
... • consists of only one kind of atom, • cannot be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either physical or chemical means, and • can exist as either atoms (e.g. argon) or molecules (e.g., nitrogen). A molecule consists of two or more atoms of the same element, or different elements, that are c ...
... • consists of only one kind of atom, • cannot be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either physical or chemical means, and • can exist as either atoms (e.g. argon) or molecules (e.g., nitrogen). A molecule consists of two or more atoms of the same element, or different elements, that are c ...
Welcome to Chemistry
... AS can be sat as a stand alone qualification over 1 year, exams are sat at the end of Y12. 2 written exams each 1 hour and 30 minutes. A level is the full 2 year qualification with all the exams at the end of Y13. ...
... AS can be sat as a stand alone qualification over 1 year, exams are sat at the end of Y12. 2 written exams each 1 hour and 30 minutes. A level is the full 2 year qualification with all the exams at the end of Y13. ...
C14_-_Organic_Chemistry
... State the type of compound present, given a chemical name ending in –ane, -ene, and –ol, or a molecular structure. ...
... State the type of compound present, given a chemical name ending in –ane, -ene, and –ol, or a molecular structure. ...
Are You suprised ?
... Example problems from previous quizzes and assignments. Matter Review Classify each of the following as a physical or a chemical property of matter. _____1. _____2. _____3. _____4. _____5. _____6. _____7. _____8. ...
... Example problems from previous quizzes and assignments. Matter Review Classify each of the following as a physical or a chemical property of matter. _____1. _____2. _____3. _____4. _____5. _____6. _____7. _____8. ...
9.1-10.5 Organic Chemistry
... formulas for saturated and unsaturated aliphatic (including cyclic) • Containing up to 10 carbon atoms in the parent chain/cyclic structure • Containing only one type of a functional group or multiple bond • Using the IUPAC nomenclature guidelines 2) Identify types of compounds from the functional g ...
... formulas for saturated and unsaturated aliphatic (including cyclic) • Containing up to 10 carbon atoms in the parent chain/cyclic structure • Containing only one type of a functional group or multiple bond • Using the IUPAC nomenclature guidelines 2) Identify types of compounds from the functional g ...
Organic chemistry

Organic chemistry is a chemistry subdiscipline involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure includes many physical and chemical methods to determine the chemical composition and the chemical constitution of organic compounds and materials. Study of properties includes both physical properties and chemical properties, and uses similar methods as well as methods to evaluate chemical reactivity, with the aim to understand the behavior of the organic matter in its pure form (when possible), but also in solutions, mixtures, and fabricated forms. The study of organic reactions includes probing their scope through use in preparation of target compounds (e.g., natural products, drugs, polymers, etc.) by chemical synthesis, as well as the focused study of the reactivities of individual organic molecules, both in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study.The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry include hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen), as well as myriad compositions based always on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (these, included in many organic chemicals in biology) and the radiostable elements of the halogens.In the modern era, the range extends further into the periodic table, with main group elements, including:Group 1 and 2 organometallic compounds, i.e., involving alkali (e.g., lithium, sodium, and potassium) or alkaline earth metals (e.g., magnesium)Metalloids (e.g., boron and silicon) or other metals (e.g., aluminium and tin)In addition, much modern research focuses on organic chemistry involving further organometallics, including the lanthanides, but especially the transition metals; (e.g., zinc, copper, palladium, nickel, cobalt, titanium and chromium)Finally, organic compounds form the basis of all earthly life and constitute a significant part of human endeavors in chemistry. The bonding patterns open to carbon, with its valence of four—formal single, double, and triple bonds, as well as various structures with delocalized electrons—make the array of organic compounds structurally diverse, and their range of applications enormous. They either form the basis of, or are important constituents of, many commercial products including pharmaceuticals; petrochemicals and products made from them (including lubricants, solvents, etc.); plastics; fuels and explosives; etc. As indicated, the study of organic chemistry overlaps with organometallic chemistry and biochemistry, but also with medicinal chemistry, polymer chemistry, as well as many aspects of materials science.